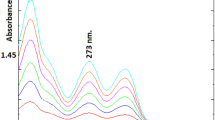
Abstract
A simple, fast, and sensitive capillary electrophoretic method was developed for determining two genotoxic impurities hydrazine and methylhydrazine and eight alkyl amines at trace levels in pharmaceutical substances using indirect photometric detection. The method development involved a systematic screening of various cationic visualizing reagents and optimization of separation conditions to obtain the best resolution and sensitivities. The optimized method was validated for specificity, precision, linearity, and accuracy. Linear calibration curves (R > 0.99) were obtained for all analytes in the range LOQ–200 % of nominal concentrations. The developed CE method was effectively implemented for estimating hydrazine and alkylamines in several active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
ICH Q3A (R) (2002) Impurities in new drug substances. http://www.ICH.org/
ICH Q3B (R2) (2006) Impurities in new drug products. http://www.ICH.org/
ICH Q3C (R5) (2011) Impurities: guidelines for residual solvents. http://www.ICH.org/
European Medicines Agency, London (2006) Guideline on the limits of genotoxic impurities. Committee for Medicinal Products (CHMP) (CPMP/SWP/5199/02, EMEA/CHMP/QWP/251344/2006)
US Department of Health and Human services, Food and Drug Administration, Centre for Drug evaluation and Research (CDER) (2008) Guidance for industry. Genotoxic and carcinogenic impurities in drug substances and products: recommended approaches
EMEA Q&A, EMEA/CHMP/SWP/431994/2007. http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/swp/43199407en.pdf
Muller L, Mauthe RJ, Riley CM, Andino MM, de Antonis D, Beels C, DeGeorge J, De Knaep AGM, Ellison D, Fagerland JA, Frank R, Fritschel B, Galloway S, Harpur E, Humfrey CDN, Jacks AS, Jagota N, Mackinnon J, Mohan G, Ness DK, O’Donovan MR, Smith MD, Vudathala G, Yotti L (2006) Reg Toxicol Pharm 44:198–211
Carlin J, Gregory N, Simmons J (1998) J Pharm Biomed Anal 17:885–890
Lovering EG, Matsui F, Curran NM, Robertson DL, Sears RW (1983) J Pharm Sci 72:965–967
Lovering EG, Matsui F, Robertson DL, Curran NM (1985) J Pharm Sci 74:105–107
Hydrazine (1999) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans 71: p 991
Knottnerus JA (2002) N-Methylhydrazine, evaluation of the carcinogenicity and genotoxicity, Dutch Expert Committee on Occupational Standards. A Committee of the Health Council of the Netherlands, Nr 2002/07OSH, The Hague
Elder DP, Snodin D, Teasdale A (2011) J Pharm Biomed Anal 54:900–910
Kean T, Miller JH, Skellern GG, Snodin D (2006) Pharmeur Sci Notes 2:23–33
Sun M, Bai L, Lui DQ (2008) J Pharm Biomed Anal 49:529–533
Hmelnickis J, Pugoviˇcs O, Kaˇzoka H, Viskna A, Susinskis I, Kokums K (2008) J Pharm Biomed Anal 48:649–656
Liu M, Ostovic J, Chen EX, Cauchon N (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:2362–2370
Khan M, Jayasree K, Reddy KVSRK, Dubey PK (2012) J Pharm Biomed Anal 58:27–33
Kumar A, Burns J, Hoffmann W, Demattio H, Malik AK, Matysik FM (2011) Electrophoresis 32:920–925
Guo L, Matysik FM, Gläser P, Engewald W (2005) Electrophoresis 26(17):3341–3348
You T, Niu L, Gui JY, Dong S, Wang E (1999) J Pharm Biomed Anal 19(1–2):231–237
Yeung ES, Kuhr WG (1991) Anal Chem 63:275A–282A
Macka M, Johns C, Doble P, Haddad PR, Altria K.D (2001) LCGC 19 (1) www.chromatographyonline.com
Foret F, Krivánková L, Bocek P (1993) Capillary zone electrophoresis. VCH Publishers, New York, pp 27–35
Xu X, Kok WT, Poppe H (1997) J Chromatogr A 786:333–345
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the management of Laurus Labs Pvt. Ltd. for supporting this work. The authors also wish to acknowledge the encouragement provided by Dr. Satyanarayana C., Dr. Srihari Raju K. and Mr. Ravindra G., Laurus Labs Pvt. Ltd. throughout this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Kumar, S., Jayasree, K. et al. Simultaneous Trace Level Determination of Potentially Genotoxic Hydrazine, Methylhydrazine and Alkylamines in Pharmaceutical Substances by CE Using Indirect Photometric Detection. Chromatographia 76, 801–809 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-013-2467-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-013-2467-x