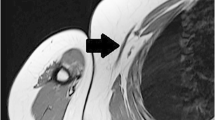
Abstract
The axillary arch is a common but rarely recognized anatomical variant of the axillary musculature. We report the first detailed presentation of the ultrasonographic features of the axillary arch and a correlation of these findings with multiplanar reformation CT images incorporating a schematic anatomical diagram in a 44-year-old woman complaining of a palpable non-tender mass in the axillary region due to a unilateral axillary arch. The clinical significance of the axillary arch is discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jelev L, Georgiev GP, Surchev L. Axillary arch in human: common morphology and variety. Definition of “clinical” axillary arch and its classification. Ann Anat. 2007;189:473–81.
Daniels IR, Querci della Rovere G. The axillary arch of Langer—the most common muscular variation in the axilla. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2000;59:77–80.
Loukas M, Noordeh N, Tubbs RS, et al. Variation of the axillary arch muscle with multiple insertions. Singapore Med J. 2009;50:e88–90.
Petrasek AJ, Semple JL, McCready DR. The surgical and oncologic significance of the axillary arch during axillary lymphadenectomy. Can J Surg. 1997;40:44–7.
Merida-Velasco JR, Rodriguez Vazquez JF, Merida Velasco JA, et al. Axillary arch: potential cause of neurovascular compression syndrome. Clin Anat. 2003;16:514–9.
Sellon JL, Murthy NS, Schmit GD, et al. Wire-guided resection of a muscular axillary arch causing neurovascular compression. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2010;19:229–33.
Ko K, Han BK, Shin JH, et al. The axillopectoral muscle seen on mammography. Clin Radiol. 2006;61:625–9.
Ando J, Kitamura T, Kuroki Y, et al. Preoperative diagnosis of the axillary arch with multidetector row computed tomography and the axillary arch in association with anatomical problems of sentinel lymph node biopsy. Breast Cancer. 2010;17:3–8.
Guy MS, Sandhu SK, Gowdy JM, et al. MRI of the axillary arch muscle: prevalence, anatomic relations, and potential consequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196:W52–7.
Miguel M, Llusa M, Ortiz JC, et al. The axillopectoral muscle (of Langer): report of three cases. Surg Radiol Anat. 2001;23:341–3.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements and informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). This retrospective study was approved by our institutional review board and informed consent was waived.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, H.J., Choi, N.J., Han, D.H. et al. Axillary arch: detailed ultrasonographic images with multiplanar CT correlation. J Med Ultrasonics 42, 121–125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-014-0563-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-014-0563-7