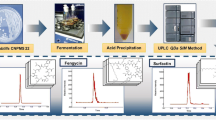
Abstract
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) is an important biofactor which can be synthesized by several bacteria. To determine the level of PQQ in a fermentation broth, a rapid and reliable UPLC-DAD-MS/MS method was developed. In this method, solid phase extraction allowed for excellent recoveries (>90 %) and eliminated interference at the same time. The pretreated sample was separated on a Waters Acquity BEH C18 column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) and detected using an ESI tandem mass spectrometer operated in negative-ion mode at a m/z range between 90.0 and 1000.0 and a DAD detector in the range from 200 to 400 nm. PQQ was observed to separate absolutely from the other components using gradient elution with water and acetonitrile. This separation also reduced the matrix effects. The assay range is 200–500 µg/mL and proved to be linear (R 2 > 0.996), accurate (≤10 % deviation), and precise (CV < 15 %). The retention time for PQQ in the column was almost 1 min due to the high column efficiency on the UPLC system. Therefore, this work provides a rapid and reliable method to quantitate the PQQ level in a fermentation broth.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Killgore J, Smidt C, Duich L, Romero-Chapman N, Tinker D, Reiser K, Melko M, Hyde D, Rucker RB (1989) Science 245:850–852
Steinberg FM, Gershwin ME, Rucker RB (1994) J Nutr 124:744–753
Kasahara T, Kato T (2003) Nature 422:832
Goosen N, Horsman H, Huien R, Putte P (1989) J Bacteriol 171:447–455
Schnider U, Keel C, Voisard C, Defage G, Haas D (1991) Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3856–3864
Toyama H, Chistoserdova L, Lidstrom ME (1997) Microbiology 143:595–602
Holscher T, Gorisch H (2006) J Bacteriology 188:7668–7676
Xiong X, Zhao Y, Ge X, Yuan SJ, Wang J (2011) Int J Mol Sci 12:8913–8923
Geiger O, Gorisch H (1987) Anal Biochem 164:418–423
Fluckiger R, Paz MA, Gallop PM (1995) Methods Enzymol 258:140–149
Wang G, Li Y, Li D, Tang Y (2008) J Chromatogr B 870:209–215
Wentao B, Jun Z, Kyung HR (2011) Talanta 83:974–979
Natsumi N, Takemichi N, Nobutaka K, Katsuhiko T, Toshiaki K, Shigeo Y, Masafumi T, Tamizi S, Tadao A (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:7258–7263
King R, Bonfiglio R, Metzler CF, Stein MC, Olah T (2000) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 11:942–950
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (21476217).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, XP., Li, PP., Hu, XM. et al. UPLC-DAD-MS/MS Method for Analysis of PQQ in Fermentation Broth. Chromatographia 78, 1185–1189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2932-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2932-9