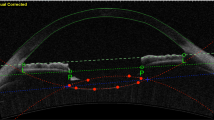
Abstract
Purpose
To describe a new method of alignment of toric intraocular lenses (IOLs) and evaluation of their rotation errors using anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT).
Methods
Twenty-nine eyes of 22 patients who had cataract extraction and implantation of an acrylic toric IOL were included. The new AS-OCT method was used for the alignment of toric IOLs and evaluation of their rotation errors. These rotation errors were evaluated and compared with those measured using the internal map of a wavefront aberrometer.
Results
The mean rotation error ± standard deviation (SD) of the toric IOLs evaluated by AS-OCT was 3.2 ± 2.2° and 3.2 ± 2.4° at 1 week and 1 month after surgery, respectively. The mean difference in the reference axis between the visits was 1.8 ± 2.1°. The mean difference between the rotation errors of the alignment axes measured by AS-OCT and the internal map was 2.5 ± 1.9° (P = 0.037).
Conclusion
The current method is clinically useful not only for the accurate alignment of toric IOLs but also for evaluating their rotation errors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amesbury EC, Miller KM. Correction of astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009;20:19–24.
Jiang Y, Le Q, Yang J, Lu Y. Changes in corneal astigmatism and high order aberrations after clear corneal tunnel phacoemulsification guided by corneal topography. J Refract Surg. 2006;22:S1083–8.
Tejedor J, Murube J. Choosing the location of corneal incision based on preexisting astigmatism in phacoemulsification. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139:767–76.
Muller-Jensen K, Fischer P, Siepe U. Limbal relaxing incisions to correct astigmatism in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 1999;15:586–9.
Bayramlar H, Totan Y, Daghoglu MC. Limbal relaxing incision for the management of mixed astigmatism after photorefractive keratectomy and laser thermal keratoplasty. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:1266.
Kaufmann C, Peter J, Ooi K, Phipps S, Cooper P, Goggin M. Limbal relaxing incisions versus on-axis incisions to reduce corneal astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:2261–5.
Sun XY, Vicary D, Montgomery P, Griffiths M. Toric intraocular lenses for correcting astigmatism in 130 eyes. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:1776–81 (discussion 81–2).
Horn JD. Status of toric intraocular lenses. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007;18:58–61.
Weinand F, Jung A, Stein A, Pfutzner A, Becker R, Pavlovic S. Rotational stability of a single-piece hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lens: new method for high-precision rotation control. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:800–3.
Nguyen TM, Miller KM. Digital overlay technique for documenting toric intraocular lens axis orientation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:1496–504.
Mendicute J, Irigoyen C, Aramberri J, Ondarra A, Montes-Mico R. Foldable toric intraocular lens for astigmatism correction in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:601–7.
Jampaulo M, Olson MD, Miller KM. Long-term Staar toric intraocular lens rotational stability. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;146:550–3.
Park SC, Kwun YK, Chung ES, Ahn K, Chung TY. Postoperative astigmatism and axis stability after implantation of the STAAR toric implantable collamer lens. J Refract Surg. 2009;25:403–9.
Zuberbuhler B, Signer T, Gale R, Haefliger E. Rotational stability of the AcrySof SA60TT toric intraocular lenses: a cohort study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2008;8:8.
Graether JM. Simplified system of marking the cornea for a toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:1498–500.
Ma JJ, Tseng SS. Simple method for accurate alignment in toric phakic and aphakic intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:1631–6.
Langenbucher A, Viestenz A, Szentmary N, Behrens-Baumann W, Viestenz A. Toric intraocular lenses—theory, matrix calculations, and clinical practice. J Refract Surg. 2009;25:611–22.
Gatinel D, Hoang-Xuan T. Measurement of combined corneal, internal, and total ocular optical quality analysis in anterior segment pathology with the OPD-scan and OPD-station. J Refract Surg. 2006;22:S1014–20.
MacRae S, Fujieda M. Slit skiascopic-guided ablation using the Nidek laser. J Refract Surg. 2000;16:S576–80.
Jin H, Limberger IJ, Ehmer A, Guo H, Auffarth GU. Impact of axis misalignment of toric intraocular lenses on refractive outcomes after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:2061–72.
Shah GD, Praveen MR, Vasavada AR, Rampal NV, Vasavada VA, Asnani PK, et al. Software-based assessment of postoperative rotation of toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:413–8.
Wolffsohn JS, Buckhurst PJ. Objective analysis of toric intraocular lens rotation and centration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:778–82.
Viestenz A, Seitz B, Langenbucher A. Evaluating the eye’s rotational stability during standard photography: effect on determining the axial orientation of toric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:557–61.
Ruhswurm I, Scholz U, Zehetmayer M, Hanselmayer G, Vass C, Skorpik C. Astigmatism correction with a foldable toric intraocular lens in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:1022–7.
Chang DF. Early rotational stability of the longer Staar toric intraocular lens: fifty consecutive cases. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:935–40.
Patel CK, Ormonde S, Rosen PH, Bron AJ. Postoperative intraocular lens rotation: a randomized comparison of plate and loop haptic implants. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:2190–5 (discussion 6).
Cha D, Kang SY, Kim SH, Song JS, Kim HM. New axis-marking method for a toric intraocular lens: mapping method. J Refract Surg. 2011;27:375–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, K., Negishi, K., Torii, H. et al. Simple and accurate alignment of toric intraocular lenses and evaluation of their rotation errors using anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol 56, 31–37 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-011-0097-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-011-0097-0