Abstract
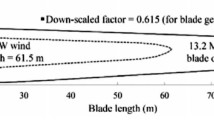
As fruitful clean energy, offshore wind turbine power develops rapidly at the coastal area of China that contributes to enabling carbon neutralization. However, the cyclic change of climatic conditions inevitably leads to fatigue issue of wind turbine. This paper makes a survey on the climate condition at Jintang island, Zhoushan islands, China within one year to perform fatigue analysis of in-service composite wind turbine blades. First, the wind velocity rose diagram measured at Jintang island is obtained by investigation, which is used to calculate the wind pressure under some wind velocity and the corresponding direction and frequency, by combining with the modified blade element momentum (BEM) theory. Second, finite element analysis (FEA) of the full-scale composite blade under different wind velocity is performed, where it is almost the first time to introduce the damage model of composites to predict progressive failure properties and stress distributions of composite skin for fatigue analysis. Finally, the fatigue life for blade with three kinds of composite materials for skin is evaluated comparatively by combining with the rainflow counting method, the S–N fatigue curve and the cumulative damage principle. Numerical results show that the fatigue life of blades with three kinds of materials for skin falls within 19–22 years, consistent with the design value of blade in China.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within its supplementary materials.
References
Rubiella, C., Hessabi, C.A., Fallah, A.S.: State of the art in fatigue modelling of composite wind turbine blades. Inter. J. Fatigue 117, 230–245 (2018)
Philippidis, T.P., Vassilopoulos, A.P.: Complex stress state effect on fatigue life of GRP laminates. Part II, theoretical formulation. Inter. J. Fatigue 24, 825–830 (2002)
Shokrieh, M.M., Rafiee, R.: Simulation of fatigue failure in a full composite wind turbine blade. Compos. Struct. 74, 332–342 (2006)
Kong, A., Kim, T., Han, D.: Investigation of fatigue life for a medium scale composite wind turbine blade. Inter. J. Fatigue 28, 1382–1388 (2006)
Sutherland, H.J., Mandell, J.F.: Optimized constant-life diagram for the analysis of fiberglass composites used in wind turbine blades. J. Solar. Energy Eng. 127, 563–569 (2005)
Fossum, P.K., Froyd, L., Dahlhaug, O.G.: Design and fatigue performance of large utility-scale wind turbine blades. J. Solar. Energy Eng. 135(3), 031019 (2013)
Grujicic, M., Arakere, G., Subramanian, E., Sellappan, V., Vallejo, A., Ozen, M.: Structural-response analysis, fatigue-life prediction, and material selection for 1 MW horizontal-axis wind-turbine blades. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 19(6), 790–801 (2010)
Lee, S., Churchfield, M., Moriarty, P., Jonkman, J., Michalakes, J.: Atmospheric and wake turbulence impacts on wind turbine fatigue loading technical report. NREL/CP-5000–53567, National Renewable Energy Laboratory Technical Report, USA (2012)
Jang, Y.J., Choi, C.W., Lee, J.H., Kang, K.W.: Development of fatigue life prediction method and effect of 10-minute mean wind speed distribution on fatigue life of small wind turbine composite blade. Renew. Energy 79, 187–198 (2015)
Tibaldi, C., Henriksen, L.C., Hansen, M.H., Bak, C.: Wind turbine fatigue damage evaluation based on a linear model and a spectral method. Wind Energy 19(7), 1289–1306 (2016)
Castelos, P.N., Balzani, C.: On the impact of multi-axial stress states on trailing edge bondlines in wind turbine rotor blades. The Science of Making Torque from Wind (TORQUE 2016), J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publishing 753, 062002 (2016)
Kulkarni, P.A., Hu, W., Dhoble, A.S., Padole, P.M.: Statistical wind prediction and fatigue analysis for horizontal-axis wind turbine composite material blade under dynamic loads. Adv. Mech. Eng. 9(9), 1–26 (2017)
Zhang, C.Z., Chen, H.P., Huang, T.L.: Fatigue damage assessment of wind turbine composite blades using corrected blade element momentum theory. Measurement 129, 102–111 (2018)
Meng, H., Lien, F.S., Glinka, G., Geiger, P.: Study on fatigue life of bend-twist coupling wind turbine blade based on anisotropic beam model and stress-based fatigue analysis method. Compos. Struct. 208, 678–701 (2019)
Liu, H.W., Zhang, Z.C., Jia, H.B., Liu, Y.J., Leng, J.S.: A modified composite fatigue damage model considering stiffness evolution for wind turbine blades. Compos. Struct. 233, 111736 (2020)
Gao, C., Sweetman, B., Tang, S.R.: Multiaxial fatigue assessment of floating offshore wind turbine blades operating on compliant floating platforms. Ocean Eng. 261, 111921 (2022)
Liu, P.F., Xu, D., Li, J.G., Chen, Z.P., Wang, S.B., Leng, J.X., Zhu, R.H., Jiao, L., Liu, W.S., Li, Z.X.: Damage mode identification of composite wind turbine blade under accelerated fatigue loads using acoustic emission and machine learning. Struct. Health Monitor. 19, 1092–1103 (2020)
Liu, P.F., Liao, B.B., Jia, L.Y., Peng, X.Q.: Finite element analysis of dynamic progressive failure of carbon fiber composite laminates under low velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 149, 408–422 (2016)
Tarfaoui, M., Shah, O.R., Nachtane, M.: Design and optimization of composite offshore wind turbine blades. J. Energ. Resour. Technol. 141(5), 051204 (2019)
Sang, S., Wen, H., Cao, A.X., Du, X.R., Zhu, X., Shi, Q., Qiu, C.H.: Dynamic modification method for BEM of wind turbine considering the joint action of installation angle and structural pendulum motion. Ocean Eng. 215, 107528 (2020)
Puck, A., Schürmann, H.: Failure analysis of FRP laminates by means of physically based phenomenological models. Compos. Sci. Technol. 58, 1045–1067 (1998)
Hasen, M.O.H.: Aerodynamics of Wind Turbines (Second version). Earthscan Press, UK and USA (2008)
Epaarachchi, J.A., Clausen, P.D.: The development of a fatigue loading spectrum for small wind turbine blades. J. Wind Eng. Indust. Aerodyna. 94(4), 207–223 (2006)
Evans, S., Dana, S., Clausen, P., Wood, D.: A simple method for modelling fatigue spectra of small wind turbine blades. Wind Energy 24(6), 549–557 (2021)
Arteaga-López, E., Angeles-Camacho, C.: Innovative virtual computational domain based on wind rose diagrams for micrositing small wind turbines. Energy 220, 119701 (2021)
Puck, A., Schürmann, H.: Failure analysis of FRP laminates by means of physically based phenomenological models. Compos. Sci. Technol. 62, 1633–1662 (2002)
Hillerborg, A., Modeer, M., Petersson, P.E.: Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements. Cement Concrete Res. 6, 773–782 (1976)
Liu, J.W., Liu, P.F., Leng, J.X., Wang, C.Z.: Finite element analysis of damage mechanisms of composite wind turbine blade by considering fluid/solid interaction. Part I: full-scale structure. Compos. Struct. 301, 116212 (2022)
Mandell, J.F., Samborsky, D.: SNL/MSU/DOE composite material fatigue database mechanical properties of composite materials for wind turbine blades version 23.0. SAND2014–6043, Sandia National Laboratories Technical Report, USA (2014)
Lapczyk, I., Hurtado, J.A.: Progressive damage modeling in fiber-reinforced materials. Compos. Part A 38, 2333–2341 (2007)
Bottasso, C.L., Campagnolo, F., Croce, A., Dilli, A., Gualdoni, F., Nielsen, M.B.: Structural optimization of wind turbine rotor blades by multilevel sectional/multibody/3D-FEM analysis. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 32, 87–116 (2014)
Ye, J.J., Chu, C.C., Cai, H., Hou, X.N., Shi, B.Q., Tian, S.H., Chen, X.F., Ye, J.Q.: A multi-scale model for studying failure mechanisms of composite wind turbine blades. Compos. Struct. 212, 220–229 (2019)
Chen, X., Zhao, W., Zhao, X.L., Xu, J.Z.: Preliminary failure investigation of a 52.3m glass/epoxy composite wind turbine blade. Eng. Fail. Anal. 44, 345–350 (2014)
Tarfaoui, M., Nachtane, M., Khadimallah, H., Saifaoui, D.: Simulation of mechanical behavior and damage of a large composite wind turbine blade under critical loads. Appl. Compos. Mater. 25, 237–254 (2018)
Liu, P.F., Liu, J.W., Wang, C.Z.: Finite element analysis of damage mechanisms of composite wind turbine blade by considering fluid/solid interaction. Part II: T-shape adhesive structure. Compos. Struct. 301, 116211 (2022)
An, Z.W., Yang, X.X., Kou, H.X.: Multiaxial fatigue life prediction of 1.5 MW wind turbine blade. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica 2020(41), 129–135 (2020)
Cardenas, D., Elizalde, H., Marzocca, P., Gallegos, S., Probst, O.: A coupled aeroelastic damage progression model for wind turbine blades. Compos. Struct. 94, 3072–3081 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would sincerely like to thank the support of Zhejiang public welfare Technology Application Research Project (No.GG22E059461), Research and evaluation facilities for service safety of major engineering materials" National Open Project Funding for major scientific and technological infrastructure of Beijing University of Science and Technology, and National Natural Science Funding of China (No.51875512).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P.F., Chen, H.Y., Wu, T. et al. Fatigue Life Evaluation of Offshore Composite Wind Turbine Blades at Zhoushan Islands of China Using Wind Site Data. Appl Compos Mater 30, 1097–1122 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10098-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-022-10098-1