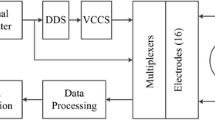
Abstract
Neuromodulation approaches to treating lower urinary tract dysfunction could be substantially improved by a sensor able to detect when the bladder is full. A number of approaches to this problem have been proposed, but none has been found entirely satisfactory. Electrical plethysmography approaches attempt to relate the electrical impedance of the bladder to its volume, but have previously focused only on the amplitudes of the measured signals. We investigated whether the phase relationships between sinusoidal currents applied through a pair of stimulating electrodes and measured through a pair of recording electrodes could provide information about bladder volume. Acute experiments in a rabbit model were used to investigate how phase-to-volume or amplitude-to-volume regression models could be used to predict bladder volumes in future recordings, with and without changes to the saline conductivity. Volume prediction errors were found to be 6.63 ± 1.12 mL using the phase information and 8.32 ± 3.88 mL using the amplitude information (p = 0.44 when comparing the phase and amplitude results, n = 6), where the volume of the filled bladder was about 25 mL. When a full/empty binary decision rule was applied based on the regression model, the difference between the actual threshold that would result from this rule and the desired threshold was found to be 4.24 ± 0.65 mL using the phase information and 106.92 ± 189.82 mL using the amplitude information (p = 0.03, n = 6). Our results suggest that phase information can form the basis for more effective and robust electrical plethysmography approaches to bladder volume measurement.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbey, J., and L. Close. Electrical impedance measurement of urinary bladder fullness. J. Microw. Pow. 18(3):305–309, 1983.
Anderson, K. D. Targeting recovery: priorities of the spinal cord-injured population. J. Neurotrauma 21:1371–1383, 2004.
Bruns, T. M., R. A. Gaunt, and D. J. Weber. Multielectrode array recordings of bladder and perineal primary afferent activity from the sacral dorsal root ganglia. J. Neural Eng. 8:056010, 2011.
Bruns, T. M., R. A. Gaunt, and D. J. Weber. Estimating bladder pressure from sacral dorsal root ganglia recordings. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2011:4239–4242, 2011.
Coosemans, J., and R. Puers. An autonomous bladder pressure monitoring system. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 123:155–161, 2005.
Elkelini, M. S., A. Abuzgaya, and M. M. Hassouna. Mechanisms of action of sacral neuromodulation. Int. Urogynecol. J. 21(Suppl 2):S439–S446, 2010.
Elkelini, M., and M. M. Hassouna. Canadian experience in sacral neuromodulation. Urol. Clin. North Am. 32:41–49, 2005.
Gill, B. C., P. C. Fletter, P. J. Zaszczurynski, A. Perlin, D. Yachia, and M. S. Damaser. Feasibility of fluid volume conductance to assess bladder volume. Neurourol. Urodyn. 27:525–531, 2008.
Jezernik, S., W. M. Grill, and T. Sinkjaer. Neural network classification of nerve activity recorded in a mixed nerve. Neurol. Res. 23:429–434, 2001.
Jezernik, S., W. M. Grill, and T. Sinkjaer. Detection and inhibition of hyperreflexia-like bladder contractions in the cat by sacral nerve root recording and electrical stimulation. Neurourol. Urodyn. 20:215–230, 2001.
Jezernik, S., J. G. Wen, N. J. Rijkhoff, J. C. Djurhuus, and T. Sinkjaer. Analysis of bladder related nerve cuff electrode recordings from preganglionic pelvic nerve and sacral roots in pigs. J. Urol. 163:1309–1314, 2000.
Keshtkar, A., A. Mesbahi, and P. Mehnati. The effect of bladder volume changes on the measured electrical impedance of the urothelium. Int. J. Bio. Eng. Tech. 1(3):287–292, 2008.
Kilgore, K. L., and N. Bhadra. Reversible nerve conduction block using kilohertz frequency alternating current. Neuromodulation 17:242–254, 2014; (discussion 254-5).
Kim, C. T., T. A. Linsenmeyer, H. Kim, and H. Yoon. Bladder volume measurement with electrical impedance analysis in spinal cord-injured patients. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 77:498–502, 1998.
Koldewijn, E. L., P. E. Van Kerrebroeck, E. Schaafsma, H. Wijkstra, F. M. Debruyne, and G. S. Brindley. Bladder pressure sensors in an animal model. J. Urol. 151:1379–1384, 1994.
Kristiansen, N. K., J. C. Djurhuus, and H. Nygaard. Design and evaluation of an ultrasound-based bladder volume monitor. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42:762–769, 2004.
Kurstjens, G. A., A. Borau, A. Rodriguez, N. J. Rijkhoff, and T. Sinkjaer. Intraoperative recording of electroneurographic signals from cuff electrodes on extradural sacral roots in spinal cord injured patients. J. Urol. 174:1482–1487, 2005.
Kurstjens, G. A. M., Dalmose, A. L., Haugland, M., Rijkhoff, N. J. M., and T. Sinkjær. Long-term electroneurographic recordings from nerve cuff electrodes on sacral nerve root in pigs. Proc. 6th Ann. Conf. IFESS, pp. 22–24, 2001.
Mathews, K. S., H. A. Wark, D. J. Warren, M. B. Christensen, N. F. Nolta, P. C. Cartwright, and R. A. Normann. Acute monitoring of genitourinary function using intrafascicular electrodes: selective pudendal nerve activity corresponding to bladder filling, bladder fullness, and genital stimulation. Urology 84:722–729, 2014.
McGee, M. J., C. L. Amundsen, and W. M. Grill. Electrical stimulation for the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction after spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 38:135–146, 2015.
Mendez, A., and M. Sawan. Chronic monitoring of bladder volume: a critical review and assessment of measurement methods. Can. J. Urol. 18:5504–5516, 2011.
Mendez, A., M. Sawan, T. Minagawa, and J. J. Wyndaele. Estimation of bladder volume from afferent neural activity. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 21:704–715, 2013.
Milsom, I., P. Abrams, L. Cardozo, R. G. Roberts, J. Thuroff, and A. J. Wein. How widespread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population-based prevalence study. BJU Int. 87:760–766, 2001.
Park, J. H., C. Kim, J. Shin, C. Im, C. S. Koh, I. S. Seo, S. J. Kim, and H. Shin. Detecting bladder fullness through the ensemble activity patterns of the spinal cord unit population in a somatovisceral convergence environment. J. Neural Eng. 10:056009, 2013.
Petrican, P., and M. A. Sawan. Design of a miniaturized ultrasonic bladder volume monitor and subsequent preliminary evaluation on 41 enuretic patients. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 6:66–74, 1998.
Provost, B., and M. Sawan. Proposed new bladder volume monitoring device based on impedance measurement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 35:691–694, 1997.
Rajagopalan, S., M. Sawan, E. Ghafar-Zadeh, O. Savadogo, and V. P. Chodavarapu. A polypyrrole-based strain sensor dedicated to measure bladder volume in patients with urinary dysfunction. Sensors 8:5081–5095, 2008.
Seif, C., B. Herberger, E. Cherwon, F. J. Martinez Portillo, M. Molitor, T. Stieglitz, G. Bohler, S. Zendler, K. P. Junemann, and P. M. Braun. Urinary bladder volumetry by means of a single retrosymphysically implantable ultrasound unit. Neurourol. Urodyn. 23:680–684, 2004.
Takayama, K., M. Takei, T. Soejima, and J. Kumazawa. Continuous monitoring of bladder pressure in dogs in a completely physiological state. Br. J. Urol. 60:428–432, 1987.
Wein, A. J. Pharmacologic options for the overactive bladder. Urology 51:43–47, 1998.
Wenzel, B. J., J. W. Boggs, K. J. Gustafson, and W. M. Grill. Detecting the onset of hyper-reflexive bladder contractions from the electrical activity of the pudendal nerve. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 13:428–435, 2005.
Yamada, A., M. Fuse, T. Aoyagi, H. Hosaka, H. Toma, and H. Yanagisawa. Preventive equipment for urinary incontinence: a device employing lower abdominal impendance changes. Int. J. Artif. Organs 17:146–150, 1994.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Physicians’ Incorporated Services Foundation (Grant #12-30), as well as by the Center for Research in Advanced Neural Implant Applications (CRANIA) at the University of Toronto. The authors wish to thank Rainer de Guzman for his help with the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Leonidas Iasemidis oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zariffa, J., Grouza, V., Popovic, M.R. et al. A Phase-Based Electrical Plethysmography Approach to Bladder Volume Measurement. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 1299–1309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1397-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1397-1