Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to estimate the prevalence of indicators of healthy food consumption among older adults with diabetes and/or hypertension and whether or not they occur more frequently than in healthy older adults.
Methods
Cross-sectional study with 1656 older adults who participated in the first wave of a longitudinal, population-based study held in Florianopolis, Southern Brazil, EpiFloripa Idoso 2009/2010, using the self-reported diagnosis of diabetes and/or hypertension as exposure variable and indicators of healthy food consumption as outcomes.
Results
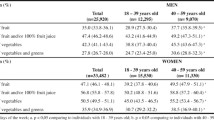
Only 22.7% (95% CI: 20.1–25.3) of females and 29.6% (95% CI:25.8–33.4) of males eat fruit ≥ 3 times/day and vegetables ≥ 2 times/day. More than one third of the sample had frequent consumption (> 2 times/week) of fats from meat/chicken, fried foods and whole milk.
Conclusion
We found that the indicators of healthy food consumption do not differ among older adults with and without diabetes and/or hypertension, indicating no adopting of the secondary prevention measures in the treatment of these diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 January 2018
The journal had been advised to revise the title so that Clarivate Analytics can try to count the citations more accurately. There’s been confusion due to the existence of another journal with the same name.
References
Boeing H, Bechthold A, Bub A, Ellinger S, Haller D, Kroke A, Leschik-Bonnet E, Müller J, Oberritter H, Schulze M, Stehle P, Watzl B (2012) Critical review: vegetables and fruit in the prevention of chronic diseases. Eur J Nutr 51:637–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-012-0380-y
Brazil (2011) Ministry of Health. Surveillance Department Health. Department of Health Situation Analysis. Strategic Action Plan for the Fight against NCDs in Brazil, 2011-2022 http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/plano_acoes_enfrent_dcnt_2011.pdf. Accessed 20 January 2017
Brazil (2014) Ministry of Health. Department of Primary Care. Food Guide for the Brazilian Population. Ministry of Health, 2ª. ed. ttp://189.28.128.100/dab/docs/portaldab/publicacoes/guia_alimentar_populacao_brasileira.pdf. Accessed 20 January 2017
Brazil (2015) Ministry of Health. Surveillance Department Health. Department of Health Situation Analysis. Vigitel Brazil 2014: Surveillance of Risk and Protective Factors for Chronic Diseases on Telephone Interviews. http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/vigitel_brasil_2014.pdf. Accessed in January 2017
Brazil (2017) Federal University of Santa Catarina. Department of Public Health. Health conditions of the elderly population of Florianópolis-EpiFloripa Idoso Study 2009-2010. http://www.epifloripa.ufsc.br/category/pesquisadores/epi_idoso. Accessed in January 2017
Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (2010) Sociodemographic and health indicators in Brazil. Studies and Research. Demographic and Socioeconomic Information. http://www.ibge.gov.br/english/estatistica/populacao/indic_sociosaude/2009/default.shtm. Accessed in January 2017
Cano-Gutierrez C, Reyes-Ortiz CA, Samper-Ternent R, Gélvez-Rueda JS, Borda MG (2015) Prevalence and factors associated to hypertension among older adults in Bogotá, Colombia. J Aging Health 27(6):1046–1065. https://doi.org/10.1177/0898264315573518
Conlin PR, Chow D, Miller ER, Svetkey LP, Lin PH, Harsha DW, Moore TJ, Sacks FM, Appel LJ (2000) The effect of dietary patterns on blood pressure control in hypertensive patients: results from the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) trial. Am J Hypertens 13(9):949–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7061(99)00284-8
Costa MFFL, Peixoto SV, César CC, Malta DC, Moura EC (2009) Health behaviors among older adults with hypertension, Brazil, 2006. Rev Saúde Pública 43:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89102009000900004
Darmon N, Drewnowski A (2008) Does social class predict diet quality? Am J Clin Nutr 87(5):1107–1117
Duncan BB, Stevens A, Schmidt MI (2012) Mortalidade por doenças crônicas no Brasil: situação em 2010 e tendências de 1991 a 2010. In: Saúde Brasil 2011: uma análise da situação de saúde e a vigilância da saúde da mulher. Saúde: Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde, Departamento de Análise de Situação de Saúde 93–104
Eckel RH, Jakicic JM, Ard JD, Jesus JM, Miller NH, Hubbard VS, Lee IM, Lichtenstein AH, Loria CM, Millen BE, Nonas CA, Sacks FM, Smith SC Jr, Svetkey LP, Wadden TA, Yanovski SZ, Kendall KA, Morgan LC, Trisolini MG, Velasco G, Wnek J, Anderson JL, Halperin JL, Albert NM, Bozkurt B, Brindis RG, Curtis LH, DeMets D, Hochman JS, Kovacs RJ, Ohman EM, Pressler SJ, Sellke FW, Shen WK, Smith SC Jr, Tomaselli GF (2014) AHA/ACC Guideline on Lifestyle Management to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(25_PA). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.003
King DE, Mainous AG, Carnemolla M, Everett CJ (2009) Adherence to healthy lifestyle habits in US adults. Am J Med 122(6):528–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.11.013
Lima-Costa MF, Matos DL, Camargos VP, Macinko J (2011) 10-year trends in the health of Brazilian elderly: evidence from the National Household Sample Survey (PNAD 1998, 2003, 2008). Ciênc Saúde Coletiva 16(9):3689–3696. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-81232011001000006
Mendoza-Sassi R, Béria JU (2001) Utilización de los servicios de salud: una revisión sistemática sobre los factores relacionados. Cad Saúde Pública 17:819–832. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2001000400016
Monteiro CA, Moura EC, Jaime PC, Claro RM (2008) Validity of food and beverage intake data obtained by telephone survey. Rev Saúde Pública 42(4):582–589. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89102008000400002
Moura EC, Morais Neto OL, Malta DC, Moura L, Silva NN, Bernal R, Claro RM, Monteiro CA (2008) Surveillance of risk-factors for chronic diseases through telephone interviews in 27 Brazilian cities (2006). Rev Bras Epidemiol. 11:20–37. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-790X2008000500003
Moura Souza A, Bezerra IN, Cunha DB, Sichieri R (2011) Avaliação dos marcadores de consumo alimentar do VIGITEL (2007-2009). Rev Bras Epidemiol 14:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-790X2011000500005
Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Silva G, Menezes AM, Monteiro CA, Barreto SM, Chor D, Menezes PR (2011) Chronic non-communicable diseases in Brazil: burden and current challenges. Lancet 377:1949–1961. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60135-9
Trujilo AJ, Fleisher LK (2013) Beyond income, access, and knowledge factors explaining the education gradient in prevention among older adults with diabetes and hypertension in Latin America. J Aging Health 25(8):1398–1424. https://doi.org/10.1177/0898264313508190
United Nations Development Programme (2013) Atlas of Human Development in Brazil, 2013. http://atlasbrasil.org.br/2013/perfil/florianopolis_sc. Accessed 20 January 2017
Williams DEM, Prevost AT, Whichelow MJ, Cox BD, Day NE, Wareham NJ (2000) A cross-sectional study of dietary patterns with glucose intolerance and others features of the metabolic syndrome. Br J Nutr 83(3):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114500000337
World Health Organization (2003). Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. Report WHO Consultation. Geneva. http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/publications/trs916/en/. Accessed 21 January 2017
World Health Organization (2004). Global Strategy on diet, physical activity and health. Geneva. http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/strategy/eb11344/strategy_english_web.pdf. Accessed 20 January 2017
World Health Organization (2005). Preventing Chronic Diseases a vital investment. Geneva. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/43314/1/9241563001_eng.pdf. Accessed 20 January 2017
World Health Organization (2013). Raised blood pressure: Situation and trends. Global Health Observatory (GHO). Geneva. http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/blood_pressure_prevalence_text/en/. Accessed 21 January 2017
World Health Organization (2014). Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014. Geneva. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/. Accessed 21 January 2017
Acknowledgments
We thank the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for financial support of this research.
Funding
This article originates from the EpiFloripa Idoso Study 2009–2010-Florianópolis Older Adults Health Survey. The EpiFloripa Idoso Study was funded by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), process no. 569834/2008-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
We declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: Due to the existence of another journal with the same name, the Publisher has added a subtitle, “From Theory to Practice.” Effective as of January 2018, the new title of this Journal is Journal of Public Health: From Theory to Practice.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cembranel, F., de Oliveira Bernardo, C., Ozcariz, S.G.I. et al. Indicators of healthy food consumption among older adults with diabetes and/or hypertension are similar to healthy older adults: results from a population based study in Southern Brazil. J Public Health 26, 331–338 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-017-0864-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-017-0864-6