Abstract
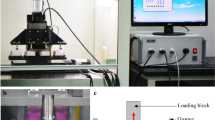
This paper describes the development and use of a direct compression stimulator for culturing explants from the meniscus of the knee and articular cartilage. Following design and fabrication of the instrument along with its data acquisition system, the function of the machine was verified by both mechanical means and tissue effect. The loading chamber can hold up to 45 5 mm diameter samples. While designed to stimulate samples up to 4 mm thick, axial displacements as little as 0.127 μm are within the theoretical capacity of the stimulator. In gene expression studies, collagen II and aggrecan expression were examined in explants from articular cartilage as well as medial and lateral menisci subjected to dynamic stimulation and static compression. These results were then compared to free swelling samples. It was found that static compression to cut thickness down-regulated aggrecan and collagen II expression in articular cartilage explants compared to free swelling controls by 94% and 90%, respectively. The application of a dynamic, intermittent, 2% oscillation around the cut thickness returned expression levels to those of free swelling controls at 4 h but not at 76 h. In medial meniscus samples, dynamic compression up-regulated aggrecan expression by 108%, but not collagen II expression, at 4 and 76 h compared to static controls. No difference in gene expression was observed for lateral meniscal explants. Thus, effects of direct compression seen in articular cartilage may not necessarily translate to the knee meniscus. The design of this stimulator will allow a variety of tissues and loading regimens to be examined. It is hoped that regimens can be found that not only return samples to the production levels of free swelling controls, but also surpass them in terms of gene expression, protein synthesis, and functional properties.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Antoniades, H. N., and C. D. Scher. Radioimmunoassay of a human serum growth factor for Balb/c-3T3 cells: Derivation from platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74:1973–1977, 1977.
Aufderheide, A. C., and K. A. Athanasiou. Mechanical stimulation toward tissue engineering of the knee meniscus. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32:1161–1174, 2004.
Bonassar, L. J., A. J. Grodzinsky, E. H. Frank, S. G. Davila, N. R. Bhaktav, and S. B. Trippel. The effect of dynamic compression on the response of articular cartilage to insulin-like growth factor-I. J. Orthop. Res. 19:11–17, 2001.
Burton-Wurster, N., M. Vernier-Singer, T. Farquhar, and G. Lust. Effect of compressive loading and unloading on the synthesis of total protein, proteoglycan, and fibronectin by canine cartilage explants. J. Orthop. Res. 11:717–729, 1993.
Buschmann, M. D., Y. A. Gluzband, A. J. Grodzinsky, and E. B. Hunziker. Mechanical compression modulates matrix biosynthesis in chondrocyte/agarose culture. J. Cell Sci. 108(Pt 4):1497–1508, 1995.
Buschmann, M. D., Y. A. Gluzband, A. J. Grodzinsky, J. H. Kimura, and E. B. Hunziker. Chondrocytes in agarose culture synthesize a mechanically functional extracellular matrix. J. Orthop. Res. 10:745–758, 1992.
Buschmann, M. D., E. B. Hunziker, Y. J. Kim, A. J. Grodzinsky, and U. o. B. S. M E Mueller Institute for Biomechanics. Altered aggrecan synthesis correlates with cell and nucleus structure in statically compressed cartilage. J. Cell Sci. 109:499–508, 1996.
Djurasovic, M., J. W. Aldridge, R. Grumbles, M. P. Rosenwasser, D. Howell, and A. Ratcliffe. Knee joint immobilization decreases aggrecan gene expression in the meniscus. Am. J. Sports Med. 26:460–466, 1998.
Dowdy, P. A., A. Miniaci, S. P. Arnoczky, P. J. Fowler, and D. R. Boughner. The effect of cast immobilization on meniscal healing. An experimental study in the dog. Am. J. Sports Med. 23:721–728, 1995.
Ferretti, M., S. Madhavan, J. Deschner, B. Rath-Deschner, E. Wypasek, and S. Agarwal. Dynamic Biophysical Strain Modulates Proinflammatory Gene Induction In Meniscal Fibrochondrocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 6:C1610–C1615, 2006.
Frank, E. H., M. Jin, A. M. Loening, M. E. Levenston, and A. J. Grodzinsky. A versatile shear and compression apparatus for mechanical stimulation of tissue culture explants. J. Biomech. 33:1523–1527, 2000.
Gray, M. L., A. M. Pizzanelli, R. C. Lee, A. J. Grodzinsky, and D. A. Swann. Kinetics of the chondrocyte biosynthetic response to compressive load and release. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 991:415–425, 1989.
Guerne, P. A., A. Sublet, and M. Lotz. Growth factor responsiveness of human articular chondrocytes: distinct profiles in primary chondrocytes, subcultured chondrocytes, and fibroblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 158:476–484, 1994.
Hansen, U., M. Schunke, C. Domm, N. Ioannidis, J. Hassenpflug, T. Gehrke, and B. Kurz. Combination of reduced oxygen tension and intermittent hydrostatic pressure: A useful tool in articular cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomech. 34:941–949, 2001.
Hunter, C. J., S. M. Imler, P. Malaviya, R. M. Nerem, and M. E. Levenston. Mechanical compression alters gene expression and extracellular matrix synthesis by chondrocytes cultured in collagen I gels. Biomaterials 23:1249–1259, 2002.
Hunter, C. J., J. K. Mouw, and M. E. Levenston. Dynamic compression of chondrocyte-seeded fibrin gels: Effects on matrix accumulation and mechanical stiffness. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 12:117–130, 2004.
Imler, S. M., A. N. Doshi, and M. E. Levenston. Combined effects of growth factors and static mechanical compression on meniscus explant biosynthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 12:736–744, 2004.
Kim, Y. J., R. L. Sah, A. J. Grodzinsky, A. H. Plaas, and J. D. Sandy. Mechanical regulation of cartilage biosynthetic behavior: Physical stimuli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 311:1–12, 1994.
Kiviranta, I., J. Jurvelin, M. Tammi, A. M. Saamanen, and H. J. Helminen. Weight bearing controls glycosaminoglycan concentration and articular cartilage thickness in the knee joints of young beagle dogs. Arthritis Rheum. 30:801–809, 1987.
Kiviranta, I., M. Tammi, J. Jurvelin, A. M. Saamanen, and H. J. Helminen. Moderate running exercise augments glycosaminoglycans and thickness of articular cartilage in the knee joint of young beagle dogs. J. Orthop. Res. 6:188–195, 1988.
Larsson, T., R. M. Aspden, and D. Heinegard. Effects of mechanical load on cartilage matrix biosynthesis in vitro. Matrix 11:388–394, 1991.
Lee, C. R., A. J. Grodzinsky, and M. Spector. Biosynthetic response of passaged chondrocytes in a type II collagen scaffold to mechanical compression. J. Biomed. Mater Res. 64A:560–569, 2003.
Levin, A. S., C. T. Chen, and P. A. Torzilli. Effect of tissue maturity on cell viability in load-injured articular cartilage explants. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 13:488–496, 2005.
Li, K. W., A. S. Wang, and R. L. Sah. Microenvironment regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity in chondrocytes: effects of culture configuration, interleukin-1, and compressive stress. Arthritis Rheum. 48:689–699, 2003.
Li, K. W., A. K. Williamson, A. S. Wang, and R. L. Sah. Growth responses of cartilage to static and dynamic compression. Clin. Orthop. S34–S48, 2001.
Lucchinetti, E., C. S. Adams, W. E. Jr. Horton, and P. A. Torzilli. Cartilage viability after repetitive loading: A preliminary report. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 10:71–81, 2002.
Maroudas, A., D. Rigler, and R. Schneiderman. Young and aged cartilage differ in their response to dynamic compression as far as the rate of glycosaminoglycan synthesis is concerned. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc. 45, 1999.
Mauck, R. L., S. B. Nicoll, S. L. Seyhan, G. A. Ateshian, and C. T. Hung. Synergistic action of growth factors and dynamic loading for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue. Eng. 9:597–611, 2003.
Mauck, R. L., S. L. Seyhan, G. A. Ateshian, C. T. Hung, and C. U. J. E. T. M. C. A. A. N. Y. N. Y. U. S. A. Department of Biomedical Engineering. Influence of seeding density and dynamic deformational loading on the developing structure/function relationships of chondrocyte-seeded agarose hydrogels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 30(8):1046–1056, 2002.
Mauck, R. L., M. A. Soltz, C. C. Wang, D. D. Wong, P. H. Chao, W. B. Valhmu, C. T. Hung, and G. A. Ateshian. Functional tissue engineering of articular cartilage through dynamic loading of chondrocyte-seeded agarose gels. J. Biomech. Eng. 122:252–260, 2000.
Messai, H., Y. Duchossoy, A. M. Khatib, A. Panasyuk, and D. R. Mitrovic. Articular chondrocytes from aging rats respond poorly to insulin-like growth factor-1: An altered signaling pathway. Mech. Ageing Dev. 115:21–37, 2000.
Murray, R. C., C. F. Zhu, A. E. Goodship, K. H. Lakhani, C. M. Agrawal, and K. A. Athanasiou. Exercise affects the mechanical properties and histological appearance of equine articular cartilage. J. Orthop. Res. 17:725–731, 1999.
Parkkinen, J. J., M. J. Lammi, H. J. Helminen, and M. Tammi. Local stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in articular cartilage explants by dynamic compression in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 10:610–620, 1992.
Plumb, M. S., and R. M. Aspden. The response of elderly human articular cartilage to mechanical stimuli in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 13:1084–1091, 2005.
Quinn, T. M., A. J. Grodzinsky, M. D. Buschmann, Y. J. Kim, and E. B. Hunziker. Mechanical compression alters proteoglycan deposition and matrix deformation around individual cells in cartilage explants. J. Cell Sci. 111 (Pt 5):573–583, 1998.
Ragan, P. M., A. M. Badger, M. Cook, V. I. Chin, M. Gowen, A. J. Grodzinsky, and M. W. Lark. Down-regulation of chondrocyte aggrecan and Col II expression correlates with increases in static compression magnitude and duration. J. Orthop. Res. 17:836–842, 1999.
Ragan, P. M., V. I. Chin, H. H. Hung, K. Masuda, E. J. Thonar, E. C. Arner, A. J. Grodzinsky, and J. D. Sandy. Chondrocyte extracellular matrix synthesis and turnover are influenced by static compression in a new alginate disc culture system. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 383:256–264, 2000.
Rodkey, W. G., K. R. Stone, and J. R. Steadman. Chapter 12: prosthetic meniscal replacement. In: Biology and Biomechanics of the Trumatized Synovial Joint: The Knee as a Model, edited by G. A. M. Finerman and F. R. Noyes. Rosemont: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 1992, pp. 221–231.
Sah, R. L. Effects of static and dynamic compression on matrix metabolism in cartilage explants. In: Articular cartilage and osteoarthritis, edited by K. E. Kuettner. New York: Raven Press, 1992, pp. 373–392.
Sah, R. L., Y. J. Kim, J. Y. Doong, A. J. Grodzinsky, A. H. Plaas, and J. D. Sandy. Biosynthetic response of cartilage explants to dynamic compression. J. Orthop. Res. 7:619–636, 1989.
Sauerland, K., R. X. Raiss, and J. Steinmeyer. Proteoglycan metabolism and viability of articular cartilage explants as modulated by the frequency of intermittent loading. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11:343–350, 2003.
Shieh, A. C., and K. A. Athanasiou. Biomechanics of single chondrocytes and osteoarthritis. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 30:307–343, 2002.
Steinmeyer, J. A computer-controlled mechanical culture system for biological testing of articular cartilage explants. J. Biomech. 30:841–845, 1997.
Steinmeyer, J., and B. Ackermann. The effect of continuously applied cyclic mechanical loading on the fibronectin metabolism of articular cartilage explants. Res. Exp. Med. (Berl.) 198:247–260, 1999.
Steinmeyer, J., and S. Knue. The proteoglycan metabolism of mature bovine articular cartilage explants superimposed to continuously applied cyclic mechanical loading. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 240:216–221, 1997.
Steinmeyer, J., S. Knue, R. X. Raiss, and I. Pelzer. Effects of intermittently applied cyclic loading on proteoglycan metabolism and swelling behaviour of articular cartilage explants. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 7:155–164, 1999.
Steinmeyer, J., P. A. Torzilli, N. Burton-Wurster, and G. Lust. A new pressure chamber to study the biosynthetic response of articular cartilage to mechanical loading. Res. Exp. Med. (Berl.) 193:137–142, 1993.
Torzilli, P. A., R. Grigiene, C. Huang, S. M. Friedman, S. B. Doty, A. L. Boskey, and G. Lust. Characterization of cartilage metabolic response to static and dynamic stress using a mechanical explant test system. J. Biomech. 30:1–9, 1997.
Upton, M. L., J. Chen, F. Guilak, and L. A. Setton. Differential effects of static and dynamic compression on meniscal cell gene expression. J. Orthop. Res. 21:963–969, 2003.
van Der Meulen, M. C., and R. Huiskes. Why mechanobiology? A survey article. J. Biomech. 35:401–414, 2002.
Waldman, S. D., C. G. Spiteri, M. D. Grynpas, R. M. Pilliar, and R. A. Kandel. Long-term intermittent shear deformation improves the quality of cartilaginous tissue formed in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 21:590–596, 2003.
Wight, M. TGF-beta1 in bovine serum. Art Sci. 19:1–3, 2001.
Wolff, J. The law of bone remodelling. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1892, xii, 126 pp.
Wong, M., P. Wuethrich, M. D. Buschmann, P. Eggli, and E. Hunziker. Chondrocyte biosynthesis correlates with local tissue strain in statically compressed adult articular cartilage. J. Orthop. Res. 15:189–196, 1997.
Zapf, J., B. Morell, H. Walter, Z. Laron, and E. R. Froesch. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and its carrier protein in various metabolic disorders. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh.) 95:505–517, 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aufderheide, A.C., Athanasiou, K.A. A Direct Compression Stimulator for Articular Cartilage and Meniscal Explants. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 1463–1474 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9157-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9157-x