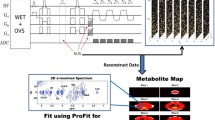
Abstract
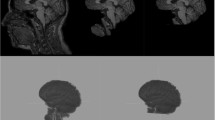
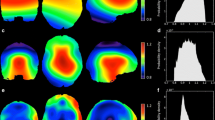
Issues with model fitting (i.e. suboptimal standard deviation, linewidth/full-width-at-half-maximum, and/or signal-to-noise ratio) in multi-voxel MRI spectroscopy, or chemical shift imaging (CSI) can result in the significant loss of usable voxels. A potential solution to minimize this problem is to estimate the value of unusable voxels by utilizing information from reliable voxels in the same image. We assessed an image restoration method called inpainting as a tool to restore unusable voxels, and compared it with traditional interpolation methods (nearest neighbor, trilinear interpolation and tricubic interpolation). In order to evaluate the performance across varying image contrasts and spatial resolutions, we applied the same techniques to a T1-weighted MRI brain dataset, and N-acetylaspartate (NAA) spectroscopy maps from a CSI dataset. For all image types, inpainting exhibited superior performance (lower normalized root-mean-square errors, NRMSE) compared to all other methods considered (p’s < 0.001). Inpainting maintained an average NRMSE of less than 5% even with 50% missing voxels, whereas the other techniques demonstrated up to three times that value, depending on the nature of the image. For CSI maps, inpainting maintained its superiority whether the previously unusable voxels were randomly distributed, or located in regions most commonly affected by voxel loss in real-world data. Inpainting is a promising approach for recovering unusable or missing voxels in voxel-wise analyses, particularly in imaging modalities characterized by low SNR such as CSI. We hypothesize that this technique may also be applicable for datasets from other imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography, or dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, D. S., A. Forsberg, A. Sandström, C. Bergan, D. Kadetoff, E. Protsenko, J. Lampa, Y. C. Lee, C. O. Höglund, C. Catana, S. Cervenka, O. Akeju, M. Lekander, G. Cohen, C. Halldin, N. Taylor, M. Kim, J. M. Hooker, R. R. Edwards, V. Napadow, E. Kosek, and M. L. Loggia. Brain glial activation in fibromyalgia—a multi-site positron emission tomography investigation. Brain Behav. Immun. 75:72–83, 2019.
Albrecht, D. S., M. Kim, O. Akeju, A. Torrado-Carvajal, R. R. Edwards, Y. Zhang, C. Bergan, E. Protsenko, A. Kucyi, A. Wasan, J. M. Hooker, V. Napadow, and M. L. Loggia. The neuroinflammatory component of negative affect in patients with chronic pain. Mol. Psychiatry 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0433-1.
Andronesi, O. C., B. A. Gagoski, and A. G. Sorensen. Neurologic 3D MR spectroscopic imaging with low-power adiabatic pulses and fast spiral acquisition. Radiology 262(2):647–661, 2012.
Andronesi, O. C., S. Ramadan, E. M. Ratai, D. Jennings, C. E. Mountford, and A. G. Sorensen. Spectroscopic imaging with improved gradient modulated constant adiabaticity pulses on high-field clinical scanners. J. Magn. Reson. 203(2):283–293, 2010.
Armanious, K., Y. Mecky, S. Gatidis, and B. Yang. Adversarial inpainting of medical image modalities. arXiv preprint arXiv:181006621 2018.
Astrakas, L. G., and M. I. Argyropoulou. Shifting from region of interest (ROI) to voxel-based analysis in human brain mapping. Pediatr. Radiol. 40(12):1857–1867, 2010.
Bertalmio, M., L. Vese, G. Sapiro, and S. Osher. Simultaneous structure and texture image inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 12(8):882–889, 2003.
Bogner, W., A. T. Hess, B. Gagoski, M. D. Tisdall, A. J. van der Kouwe, S. Trattnig, B. R. Rosen, and O. C. Andronesi. Real-time motion- and B0-correction for LASER-localized spiral-accelerated 3D-MRSI of the brain at 3 T. Neuroimage 88:22–31, 2014.
Chan, T., and J. Shen. Variational image inpainting. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 58(5):579–619, 2005.
Criminisi, A., P. Pérez, and K. Toyama. Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(9):1200–1212, 2004.
Elharrouss, O., N. Almaadeed, S. Al-Maadeed, and Y. Akbari. Image inpainting: a review. Neural Process. Lett. 51:2007–2028, 2019.
Garcia, D. Robust smoothing of gridded data in one and higher dimensions with missing values. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 54(4):1167–1178, 2010.
Giuliani, N. R., V. D. Calhoun, G. D. Pearlson, A. Francis, and R. W. Buchanan. Voxel-based morphometry versus region of interest: a comparison of two methods for analyzing gray matter differences in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 74(2–3):135–147, 2005.
Graveron-Demilly, D. Quantification in magnetic resonance spectroscopy based on semi-parametric approaches. MAGMA 27(2):113–130, 2014.
Guillemot, C., and O. Le Meur. Image inpainting. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 31(1):127–144, 2014.
Guizard, N., K. Nakamura, P. Coupé, V. S. Fonov, D. L. Arnold, and D. L. Collins. Non-local means inpainting of MS lesions in longitudinal image processing. Front. Neurosci. 9:456, 2015.
Hayasaka, S., and P. J. Laurienti. Comparison of characteristics between region-and voxel-based network analyses in resting-state fMRI data. Neuroimage 50(2):499–508, 2010.
Kikinis, R., S. D. Pieper, and K. G. Vosburgh. 3D Slicer: a platform for subject-specific image analysis, visualization, and clinical support. In: Intraoperative Imaging and Image-Guided Therapy, edited by F. A. Jolesz. New York: Springer, 2014, pp. 277–289.
Liu, D., X. Sun, F. Wu, S. Li, and Y. Zhang. Image compression with edge-based inpainting. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 17(10):1273–1287, 2007.
Loggia, M. L., D. B. Chonde, O. Akeju, G. Arabasz, C. Catana, R. R. Edwards, E. Hill, S. Hsu, D. Izquierdo-Garcia, R. R. Ji, M. Riley, A. D. Wasan, N. R. Zürcher, D. S. Albrecht, M. G. Vangel, B. R. Rosen, V. Napadow, and J. M. Hooker. Evidence for brain glial activation in chronic pain patients. Brain 138(Pt 3):604–615, 2015.
Ostuni, J. L., A. K. Santha, V. S. Mattay, D. R. Weinberger, R. L. Levin, and J. A. Frank. Analysis of interpolation effects in the reslicing of functional MR images. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 21(5):803–810, 1997.
Parker, J., R. V. Kenyon, and D. E. Troxel. Comparison of interpolating methods for image resampling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2(1):31–39, 1983.
Prados, F., M. J. Cardoso, B. Kanber, O. Ciccarelli, R. Kapoor, C. A. M. Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, and S. Ourselin. A multi-time-point modality-agnostic patch-based method for lesion filling in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 139:376–384, 2016.
Provencher, S. W. Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn. Reson. Med. 30(6):672–679, 1993.
Rane, S., G. Sapiro, and M. Bertalmio. Structure and texture filling-in of missing image blocks in wireless transmission and compression applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 12(3):296–303, 2003.
Sdika, M., and D. Pelletier. Nonrigid registration of multiple sclerosis brain images using lesion inpainting for morphometry or lesion mapping. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30(4):1060–1067, 2009.
Smith, S., T. Levante, B. Meier, and R. Ernst. Computer-simulations in magnetic-resonance—an object-oriented programming approach. J. Magn. Reson. A 106(1):75–105, 1994.
Snook, L., C. Plewes, and C. Beaulieu. Voxel based versus region of interest analysis in diffusion tensor imaging of neurodevelopment. Neuroimage 34(1):243–252, 2007.
Thévenaz, P., T. Blu, and M. Unser. Image interpolation and resampling. In: Handbook of Medical Image Processing and Analysis2nd, edited by I. N. Bankman. Cambridge: Academic, 2009, pp. 465–493.
Torrado-Carvajal, A., D. S. Albrecht, J. Lee, O. C. Andronesi, E. Ratai, V. Napadow, and M. L. Loggia. Inpainting as a technique for estimation of missing voxels in chemical shift imaging. bioRxiv preprint bioRxiv:2002.02.17.952325.
Wang, G., D. Garcia, Y. Liu, R. de Jeu, and A. Dolman. A three-dimensional gap filling method for large geophysical datasets: application to global satellite soil moisture observations. Environ. Model. Softw. 30:139–142, 2012.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) 1R21NS087472-01A1 (MLL), 1R01NS095937-01A1 (MLL), 1R01NS094306-01A1 (MLL), 1R01DA047088-01 (MLL/EMR), R01CA190901 (EMR) and Department of Defense (DoD) W81XWH-14-1-0543 (MLL). This work was also supported by the NIH Office of the Director OT2-OD023867 (VN); National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) P01-AT009965 (VN), R61-AT009306 (VN), R33-AT009306 (VN), R01-AT007550 (VN); and National Institute for Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) R01-AR064367 (VN). No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Agata A. Exner oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torrado-Carvajal, A., Albrecht, D.S., Lee, J. et al. Inpainting as a Technique for Estimation of Missing Voxels in Brain Imaging. Ann Biomed Eng 49, 345–353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02556-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02556-3