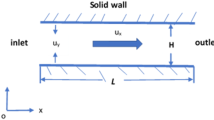
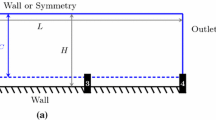
Abstract
Computational modeling and simulation can provide an effective predictive capability for flow properties of the confined fluids in micro/nanoscales. In this paper, considering the boundary slip at the fluid–solid interface, the motion property of fluids confined in parallel-plate nanochannels are investigated to couple the atomistic regime to continuum. The corrected second-order slip boundary condition is used to solve the Navier–Stokes equations for confined fluids. Molecular dynamics simulations for Poiseuille flows are performed to study the influences of the strength of the solid–fluid coupling, the fluid temperature, and the density of the solid wall on the velocity slip at the fluid boundary. For weak solid–fluid coupling strength, high temperature of the confined fluid and high density of the solid wall, the large velocity slip at the fluid boundary can be obviously observed. The effectiveness of the corrected second-order slip boundary condition is demonstrated by comparing the velocity profiles of Poiseuille flows from MD simulations with that from continuum.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MP, Tidesley DJ (1987) Computer simulation of liquids. Oxford University Press, New York
Barrat JL, Bocquet L (1999a) Large slip effect at a nonwetting fluid-solid interface. Phys Rev Lett 82:4671–4674. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.4671
Barrat JL, Bocquet L (1999b) Influence of wetting properties on hydrodynamic boundary conditions at a fluid/solid interface. Faraday Discuss 112:119–127. doi:10.1039/A809733J
Batchelor GK (1967) An introduction to fluid mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Baudry J, Charlaix E, Tonch A (2001) Experimental evidence for a large slip effect at a nonwetting fluid–solid interface. Langmuir 17:5232–5236. doi:10.1021/la0009994
Beebe DJ, Mensing GA, Walker GM (2002) Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 4:261–286. doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.4.112601.125916
Beskok A, Karniadakis GE, Trimmer W (1996) Rarefaction and compressibility effects in gas microflows. J Fluids Eng 118:448–456. doi:10.1115/1.2817779
Bitsanis I, Vanderlick TK, Tirrel M, Davis HT (1988) A tractable molecular theory of flow in strongly inhomogeneous fluids. J Chem Phys 89:3152–3162. doi:10.1063/1.454972
Bocquet L, Barrat JL (1994) Hydrodynamic boundary conditions, correlation functions, and Kubo relations for confined fluids. Phys Rev E 49:3079–3092. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.49.3079
Cao BY, Chen M, Guo ZY (2005) Temperature dependence of the tangential momentum accommodation coefficient for gases. Appl Phys Lett 86:091905. doi:10.1063/1.1871363
Cao BY, Chen M, Guo ZY (2006) Liquid flow in surface-nanostructured channels studied by molecular dynamics simulation. Phys Rev E 74:066311. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.74.066311
Choi CH, Westin KJA, Breuer KS (2003) Apparent slip flows in hydrophilic and hydrophobic microchannels. Phys Fluids 15:2897–2902. doi:10.1063/1.1605425
Cieplak M, Koplik J, Banavar JR (2001) Boundary conditions at a fluid-solid interface. Phys Rev Lett 86:803–806. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.803
Colin S, Lalonde P, Caen R (2004) Validation of a second-order slip flow model in rectangular microchannels. Heat Transf Eng 25:23–30. doi:10.1080/01457630490280047
Cottin-Bizonne C, Cross B, Steinberger A, Charlaix E (2005) Boundary slip on smooth hydrophobic surfaces: Intrinsic effects and possible artifacts. Phys Rev Lett 94:056102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.056102
Curry JE (2000) Structure of a model lubricant in a mica slit pore. J Chem Phys 113:2400. doi:10.1063/1.482055
Demirel AL, Granick S (2001) Origins of solidification when a simple molecular fluid is confined between two plates. J Chem Phys 115:1498–1512. doi:10.1063/1.1380207
Finger GW, Kapat JS, Bhattacharya A (2007) Molecular dynamics simulation of adsorbent layer effect on tangential momentum accommodation coefficient. J Fluids Eng 129:31–39. doi:10.1115/1.2375128
Granick S (1991) Motions and relaxations of confined liquids. Science 253:1374–1379. doi:10.1126/science.253.5026.1374
Grest GS, Kremer K (1986) Molecular dynamics simulation for polymers in the presence of a heat bath. Phys Rev A 33:3628–3631. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.33.3628
Guo ZL, Shi BC, Zheng CG (2007) An extend Navier–Stokes formulation for gas flows in the Knudsen layer near a wall. EPL 80:24001–24006. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/80/24001
Ho CM, Tai YC (1998) Micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and fluid flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 30:579–612. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.30.1.579
Joly L, Ybert C, Bocquet L (2006) Probing the nanohydrodynamics at liquid-solid interfaces using thermal motion. Phys Rev Lett 96:046101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.046101
Joseph P, Tabeling P (2005) Direct measurement of the apparent slip length. Phys Rev E 71:035303(R). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.71.035303
Karniadakis GE, Beskok A (2002) Micro flows: fundamentals and simulation. Springer-Verlag, New York
Koplik J, Banavar JR, Willemsen JF (1989) Molecular dynamics of fluid flow at solid surfaces. Phys Fluids A 1:781–794. doi:10.1063/1.857376
Lamb H (1932) Hydrodynamics. Dover, New York
Li ZG (2009) Surface effects on friction-induced fluid heating in nanochannel flows. Phys Rev E 79:026312. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.79.026312
Li J, Liao DY, Yip S (1998) Coupling continuum to molecular-dynamics simulation: reflecting particle method and the field estimator. Phys Rev E 57:7259–7267. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.57.7259
Liu C, Li ZG (2009) Flow regimes and parameter dependence in nanochannel flows. Phys Rev E 80:036302. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.80.036302
Martini A, Hsu H, Patankar NA, Lichter S (2008) Slip at high shear rates. Phys Rev Lett 100:206001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.206001
Morris DL, Hannon L, Garcia AL (1992) Slip length in a dilute gas. Phys Rev A 46:5279–5281. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.46.5279
Neto C, Evans DR, Bonaccurso E (2005) Boundary slip in Newtonian liquids: a review of experimental studies. Rep Prog Phys 68:2859–2897. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/68/12/R05
Niavarani A, Priezjev NV (2010) Modeling the combined effect of surface roughness and shear rate on slip flow of simple fluids. Phys Rev E 81:011606. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.81.011606
Nie XB, WN E, Chen SY, Robbins MO (2004) A continuum and molecular dynamics hybrid method for micro- and nano-fluid flow. J Fluid Mech 500:55–64. doi:10.1017/S0022112003007225
O’Connell ST, Thompson PA (1995) Molecular dynamics-continuum hybrid computations: a tool for studying complex fluid flows. Phys Rev E 52(6):R5792–R5795. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.52.R5792
Pit R, Hervet H, Leger L (2000) Direct experimental evidence of slip in hexadecane: solid interfaces. Phys Rev Lett 85:980–983. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.980
Priezjev NV (2007) Rate-dependent slip boundary conditions for simple fluids. Phys Rev E 75:051605. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.75.051605
Rabczuk T, Xiao SP, Sauer M (2006) Coupling of meshfree methods with finite elements: basic concepts and test results. Commun Numer Methods Eng 22(10):1031–1065. doi:10.1002/cnm.871
Schaaf SA, Chambre PL (1961) Flow of rarefied gases. Princeton University, Princeton, NJ
Sokhan VP, Nicholson D, Quirke N (2001) Fluid flow in nanopores: an examination of hydrodynamic boundary conditions. J Chem Phys 115:3878–3887. doi:10.1063/1.1387976
Thompson PA (1990) Shear flow near solids: epitaxial order and flow boundary conditions. Phys Rev A 41:6830–6837. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.41.6830
Thompson PA, Troian SM (1997) A general boundary condition for liquid flow at solid surfaces. Nature 389:360–362. doi:10.1038/38686
Todd BD, Hansen JS (2008) Nonlocal viscous transport and the effect on fluid stress. Phys Rev E 78:051202. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.78.051202
Todd BD, Hansen JS, Daivis PJ (2008) Nolocal shear stress for homogeneous fluids. Phys Rev Lett 100:195901. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.195901
Travis KP, Todd BD, Evans DJ (1997) Departure from Navier–Stokes hydrodynamics in confined liquids. Phys Rev E 55(4):4288–4295. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.55.4288
Tretheway DC, Meinhart CD (2002) Apparent fluid slip at hydrophobic microchannel walls. Phys Fluids 14:L9–L12. doi:10.1063/1.1432696
Voronov RS, Papavassiliou DV, Lee LL (2006) Boundary slip and wetting properties of interfaces: correlation of the contact angle with the slip length. J Chem Phys 124:204701. doi:10.1063/1.2194019
Wang S, Liu H (2010) Modeling brittle-ductile failure transition with meshfree method. Int J Impact Eng 37(7):783–791. doi:10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.01.006
Watanabe K, Udagawa Y, Udagawa H (1999) Drag reduction of Newtonian fluid in a circular pipe with a highly water-repellent wall. J Fluid Mech 381:225–238. doi:10.1017/S0022112098003747
Yen TH, Soong CY, Tzeng PY (2007) Hybrid molecular dynamics-continuum simulation for nano/mesoscale channel flows. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:665–675. doi:10.1007/s10404-007-0154-7
Zhang H, Zhang BJ, Zhang JJ (2004) Shear viscosity of simple fluids in porous media: molecular dynamics simulations and correlation models (II): methane in silicate pores. Chem Phys Lett 397:233–236. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2004.08.122
Zhang ZQ, Zhang HW, Ye HF (2009) Pressure-driven flow in parallel-plate nanochannels. Appl Phys Lett 95:154101. doi:10.1063/1.3247892
Zhang HW, Zhang ZQ, Zheng YG, Ye HF (2010) Corrected second-order slip boundary condition for fluid flows in nanochannels. Phys Rev E 81:066303. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.81.066303
Zhu YX, Granick S (2002) Limits of the hydrodynamic no-slip boundary condition. Phys Rev Lett 88(10):106102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.106102
Zhu YX, Granick S (2003) Reassessment of solidification in fluids confined between mica sheets. Langmuir 19:8148–8151. doi:10.1021/la035155+
Acknowledgments
The supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11072051, 10721062, 90715037, 51021140004), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University of China (PCSIRT), the 111 Project (No.B08014), the National Key Basic Research Special Foundation of China (2010CB832704), and initial funding of Jiangsu University (11JDG024) are gratefully acknowledged. We acknowledge the reviewers’ comments and suggestions very much, which are valuable in improving the quality of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhang, Z. & Ye, H. Molecular dynamics-based prediction of boundary slip of fluids in nanochannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 12, 107–115 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0853-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0853-y