Abstract
Backgrounds
Imatinib-up-regulated lncRNA (lncRNA-IUR) is a recently identified tumor suppressor, while its role in ESCC is unknown. This study aimed to investigate the role of lncRNA-IUR in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods
Between April 2011 and April 2014, the Second Hospital of Jilin University admitted a total of 98 ESCC patients, from whom the present study selected 50 cases (33 males and 17 females; 43–67 years; 54.8 ± 6.0 year). ESCC cells and transient transfections, qPCR, RNA interaction analysis, western blot, CCK-8 assay, and cell apoptosis analysis were applied.
Results
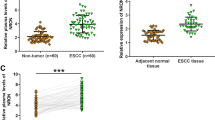
We found that IUR was down-regulated in ESCC, and low levels of IUR predicted poor survival of ESCC patients. In ESCC cells, IUR expression levels were significantly and positively correlated with PTEN mRNA. Bioinformatics analysis showed that IUR may sponge miR-21, which can target PTEN. In ESCC cells, IUR over-expression led to the increased expression levels of PTEN; while miR-21 over-expression led to decreased expression levels of PTEN. IUR and miR-21 failed to affect each other. Cell proliferation and apoptosis analysis showed that IUR and PTEN over-expression inhibited cancer cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis; while miR-21 over-expression played an opposite role. In addition, miR-21 over-expression attenuated the effects of IUR over-expression on PTEN expression and cell proliferation.
Conclusion
Therefore, IUR may up-regulate PTEN by sponging miR-21 to regulate cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis in ESCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin DC, Wang MR, Koeffler HP. Genomic and epigenomic aberrations in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and implications for patients. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(2):374–89. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.066.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–32. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338.
Kashima H, Noma K, Ohara T, Kato T, Katsura Y, Komoto S, Sato H, Katsube R, Ninomiya T, Tazawa H, Shirakawa Y, Fujiwara T. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) promote the lymph node metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(4):828–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31953.
Muto M, Minashi K, Yano T, Saito Y, Oda I, Nonaka S, Omori T, Sugiura H, Goda K, Kaise M, Inoue H, Ishikawa H, Ochiai A, Shimoda T, Watanabe H, Tajiri H, Saito D. Early detection of superficial squamous cell carcinoma in the head and neck region and esophagus by narrow band imaging: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(9):1566–72. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.25.4680.
Gao YB, Chen ZL, Li JG, Hu XD, Shi XJ, Sun ZM, Zhang F, Zhao ZR, Li ZT, Liu ZY, Zhao YD, Sun J, Zhou CC, Yao R, Wang SY, Wang P, Sun N, Zhang BH, Dong JS, Yu Y, Luo M, Feng XL, Shi SS, Zhou F, Tan FW, Qiu B, Li N, Shao K, Zhang LJ, Zhang LJ, Xue Q, Gao SG, He J. Genetic landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2014;46(10):1097–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3076.
Lin DC, Hao JJ, Nagata Y, Xu L, Shang L, Meng X, Sato Y, Okuno Y, Varela AM, Ding LW, Garg M, Liu LZ, Yang H, Yin D, Shi ZZ, Jiang YY, Gu WY, Gong T, Zhang Y, Xu X, Kalid O, Shacham S, Ogawa S, Wang MR, Koeffler HP. Genomic and molecular characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2014;46(5):467–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2935.
Georgescu MM. PTEN tumor suppressor network in PI3K-Akt pathway control. Genes Cancer. 2010;1(12):1170–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911407325.
Li H, Gao Q, Guo L, Lu SH. The PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates stem-like cells in primary esophageal carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11(11):950–8. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.11.11.15531.
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K, Yang GH. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411(11–12):846–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2010.02.074.
Paraskevopoulou MD, Hatzigeorgiou AG. Analyzing MiRNA–LncRNA interactions. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1402:271–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3378-5_21.
Wang X, Yang J, Guo G, Feng R, Chen K, Liao Y, Zhang L, Sun L, Huang S, Chen JL. Novel lncRNA-IUR suppresses Bcr-Abl-induced tumorigenesis through regulation of STAT5-CD71 pathway. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1013-3.
Hueman MT, Wang H, Yang CQ, Sheng L, Henson DE, Schwartz AM, Chen D. Creating prognostic systems for cancer patients: a demonstration using breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018;7(8):3611–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1629.
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH, Pfeffer LM. The role of miR-21 in cancer. Drug Dev Res. 2015;76(6):270–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21257.
Yang Y, Guo JX, Shao ZQ. miR-21 targets and inhibits tumor suppressor gene PTEN to promote prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion: an experimental study. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017;10(1):87–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.09.011.
Wu XS, Wang F, Li HF, Hu YP, Jiang L, Zhang F, Li ML, Wang XA, Jin YP, Zhang YJ, Lu W, Wu WG, Shu YJ, Weng H, Cao Y, Bao RF, Liang HB, Wang Z, Zhang YC, Gong W, Zheng L, Sun SH, Liu YB. LncRNA-PAGBC acts as a microRNA sponge and promotes gallbladder tumorigenesis. EMBO Rep. 2017;18(10):1837–53. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201744147.
Acknowledgements
We received the financial support from China medical foundation (No. 318.2204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW: manuscript writing, funding acquisition, literature search; PYH, LZ, and JDL: literature search and data analysis; YZ: study design, data analysis, statistical analysis, and manuscript review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Hua, P., Zhang, L. et al. LncRNA-IUR up-regulates PTEN by sponging miR-21 to regulate cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus 17, 298–304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-020-00724-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-020-00724-x