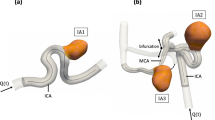
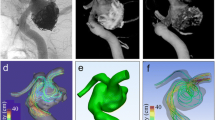
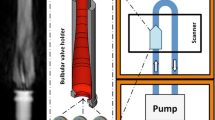
Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to investigate the performance of k-t BLAST (Broad-use Linear Acquisition Speed-up Technique) accelerated time-resolved 3D PC-MRI compared to SENSE (SENSitivity Encoding) acceleration in an in vitro and in vivo intracranial aneurysm.
Materials and methods
Non-accelerated, SENSE and k-t BLAST accelerated time-resolved 3D PC-MRI measurements were performed in vivo and in vitro. We analysed the consequences of various temporal resolutions in vitro.
Results
Both in vitro and in vivo measurements showed that the main effect of k-t BLAST was underestimation of velocity during systole. In the phantom, temporal blurring decreased with increasing temporal resolution. Quantification of the differences between the non-accelerated and accelerated measurements confirmed that in systole SENSE performed better than k-t BLAST in terms of mean velocity magnitude. In both in vitro and in vivo measurements, k-t BLAST had higher SNR compared to SENSE. Qualitative comparison between measurements showed good similarity.
Conclusion
Comparison with SENSE revealed temporal blurring effects in k-t BLAST accelerated measurements.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PC-MRI:
-
Phase contrast MRI
- k-t BLAST:
-
Broad-use linear acquisition speed-up technique
- SENSE:
-
Sensitivity encoding
- FFE:
-
Fast field echo
- TOF:
-
Time of flight
- NSA:
-
Number of signal averages
References
Proust F, Gerardin E, Chazal J (2008) Unruptured intracranial aneurysm and microsurgical exclusion: the need of a randomized study of surgery versus natural history. J Neuroradiol 35(2):109–115
Spelle L, Pierot L (2008) Endovascular treatment of non-ruptured intracranial aneurysms: critical analysis of the literature. J Neuroradiol 35(2):116–120
Kayembe KN, Sasahara M, Hazama F (1984) Cerebral aneurysms and variations in the circle of Willis. Stroke 15(5):846–850
Chien A, Castro MA, Tateshima S, Sayre J, Cebral J, Vinuela F (2009) Quantitative hemodynamic analysis of brain aneurysms at different locations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(8):1507–1512
Wigstrom L, Sjoqvist L, Wranne B (1996) Temporally resolved 3D phase-contrast imaging. Magn Reson Med 36(5):800–803
Bammer R, Hope TA, Aksoy M, Alley MT (2007) Time-resolved 3D quantitative flow MRI of the major intracranial vessels: initial experience and comparative evaluation at 1.5T and 3.0T in combination with parallel imaging. Magn Reson Med 57(1):127–140
Pelc NJ, Bernstein MA, Shimakawa A, Glover GH (1991) Encoding strategies for three-direction phase-contrast MR imaging of flow. J Magn Reson Imaging 1(4):405–413
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P (1999) SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 42(5):952–962
Thunberg P, Karlsson M, Wigstrom L (2003) Accuracy and reproducibility in phase contrast imaging using SENSE. Magn Reson Med 50(5):1061–1068
Brisman JL, Song JK, Newell DW (2006) Cerebral aneurysms. N Engl J Med 355(9):928–939
Tsao J, Boesiger P, Pruessmann KP (2003) k-t BLAST and k-t SENSE: dynamic MRI with high frame rate exploiting spatiotemporal correlations. Magn Reson Med 50(5):1031–1042
Marshall I (2006) Feasibility of k-t BLAST technique for measuring “seven-dimensional” fluid flow. J Magn Reson Imaging 23(2):189–196
Stadlbauer A, van der Riet W, Crelier G, Salomonowitz E (2010) Accelerated time-resolved three-dimensional MR velocity mapping of blood flow patterns in the aorta using SENSE and k-t BLAST. Eur J Radiol 75(1):e15–e21
Stadlbauer A, van der Riet W, Globits S, Crelier G, Salomonowitz E (2009) Accelerated phase-contrast MR imaging: comparison of k-t BLAST with SENSE and Doppler ultrasound for velocity and flow measurements in the aorta. J Magn Reson Imaging 29(4):817–824
Lutz A, Bornstedt A, Manzke R, Etyngier P, Nienhaus GU, Rasche V (2011) Acceleration of tissue phase mapping by k-t BLAST: a detailed analysis of the influence of k-t-BLAST for the quantification of myocardial motion at 3T. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 13:5
Carlsson M, Toger J, Kanski M, Bloch KM, Stahlberg F, Heiberg E, Arheden H (2011) Quantification and visualization of cardiovascular 4D velocity mapping accelerated with parallel imaging or k-t BLAST: head to head comparison and validation at 1.5 T and 3 T. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 13:55
Thunberg P, Emilsson K, Rask P, Kähäri A (2012) Flow and peak velocity measurements in patients with aortic valve stenosis using phase contrast MR accelerated with k-t BLAST. Eur J Radiol 81(9):2203–2207. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.06.034
Tsao J, Kozerke S, Boesiger P, Pruessmann KP (2005) Optimizing spatiotemporal sampling for k-t BLAST and k-t SENSE: application to high-resolution real-time cardiac steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med 53(6):1372–1382
Baltes C, Kozerke S, Hansen MS, Pruessmann KP, Tsao J, Boesiger P (2005) Accelerating cine phase-contrast flow measurements using k-t BLAST and k-t SENSE. Magn Reson Med 54(6):1430–1438
Tsao J, Tarnavaski O, Privetera M, Shetty S (2006) k-t denoising: exploiting spatiotemporal correlations for signal-to-noise improvement in dynamic imaging. Proceedings of the 14th annual meeting of ISMRM, Seattle, Washington, USA: 690
van Ooij P, Guédon A, Poelma C, Schneiders J, Rutten MCM, Marquering HA, Majoie CB, vanBavel E, Nederveen AJ (2012) Complex flow patterns in a real-size intracranial aneurysm phantom: phase contrast MRI compared with particle image velocimetry and computational fluid dynamics. NMR Biomed 25(1):14–26
Lenz GW, Haacke EM, White RD (1989) Retrospective cardiac gating: a review of technical aspects and future directions. Magn Reson Imaging 7(5):445–455
Hansen MS, Kozerke S, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, Pedersen EM, Tsao J (2004) On the influence of training data quality in k-t BLAST reconstruction. Magn Reson Med 52(5):1175–1183
de Zwart JA, Ledden PJ, Kellman P, van Gelderen P, Duyn JH (2002) Design of a SENSE-optimized high-sensitivity MRI receive coil for brain imaging. Magn Reson Med 47(6):1218–1227
Bernstein MA, Shimakawa A, Pelc NJ (1992) Minimizing TE in moment-nulled or flow-encoded two-and three-dimensional gradient-echo imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2(5):583–588
Lotz J, Meier C, Leppert A, Galanski M (2002) Cardiovascular flow measurement with phase-contrast MR imaging: basic facts and implementation. Radiographics 22(3):651–671
Li C, Xu C, Gui C, Fox MD (2005) Level set evolution without re-initialization: a new variational formulation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognotion (CVPR), San diego, USA, p 430–436
Price RR, Axel L, Morgan T, Newman R, Perman W, Schneiders N, Selikson M, Wood M, SR T (1990) Quality assurance methods and phantoms for magnetic resonance imaging: report of AAPM nuclear magnetic resonance Task Group No. 1. Med Phys 17(2):287–295
Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO (2007) Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(2):375–385
Plein S, Ryf S, Schwitter J, Radjenovic A, Boesiger P, Kozerke S (2007) Dynamic contrast-enhanced myocardial perfusion MRI accelerated with k-t sense. Magn Reson Med 58(4):777–785
Reeder SB, Wintersperger BJ, Dietrich O, Lanz T, Greiser A, Reiser MF, Glazer GM, Schoenberg SO (2005) Practical approaches to the evaluation of signal-to-noise ratio performance with parallel imaging: application with cardiac imaging and a 32-channel cardiac coil. Magn Reson Med 54(3):748–754
Conturo TE, Smith GD (1990) Signal-to-noise in phase angle reconstruction: dynamic range extension using phase reference offsets. Magn Reson Med 15(3):420–437
Bernstein MA, Ikezaki Y (1991) Comparison of phase-difference and complex-difference processing in phase-contrast MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 1(6):725–729
Satoh T, Omi M, Ohsako C, Katsumata A, Yoshimoto Y, Tsuchimoto S, Onoda K, Tokunaga K, Sugiu K, Date I (2005) Influence of perianeurysmal environment on the deformation and bleb formation of the unruptured cerebral aneurysm: assessment with fusion imaging of 3D MR cisternography and 3D MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(8):2010–2018
Kellman P, McVeigh ER (2005) Image reconstruction in SNR units: a general method for SNR measurement. Magn Reson Med 54(6):1439–1447
de Zwart JA, Ledden PJ, van Gelderen P, Bodurka J, Chu R, Duyn JH (2004) Signal-to-noise ratio and parallel imaging performance of a 16-channel receive-only brain coil array at 3.0 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 51(1):22–26
Kozerke S, Tsao J, Razavi R, Boesiger P (2004) Accelerating cardiac cine 3D imaging using k-t BLAST. Magn Reson Med 52(1):19–26
Cebral JR, Castro MA, Burgess JE, Pergolizzi RS, Sheridan MJ, Putman CM (2005) Characterization of cerebral aneurysms for assessing risk of rupture by using patient-specific computational hemodynamics models. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(10):2550–2559
Mut F, Lohner R, Chien A, Tateshima S, Vinuela F, Putman C, Cebral J (2011) Computational hemodynamics framework for the analysis of cerebral aneurysms. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 27(6):822–839
Chang W, Kecskemeti S, Frydrychowicz A, Landgraf B, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Wu Y, Johnson K, Wieben O, Mistretta C, Turski P (2011) Calculation of wall shear stress in intracranial cerebral aneurysms using high resolution phase contrast MRA (PC-VIPR). Proceedings of the international society of magnetic resonance in medicine 19:3307
Hsiao A, Lustig M, Alley MT, Murphy M, Vasanawala SS (2011) Quantitative assessment of blood flow with 4D phase-contrast MRI and autocalibrating parallel imaging compressed sensing. Proceedings of the international society of magnetic resonance in medicine 19:1190
Pedersen H, Kozerke S, Ringgaard S, Nehrke K, Kim WY (2009) k-t PCA: temporally constrained k-t BLAST reconstruction using principal component analysis. Magn Reson Med 62(3):706–716
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Gertjan Bon from the University of Amsterdam for the glass blowing of the phantom and Paul Groot of the Department of Radiology of the Academic Medical Centre/University of Amsterdam for the inventive ECG signal acquisition. The authors would also like to thank Gustav Strijkers of the Department of Biomedical NMR of the University of Technology Eindhoven for advice on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Ooij, P., Guédon, A., Marquering, H.A. et al. k-t BLAST and SENSE accelerated time-resolved three-dimensional phase contrast MRI in an intracranial aneurysm. Magn Reson Mater Phy 26, 261–270 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-012-0336-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-012-0336-5