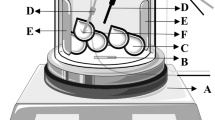
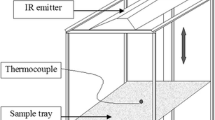
Abstract
A series of field bioassays was conducted to evaluate the effects of electric infrared (IR) penetration on microbial disinfection and insect control as well as on the organoleptic characteristics of dried black currants (Corinthian currants, Vitis vinifera L. var. Apyrena). A continuous IR processor was placed in the production line of an industrial facility and was used for the field assays. In a series of bioassays, currants were fed into the IR processor and examined with and without process agitation at different treatment parameters including retention times (ranging from 30 to 35 s) and various peak temperatures (45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70 and 75 °C). Samples of processed currants were randomly selected for microbial analysis, as well as for determination of organoleptic characteristics. Infrared treatment resulted in a significant reduction of total viable counts, yeasts and moulds by factors ranging from 10 to 300. Increase of treatment time and peak temperature was positively correlated with microbial reduction. Sensory attributes were not affected up to 60 °C, while crystalline texture and overall acceptance were affected by IR treatment at 70 °C. With respect to currant phenolics, antioxidants that have potential benefits to human health, IR heating resulted in almost the same effect up to 65 °C, i.e. approximately 20 % reduction; higher peak temperatures further lowered total phenolic values. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) formation was low up to 55 °C, while increased at higher temperatures; however, values still remained low as compared with dried fruit HMF levels. In another series of bioassays, golden sultanas were artificially infested with larvae of Ephestia elutella and adults of Oryzaephilus surinamensis and Tribolium confusum and treated with IR in agitating flow process at different peak temperatures (45, 50, 55, 60, 65 and 70 °C). Finally, a batch series of non-agitated flow process tests were conducted in glass Petri dishes. Briefly, O. surinamensis and T. confusum adults were exposed to IR penetration for different time exposure intervals (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10 and 20 s) with and without the presence of currants and sultanas. In the bioassays with infested sultanas, all IR treatments with agitation provided complete control of the insect species tested, since IR-treated sultanas were found free of insects even 1 year after treatment. For exposure intervals higher than 4 s in the non-agitated flow process, all adults of O. surinamensis and T. confusum were killed in glass Petri dishes consisting of insects only and without the presence of currants and sultanas. In contrast, the presence of currants and sultanas in the non-agitated flow process reduced significantly the killing rate efficacy of IR against the insect species tested, especially on the individuals located beneath the sultanas and currants and where the infrared light could not penetrate them. Our results suggest that electric infrared heating with light source penetration could be a valuable tool for rapid and successful reduction of the microbial load and post-harvest insect disinfestation of dry currants and sultanas, provided that adequate agitation within the infrared process chamber is achieved so that sultanas and currants could be penetrated consistently in a three-dimensional manner.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed M (2001) Disinfestation of stored grains, pulses, dried fruits and nuts, and other dried foods. In: Molins RA (ed) Food irradiation: principles and applications. Wiley, New York, pp 77–101
Aitken AD (1975) Insect Travelers, I: Coleoptera. In: Technical Bulletin, Vol. 31. HMSO, London
Alfaifi B, Tang J, Jiao Y, Wang S, Rasco B, Jiao S, Sablani S (2014) Radio frequency disinfestation treatments for dried fruit: model development and validation. J Food Eng 120:268–276
Arnous A, Makris DP, Kefalas P (2002) Correlation of pigment and flavanol content with antioxidant properties in selected aged regional wines from Greece. J Food Compos Anal 15:655–665
Bell CH (2000) Fumigation in the 21st century. Crop Prot 19:563–569
Braeckman L, Ronsse F, Cueva HP, Pieters J (2009) Influence of combined IR grilling and hot air cooking conditions on moisture and fat content, texture and color attributes of meat patties. J Food Eng 93:437–443
Brandl MT, Zhongli P, Huynh S, Yi Z, McHugh TH (2008) Reduction of Salmonella Enteritidis population sizes on almond kernels with infrared heat. J Food Prot 71:897–902
Buchelos CTh (1980) Moth populations at a typical flour mill. Ann Benaki Instit Phytopathol 12:188–197
Çaglarirmak N (2006) Ochratoxin A, hydroxymethylfurfural and vitamin C levels of sun-dried grapes and sultanas. J Food Process Preserv 30:549–562
Capuano E, Fogliano V (2011) Acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF): a review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food and mitigation strategies. LWT—Food Sci Technol 44:793–810
Cetinkaya N, Ozyardımci B, Denli E, Ic E (2006) Radiation processing as a post-harvest quarantine control for raisins, dried figs and dried apricots. Radiat Phys Chem 75:424–431
Chiou A, Karathanos VT, Mylona A, Salta FN, Preventi F, Andrikopoulos NK (2007) Currants (Vitis vinifera L.) content of simple phenolics and antioxidant activity. Food Chem 102:516–522
Chiou A, Panagopoulou EA, Gatzali F, De Marchi S, Karathanos VT (2014) Anthocyanins content and antioxidant capacity of Corinthian currants (Vitis vinifera L., var. Apyrena). Food Chem 146:157–165
Cogburn RR (1967) Infrared radiation effect on reproduction by three species of stored-product insects. J Econ Entomol 60:548–550
Cogburn RR, Brower JH, Tilton EW (1971) Combination of gamma and infrared radiation for control of the Angoumois grain moth in wheat. J Econ Entomol 64:923–925
Collins PJ, Lambkin TM, Bridgeman BW, Pulvirenti C (1993) Resistance to grain protectant insecticides in coleopterous pests of stored cereals in Queensland. Aust J Econ Entomol 86:239–245
Del Rio D, Rodriguez-Mateos A, Spencer JPE, Tognolini M, Borges G, Crozier A (2013) Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:1818–1892
Fields PG, White NDG (2002) Alternatives to methyl bromide treatments for stored-product and quarantine insects. Annu Rev Entomol 47:331–359
Gabel MM, Pan Z, Amaratunga KSP, Harris LJ, Thompson JF (2006a) Catalytic infrared dehydration of onions. J Food Sci 71:351–357
Gabel MM, Pan Z, Amaratunga KSP, Harris LJ, Thompson JF (2006b) Catalytic infrared dehydration of onions. J Food Sci 71:351–357
Guedes RNC, Dover BA, Kambhampati S (1996) Resistance to chlorpyrifosmethyl, pirimiphos-methyl, and malathion in Brazilian and US populations of Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae). J Econ Entomol 89:27–32
Hagstrum DW, Flinn PW (2014) Modern stored-product insect pest management. J Plant Prot Res 54:205–210
Hamanaka D, Uchino T, Furuse N, Han W, Tanaka SI (2006) Effect of the wavelength of infrared heaters on the inactivation of bacterial spores at various water activities. Int J Food Microbiol 108:281–285
Hamanaka D, Norimura N, Baba N, Mano K, Kakiuchi M, Tanaka F, Toshitaka UT (2011) Surface decontamination of fig fruit by combination of infrared radiation heating with ultraviolet irradiation. Food Control 22:375–380
Heist J, Cremer ML (1990) Sensory quality and energy use for baking of molasses cookies prepared with bleached and unbleached flour and baked in infrared, forced air convection, and conventional deck ovens. J Food Sci 55:1095–1101
Huang L (2004) Infrared surface pasteurization of turkey frankfurters. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 5:345–351
Huang L, Sites J (2008) Elimination of Listeria monocytogenes on hotdogs by infrared surface treatment. J Food Sci 73:27–31
ICGFI International Consultative Group on Food Irradiation (1995) Code of good irradiation practice for insect disinfestation of dried fruits and tree nuts. ICGFI Document No 20, Vienna, IAEA
James C, Lechevalier V, Ketteringham L (2002) Surface pasteurization of shell eggs. J Food Eng 53:193–197
Johnson JA, Vail PV, Brandl DG, Tebbets JS, Valero KA (2002) Integration of nonchemical treatments for control of postharvest pyralid moths (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in almonds and raisins. J Econ Entomol 95:190–199
Karadeniz F, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE (2000) Polyphenolic composition of raisins. J Agric Food Chem 48:5343–5350
Khamis M (2009) Effects of flameless catalytic infrared radiation on stored wheat insects and wheat quality. M.Sc. thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan
Khamis M, Subramanyam Bh, Flinn PW, Dogan H, Jager A, Gwirtz JA (2010) Susceptibility of various life stages of Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) to flameless catalytic infrared radiation. J Econ Entomol 103:1508–1516
Khamis M, Subramanyam Bh, Flinn PW, Dogan H, Gwirtz JA (2011a) Susceptibility of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) life stages to flameless catalytic infrared radiation. J Econ Entomol 104:325–330
Khamis M, Subramanyam Bh, Dogan H, Gwirtz JA (2011b) Flameless catalytic infrared radiation used for grain disinfestation does not affect hard red winter wheat quality. J Stored Prod Res 47:204–209
Khamis M, Subramanyam Bh, Dogan H, Flinn PW, Gwirtz JA (2011c) Effects of flameless catalytic infrared radiation on Sitophilus oryzae (L.) life stages. J Stored Prod Res 47:173–178
Khir R, Pan Z, Salim A, Hartsough BR, Mohamed S (2011) Moisture diffusivity of rough rice under infrared radiation drying. Food Sci Technol 44:1126–1132
Khir R, Pan Z, Thompson JF, El-Sayed AS, Hartsough BR, El-Amir MS (2014) Moisture removal characteristics of thin layer rough rice under sequenced infrared radiation heating and cooling. J Food Process Preserv 38:430–440
Kirkpatrick RL (1975) Infrared radiation for control of lesser grain borers and rice weevils in bulk wheat. J Kansas Entomol Soc 48:100–104
Kirkpatrick RL, Tilton EW (1972) Infrared radiation to control adult stored-product Coleoptera. J Ga Entomol Soc 7:73–75
Kirkpatrick RL, Brower JH, Tilton EW (1972) A comparison of microwave and infrared radiation to control rice weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in wheat. J Kansas Entomol Soc 45:434–438
Kowalski S (2013) Changes of antioxidant activity and formation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in honey during thermal and microwave processing. Food Chem 141:1378–1382
Krishnamurthy K, Jun S, Irudayaraj J, Demirci A (2008a) Efficacy of infrared heat treatment for inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. J Food Process Eng 31:798–816
Krishnamurthy K, Khurana HK, Soojin J, Irudayaraj J, Demirci A (2008b) Infrared heating in food processing: an overview. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 7:2–13
Lee S-C, Kim J-H, Jeong S-M, Kim D-R, Ha J-U, Nam KC, Ahn DU (2003) Effect of far-infrared radiation on the antioxidant activity of rice hulls. J Agric Food Chem 51:4400–4403
McDonough MX, Campabadal CA, Mason LJ, Maier DE, Denvir A, Woloshuk CP (2011) Ozone application in a modified screw conveyor to treat grain for insect pests, fungal contaminants and mycotoxins. J Stored Prod Res 47:249–254
Mestdagh F, De Wilde T, Delporte K, Van Peteghem C, De Meulenaer B (2008) Impact of chemical pre-treatments on the acrylamide formation and sensorial quality of potato crisps. Food Chem 106:914–922
Murkovic M, Pichler N (2006) Analysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfual in coffee, dried fruits and urine. Mol Nutr Food Res 50:842–846
Nayak MK, Holloway JC, Emery RN, Pavic H, Bartleta J, Collins PJ (2013) Strong resistance to phosphine in the rusty grain beetle, Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Stephens) (Coleoptera: Laemophloeidae): its characterisation, a rapid assay for diagnosis and its distribution in Australia. Pest Manag Sci 69:48–53
Nazari SH (2014) Impact of using infrared irradiation energy in food processing. Energy Educ Sci Technol Part A 32:1387–1396
Opit GP, Phillips TW, Aikins MJ, Hasan MM (2012) Phosphine resistance in Tribolium castaneum and Rhyzopertha dominica from stored wheat in Oklahoma. J Econ Entomol 105:1107–1114
Phillips TW, Throne JE (2010) Biorational approaches to managing stored-product insects. Annu Rev Entomol 55:375–397
Pimentel MAG, Faroni LRD, da Silva FH, Batista MD, Guedes RNC (2010) Spread of phosphine resistance among Brazilian populations of three species of stored product insects. Neotrop Entomol 39:101–107
Ramaswamy R, Krishnamurthy K, Jun S (2012) Microbial decontamination of food by infrared (IR) heating. In: Ngadi MO, Demirci A (eds) Microbial decontamination in the food Industry: novel methods and applications. Elsevier Ltd, New York, pp 450–471
Rastogi NK (2012) Recent trends and developments in infrared heating in food processing. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 52:737–760
Sawai J, Sagara K, Kasai S, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Kokugan T, Shimizu M, Kojima H (2000) Far infrared irradiation induced injuries to Escherichia coli at below the lethal temperature. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 24:19–24
Şevik R, Şen L, Nas S (2014) Determination of color quality and hmf content of unprocessed sultanas obtained from different vineyards. Int J Res Agric Food Sci 2:32–42
Shi J, Pan Z, McHugh TH, Wood D, Hirschberg E, Olson D (2008) Drying and quality characteristics of fresh and sugar-infused blueberries dried with infrared radiation heating. Food Sci Technol 41:1962–1972
Shyue BH, En CL, Fu JW, Sheu DW (1996) The study on processing of smoked mackerel slices by far infrared heating. Food Sci Taiwan 23:801–808
Sogi DS, Siddiq M, Roidoung S, Dolan KD (2012) Total phenolics, carotenoids, ascorbic acid, and antioxidant properties of fresh-cut mango (Mangifera indica L., cv. Tommy Atkin) as affected by infrared heat treatment. J Food Sci 77:C1197–C1202
Staack N, Ahrné L, Borch E, Knorr D (2008) Effect of infrared heating on quality and microbial decontamination in paprika powder. J Food Eng 86:17–24
Subramanyam B, Harein PK, Cutkomp LK (1989) Organophosphate resistance in adults of red flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) and sawtoothed grain beetle (Coleoptera: Cucujidae) infesting barley stored on farms in Minnesota. J Econ Entomol 82:989–995
Tanaka F, Verboven P, Scheerlinck N, Morita K, Iwasaki K, Nicolai B (2007) Investigation of far infrared radiation heating as an alternative technique for surface decontamination of strawberry. J Food Eng 79:445–452
Tilton EW, Schroeder HW (1961) The effect of infrared radiation on immature insects in kernels of rough rice. Rice J 64:23–25
Tilton EW, Schroeder HW (1963) Some effects of infrared irradiation on the mortality of immature insects in kernels of rough rice. J Econ Entomol 56:727–730
Tilton EW, Brower JH, Brown GA, Kirkpatrick RL (1972) Infrared radiation to control adult stored-product Coleoptera. J Ga Entomol Soc 7:73–75
Tilton EW, Vardell HH, Jones RD (1983) Infrared heating with vacuum for control of the lesser grain borer, (Rhyzopertha dominica F.) and rice weevil (Sitophilus oryzae (L.)) infesting wheat. J Ga Entomol Soc 18:61–64
Vail PV, Tebbets JS, Cowan DC, Jenner KE (1991) Efficacy and persistence of a granulosis virus against infestations of Plodia interpunctella (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on raisins. J Stored Prod Res 27:103–107
Yung SS, Wen CS, Ming HC, Jean YH (2008) Effect of far infrared oven on the qualities of bakery products. J Culin Sci Technol 6:105–118
Zar HJ (1999) Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc., Upper Saddle River
Zettler JL, Cuperus GW (1990) Pesticide resistance in Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) and Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) in wheat. J Econ Entomol 83:1677–1681
Zheng Y, Shi J, Pan Z (2012) Biochemical characteristics and thermal inhibition kinetics of polyphenol oxidase extracted from Thompson seedless grape. Eur Food Res Technol 234:607–616
Zilic S, Mogol BA, Glu GA, Serpen A, Babi M, Gökmen V (2013) Effects of infrared heating on phenolic compounds and Maillard reaction products in maize flour. J Cereal Sci 58:1–7
Zilic S, Mogol BA, Akıllıoglu G, Serpen A, Delica N, Gokmen V (2014) Effects of extrusion, infrared and microwave processing on Maillard reaction products and phenolic compounds in soybean. J Sci Food Agric 94:45–51
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the research grant “Integrated management of insect pests and microbial infestation during processing, storage and transportation of currants by using non-chemical, ecologically compatible methods: sustainability in practice” (Grant Number 1422-BET-2013, General Secretariat for Research and Technology, Greek Ministry of Education, Research and Religious Affairs).
Author contribution statement
CGA, AC and VK conceived and designed research. CGA, CIR, AKa, EN, EP and AKo conducted experiments. CGA, AC, CIR and VK analysed data. CGA, AC, CIR and VK contributed to writing the paper with CGA as the lead. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Traugott.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athanassiou, C.G., Chiou, A., Rumbos, C.I. et al. Effects of electric infrared heating with light source penetration on microbial and entomological loads of dried currants and their organoleptic characteristics. J Pest Sci 89, 931–943 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-015-0727-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-015-0727-2