Abstract
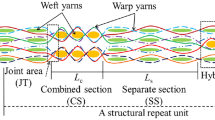
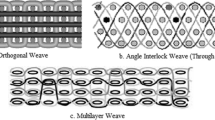
3D interlock woven fabrics are promising materials to replace the 2D structures in the field of ballistic protection. The structural complexity of this material caused many difficulties in numerical modeling. This paper presents a new tool that permits to generate a geometry model of any woven fabric, then, mesh this model in shell or solid elements, and apply the mechanical properties of yarns to them. The tool shows many advantages over existing software. It is very handy in use with an organization of the functions in menu and using a graphic interface. It can describe correctly the geometry of all textile woven fabrics. With this tool, the orientation of the local axes of finite elements following the yarn direction facilitates defining the yarn mechanical properties in a numerical model. This tool can be largely applied because it is compatible with popular finite element codes such as Abaqus, Ansys, Radioss etc. Thanks to this tool, a finite element model was carried out to describe a ballistic impact on a 3D warp interlock Kevlar KM2® fabric. This work focuses on studying the effect of friction onto the ballistic impact behavior of this textile interlock structure. Results showed that the friction among yarns affects considerably on the impact behavior of this fabric. The effect of the friction between projectile and yarn is less important. The friction plays an important role in keeping the fabric structural stability during the impact event. This phenomenon explained why the projectile is easier to penetrate this 3D warp interlock fabric in the no-friction case. This result also indicates that the ballistic performance of the interlock woven fabrics can be improved by using fibers with great friction coefficients.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miravete, A.: 3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials. Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press LLC (2007)
Bhatnagar, A.: Military and law enforcement applications of lightweight ballistic materials. In: Bhatnagar, A. (ed.) Lightweight ballistic composites - Military and law-enforcement applications, pp. 364–397. Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press LLC (2006)
Cunniff, P.M.: An analysis of the system effects in woven fabrics under ballistic impact. Text. Res. J. 56, 45–60 (1992)
Chocron-Benloulo, I.S., Rodriguez, J., Sauchez-Galvez, V.: A simple analytical model to simulate textile fabric ballistic behavior. Text. Res. J. 67, 520–527 (1997)
Navarro, C.: Simplified modeling of the ballistic behavior of fabrics and fiber-reinforced polymeric matrix composites. Key. Engng. Mater. 383–400 (1998)
Gu, B.: Analytical modeling for the ballistic perforation of planar plain-woven fabric target by projectile. Compos. B 34, 361–371 (2003)
Barauskas, R., Abraitienne, A.: Computational analysis of impact of a bullet against the multilayer fabrics in LS-DYNA. Int. J. Impact Eng. 34, 1286–1305 (2007)
Duan, Y., Keefe, M., Wetzel, E.D., Bogetti, T.A., Powers, B., Kirkwood, J.E., Kirkwood, K.M.: Effects of friction on the ballistic performance of a high-strength fabric structure. WIT Transactions on Engineering Sciences, Impact Loading of Lightweight Structures, Alves, M., Jones, N. (Editors). 219–229 (2005)
Duan, Y., Keefe, M., Bogetti, T.A., Cheeseman, B.A.: Modeling friction effects on the ballistic impact behavior of a single-ply high-strength fabric. Int. J. Impact Eng. 31, 996–1012 (2005)
Duan, Y., Keefe, M., Bogetti, T.A., Cheeseman, B.A.: Modeling the role of friction during ballistic impact of a high-strength plain-weave fabric. Compos. Struct. 68(3), 331–337 (2005)
Duan, Y., Keefe, M., Bogetti, T.A., Powers, B.: Finite element modeling of transverse impact on a ballistic fabric. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 48, 33–43 (2006)
Duan, Y., Keefe, M., Bogetti, T.A., Cheeseman, B.A., Powers, B.: A numerical investigation of the influence of friction on energy absorption by a high-strength fabric subjected to ballistic impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 32, 1299–1312 (2006)
Rao, M.P., Duan, Y., Keefe, M., Powers, B.M., Bogetti, T.A.: Modeling the effects of yarn material properties and friction on the ballistic impact of a plain-weave fabric. Compos. Struct. 89, 556–566 (2009)
Joo, K., Kang, T.J.: Numerical analysis of energy absorption mechanism in multiply fabric impacts. Text. Res. J. 78, 561–576 (2008)
Talebi, H., Wong, S.V., Hamouda, A.M.S.: Finite element evaluation of projectile nose angle effects in ballistic perforation of high strength fabric. Compos. Struct. 87, 314–320 (2009)
Lim, C.T., Shim, V.P.W., Ng, Y.H.: Finite-element modeling of the ballistic impact of fabric armor. Int. J. Impact Eng. 28(1), 13–31 (2003)
Tabiei, A., Nilakantan, G.: Ballistic impact of dry woven fabric composites: a review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 61(1), 010801 (2008) (13 pages)
De Luycker, D., Morestin, F., Boisse, P., Marsal, D.: Simulation of 3D interlock composite performing. Compos. Struct. 88, 615–623 (2009)
Taylor, D., Seyam, A.F.M., Powell, N.B.: Three-dimensional woven composites for automotive applications. 9th Annual Internatinal Conference on Textile Composites, Newark, United states (2008)
Hu, J.: 3-D fibrous assemblies, properties, applications and modelling of three-dimensional textile structures. Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press LLC (2008)
Ha-Minh, C., Kanit, T., Boussu, F., Imad, A.: Numerical multi-scale modeling for textile woven fabric against ballistic impact. Comput. Mater. Sci. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.commatsci.2011.02.029
Yi, H.L., Ding, X.: Conventional approach on manufacturing 3D woven preforms used for Composites. J. Ind. Text. 34, 39–50 (2004)
Sherburn, M.: Geometric and mechanical modelling of textiles. PhD thesis, The University of Nottingham (2007)
Searles, K., Odegard, G., Kumosa, M.: Micro- and mesomechanics of 8-harness satin woven fabric composites: I - evaluation of elastic behavior. Compos. A 32, 1627–1655 (2001)
Hivet, G., Boisse, P.: Consistent 3D geometrical model of fabric elementary cell: application to a meshing preprocessor for 3D finite element analysis. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 42, 25–49 (2005)
Lomov, S., Verpoest, I., Robitaille, F.: Manufacturing and internal geometry of textiles. Design and manufacture of textile composites. In: Long, A.C. (ed), Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press LLC. 1–61 (2005)
Verpoest, I., Lomov, S.: Virtual textile composites software WiseTex: integration with micro-mechanical, permeability and structural analysis. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 2563–2574 (2005)
Birkefeld, K., Röder, M., von Reden, T., Bulat, M., Drechsler, K.: Characterization of biaxial and triaxial braids: fiber architecture and mechanical properties. Int. J. Appl. Compos. Mater. (2011). doi:10.1007/s10443-011-9190-2
RADIOSS Theory version 90 manual (2008)
‘Altair HyperMesh 10.0’. Altair Engineering Inc. (2009)
Cheng, M., Chen, W.: Mechanical properties of Kevlar® KM2® single fiber. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 123, 197–203 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha-Minh, C., Boussu, F., Kanit, T. et al. Effect of Frictions on the Ballistic Performance of a 3D Warp Interlock Fabric: Numerical Analysis. Appl Compos Mater 19, 333–347 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-011-9202-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-011-9202-2