Abstract
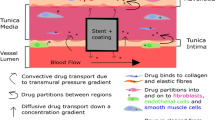
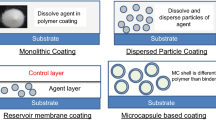
An overview of diffuse interface models specific to drug-eluting stent coatings is presented. Microscale heterogeneities, both in the coating and use environment, dictate the performance of these coatings. Using diffuse interface methods, these heterogeneities can be explicitly incorporated into the model equations with relative ease. This enables one to predict the complex microstructures that evolve during coating fabrication and subsequent impact on drug release. Examples are provided that illustrate the wide range of phenomena that can be addressed with diffuse interface models including: crystallization, constrained phase separation, hydrolytic degradation, and heterogeneous binding. Challenges associated with the lack of material property data and numerical solution of the model equations are also highlighted. Finally, in light of these potential drawbacks, the potential to utilize diffuse interface models to help guide product and process development is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abizaid, A. and J. R. Costa. New drug-eluting stents: an overview on biodegradable and polymer-free next-generation stent dystems. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 3(4):384–393, 2010.
Allen, S. and J. Cahn. A microscopic theory of domain wall motion and its experimental verification in Fe-Al alloy domain growth kinetics. J. Phys. 38:C7–C51, 1977.
Alsoy, S. and J. L. Duda. Modeling of multicomponent drying of polymer films. AIChE J. 45(4):896–905, 1999.
Barocas, V., W. Drasler II, T. Girton, I. Guler, D. Knapp, J. Moeller, and E. Parsonage. A dissolution-diffusion model for the TAXUS™ drug-eluting stent with surface burst estimated from continuum percolation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 90B(1):267–274, 2008.
Belu, A., C. Mahoney, and K. Wormuth. Chemical imaging of drug eluting coatings: combining surface analysis and confocal raman microscopy. J. Control. Release 126:111–121, 2008.
Cahn, J. W., and W. C. Carter. Crystal shapes and phase equilibria: a common mathematical basis. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27(6):1431–1440, 1996.
Cahn, J., and J. Hilliard. Free energy of nonuniform systems. I. Interfacial free energy. J. Chem. Phys. 28:258–67, 1958.
de Groot, S. R., and P. Mazur. Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics. Dover Books on Physics Series. Mineola: Dover Publications, 1984.
Duarte, Í., J. L. Santos, J. F. Pinto, and M. Temtem. Screening methodologies for the development of spray-dried amorphous solid dispersions. Pharm. Res. 32(1):222–237, 2014.
Duda, J., Y. Ni, and J. Vrentas. An equation relating self-diffusion and mutual diffusion coefficients in polymer-solvent systems. Macromolecules 12(3):459–462, 1979.
Flory, P. Thermodynamics of high polymer solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 9(8):660, 1941.
Forrey, C., D. M. Saylor, J. S. Silverstein, J. F. Douglas, E. M. Davis, and Y. A. Elabd. Prediction and validation of diffusion coefficients in a model drug delivery system using microsecond atomistic molecular dynamics simulation and vapour sorption analysis. Soft Matter 10(38):7480–7494, 2014.
Frenkel, D., and B. Smit. Understanding Molecular Simulation, 2nd edn. Orlando: Academic Press, Inc., 2001.
Guo, J., D. M. Saylor, E. P. Glaser, and D. V. Patwardhan. Impact of artificial plaque composition on drug transport. J. Pharm. Sci. 102(6):1905–1914, 2013.
Gupta, J., C. Nunes, S. Vyas, and S. Jonnalagadda. Prediction of solubility parameters and miscibility of pharmaceutical compounds by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 115(9):2014–2023, 2011.
Guyer, J. E., W. J. Boettinger, J. A. Warren, and G. B. McFadden. Phase field modeling of electrochemistry. I. Equilibrium. Phys. Rev. E 69:021603, 2004.
Hansen, C. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007.
Heroux, M. A., R. A. Bartlett, V. E. Howle, R. J. Hoekstra, J. J. Hu, T. G. Kolda, R. B. Lehoucq, K. R. Long, R. P. Pawlowski, E. T. Phipps, A. G. Salinger, H. K. Thornquist, R. S. Tuminaro, J. M. Willenbring, A. Williams, and K. S. Stanley. An overview of the trilinos project. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 31(3):397–423, 2005.
Horner, M., S. Joshi, V. Dhruva, S. Sett, and S. F. C. Stewart. A two-species drug delivery model is required to predict deposition from drug-eluting stents. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 1(3):225–234, 2010.
Kamath, K., J. Barry, and K. Miller. The TAXUS™drug-eluting stent: a new paradigm in controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58:412–36, 2006.
Kim, C. S., D. M. Saylor, M. K. McDermott, D. V. Patwardhan, and J. A. Warren. Modeling solvent evaporation during the manufacture of controlled drug-release coatings and the impact on release kinetics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 90(2):688–699, 2009.
Lemos, P., P. Serruys, and J. Sousa. Drug-eluting stents. Circulation 107(24):3003–3007, 2003.
Levin, A. D., N. Vukmirovic, C. W. Hwang, and E. R. Edelman. Specific binding to intracellular proteins determines arterial transport properties for rapamycin and paclitaxel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101(25):9463–9467, 2004.
Mahieu, A., J. F. Willart, E. Dudognon, F. Danède F, and M. Descamps. A new protocol to determine the solubility of drugs into polymer matrixes. Mol. Pharm. 10(2):560–566, 2013.
McDermott, M. K. (private communication).
McDermott, M. K., D. M. Saylor, R. Casas, B. J. Dair, J. Guo, C. S. Kim, C. M. Mahoney, K. Ng, S. K. Pollack, and D. V. Patwardhan. Microstructure and elution of tetracycline from block copolymer coatings. J. Pharm. Sci. 99(6):2777–2785, 2010.
McGinty, S., S. McKee, C. McCormick, and M. Wheel. Release mechanism and parameter estimation in drug-eluting stent systems: analytical solutions of drug release and tissue transport. Math. Med. Biol., (2014). doi:10.1093/imammb/dqt025.
Michels, J. J., and E. Moons. Simulation of surface-directed phase separation in a solution-processed polymer/PCBM blend. Macromolecules 46(21):8693–8701, 2013.
Occhipinti, P., and P. C. Griffiths. Quantifying diffusion in mucosal systems by pulsed-gradient spin-echo NMR. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60(15):1570–1582, 2008.
Ohta, T., and K. Kawasaki. Equilibrium morphology of block copolymer melts. Macromolecules 19(10):2621–2632, 1986.
Saylor, D. M., J. E. Guyer, D. Wheeler, and J. A. Warren. Predicting microstructure development during casting of drug-eluting coatings. Acta Biomater. 7(2):604–613, 2011.
Saylor, D. M., C. S. Kim, D. V. Patwardhan, and J. A. Warren. Diffuse-interface theory for structure formation and release behavior in controlled drug release systems. Acta Biomater. 3(6):851–864, 2007.
Saylor, D. M., J. E. Soneson, J. J. Kleinedler, M. Horner, and J. A. Warren. A structuresensitive continuum model of arterial drug deposition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 82(C):468–478, 2015.
Silva, G., J. Eckelt, M. Gonçalves, and B. Wolf. Thermodynamics of pseudo-ternary systems as a tool to predict the morphologies of cellulose acetate/polystyrene blends cast from tetrahydrofuran solutions. Polymer 44(4):1075–1080, 2003.
Spencer, P. J. A brief history of CALPHAD. Calphad 32(1):1–8, 2008.
Torquato, S. Random Heterogeneous Materials: Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties. Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics. New York: Springer, 2002.
Tzafriri, A. R., A. Groothuis, G. S. Price, and E. R. Edelman. Stent elution rate determines drug deposition and receptor-mediated effects. J. Control. Release 161(3):1–9, 2010.
Tzafriri, A. R., A. D. Levin, and E. R. Edelman. Diffusion-limited binding explains binary dose response for local arterial and tumour drug delivery. Cell Prolif. 42(3):348–363, 2009.
Tzafriri, A. R., N. Vukmirovic, V. B. Kolachalama, I. Astafieva, and E. R. Edelman. Lesion complexity determines arterial drug distribution after local drug delivery. J. Control. Release 142(3):332–338, 2010.
Ukmar, T., M. Gaberšček, F. Merzel, and A. Godec. Modus operandi of controlled release from mesoporous matrices: a theoretical perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(33):15311–15317, 2011.
Von Meerwall, E, E. Amis, and J. Ferry. Self-diffusion in solutions of polystyrene in tetrahydrofuran: comparison of concentration dependences of the diffusion coefficients of polymer, solvent, and a ternary probe component. Macromolecules 18(2):260–266, 1985.
Vrentas, J., and J. Duda. Diffusion in polymer–solvent systems. I. Reexamination of the free-volume theory. J. Polym. Sci. 15(3):403–416, 1977.
Welland, M. J., D. Wolf, and J. E. Guyer. Multicomponent phase-field model for extremely large partition coefficients. Phys. Rev. E 89(1):012409, 2014.
Wodo, O., and B. Ganapathysubramanian. Modeling morphology evolution during solvent-based fabrication of organic solar cells. Comput. Mater. Sci. 55:113–126, 2012.
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Disclaimers
The mention of commercial products, their source, or their use in connection with the material reported herein is not to be construed as either an actual or implied endorsement of the US Food and Drug Administration. Certain commercial equipment, instruments, or materials are identified in this paper in order to specify the experimental procedure adequately. Such identification is not intended to imply recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, nor is it intended to imply that the materials or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Associate Editor Sean McGinty oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saylor, D.M., Forrey, C., Kim, CS. et al. Diffuse Interface Methods for Modeling Drug-Eluting Stent Coatings. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 548–559 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1375-7