Abstract
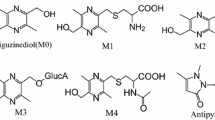
The purpose of this study is to develop and validate a rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPT) and its major metabolites (M1, M2, M7) in rat plasma. Diazepam was used as the internal standard. The method involves a simple liquid–liquid extraction with ethyl acetate. Chromatographic separation was accomplished on a Shim-pack VP-ODS analytical column (2.0 mm × 150 mm, 5 μm) with gradient elution using a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and water (containing 0.1 % formic acid) at a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1. The detection was performed by multiple reaction monitoring mode via a positive electrospray ionization interface. The calibration curves were linear for all analytes over investigated range. The lower limits of quantification were 7.734 ng mL−1 for DPT, 1.973 ng mL−1 for M1, 7.969 ng mL−1 for M2, and 1.973 ng mL−1 for M7, respectively. The intra- and inter-day precision values were less than 10.59 %, and the accuracy ranged from −6.787 to 12.74 %. The extraction recoveries of the analytes were higher than 90 % and in this method no apparent matrix effect was observed. The validated method was successfully applied to pharmacokinetic study of DPT and its main metabolites in rat plasma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koulman A, Bos R, Medarde M, Pras N, Quax WJ (2001) A fast and simple GC MS method for lignan profiling in Anthriscus sylvestris and biosynthetically related plant species. Planta Med 67:858–862
Wong SK, Tsui SK, Kwan SY, Su XL, Lin RC (2000) Identification and characterization of Podophyllum emodi by API-LC/MS/MS. J Mass Spectrom 35:1246–1251
Ikeda R, Nagao T, Okabe H, Nakano Y, Matsunaga H, Katano M, Mori M (1998) Antiproliferative constituents in umbelliferae plants. IV. Constituents in the fruits of Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. Chem Pharm Bull 46:875–878
Gordaliza M, Castro MA, García-Grávalos MD, Ruiz P, Miguel del Corral JM, San Feliciano A (1994) Antineoplastic and antiviral activities of podophyllotoxin related lignans. Arch Pharm 327:175–179
Sudo K, Konno K, Shigeta S, Yokota T (1998) Inhibitory effects of podophyllotoxin derivatives on herpes simplex virus replication. Antivir Chem Chemother 9:263–267
Chen JJ, Chang YL, Teng CM, Chen IS (2000) Anti-platelet aggregation alkaloids and lignans from Hernandia nymphaeifolia. Planta Med 66:251–256
Lee SH, Son MJ, Ju HK, Lin CX, Moon TC, Choi H, Son JK, Chang HW (2004) Dual inhibition of cyclooxygenases-2 and 5-lipoxygenase by deoxypodophyllotoxin in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Biol Pharm Bull 27:786–788
Jin M, Moo TC, Quan ZQ, Lee E, Kim YK, Yang JH, Suh S, Jeong TC, Lee SH, Kim C, Chang HW (2008) The naturally occurring flavolignan, deoxypodophyllotoxin, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS expression through the NF-kappaB activation in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1312–1315
Xu P, Sun Q, Wang X, Zhang S, An S, Cheng J et al (2010) Pharmacological effect of deoxypodophyllotoxin: a medicinal agent of plant origin, on mammalian neurons. Neurotoxicology 31:680–686
Bianchi E, Caldwell ME, Cole JR (1968) Antitumor agents from Bursera microphylla (Burseraceae) I. Isolation and characterization of deoxypodophyllotoxin. J Pharm Sci 57:696–697
Vasilev NP, Julsing MK, Koulman A, Clarkson C, Woerdenbag HJ, Ionkova I, Bos R, Jaroszewski JW, Kayser O, Quax WJ (2006) Bioconversion of deoxypodophyllotoxin into epipodophyllotoxin in E. Coli using human cytochrome P450 3A4. J Biotechnol 126:383–393
Lee SK, Jun IN, Yoo HH, Kim JH, Seo YM, Kang MJ, Lee SH, Jeong TC, Kim DH (2008) Characterization of in vitro metabolite of deoxypodophyllotoxin in human and rat liver microsomes using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:52–58
Lee SK, Kim Y, Jin C, Lee SH, Kang MJ, Jeong TC, Jeong SY, Kim DH, Yoo HH (2010) Inhibitory effects of deoxypodophyllotoxin from Anthriscus sylvestris on human CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. Planta Med 76:701–704
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Science foundation of China (No. 81473273, No. 81373482, and No. 81573490), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2015PT042, ZD2014YX0026, PT2014YX0057), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the policy directive program of Jiangsu Province (BY2015072-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Chen, Y., Xie, Q. et al. Simultaneous Determination of Deoxypodophyllotoxin and Its Major Metabolites in Rat Plasma by a Sensitive LC–MS/MS Method and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study. Chromatographia 79, 53–61 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2992-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2992-x