Abstract
Object
Parallel transmission facilitates a relatively direct control of the RF transmit field. This is usually applied to improve the RF field homogeneity but might also allow a reduction of the specific absorption rate (SAR) to increase freedom in sequence design for high-field MRI. However, predicting the local SAR is challenging as it depends not only on the multi-channel drive but also on the individual patient.
Materials and methods
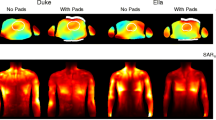
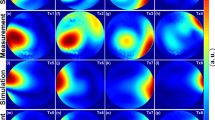
The potential of RF shimming for SAR management is investigated for a 3 T body coil with eight independent transmit elements, based on Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) simulations. To address the patient-dependency of the SAR, nine human body models were generated from volunteer MR data and used in the simulations. A novel approach to RF shimming that enforces local SAR constraints is proposed.
Results
RF shimming substantially reduced the local SAR, consistently for all volunteers. Using SAR constraints, a further SAR reduction could be achieved with only minor compromises in RF performance.
Conclusion
Parallel transmission can become an important tool to control and manage the local SAR in the human body. The practical use of local SAR constraints is feasible with consistent results for a variety of body models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katscher U, Börnert P, Leussler C, van den Brink J (2003) Transmit sense. Magn Reson Med 49(1): 144–150
Zhu Y (2004) Parallel excitation with an array of transmit coils. Magn Reson Med 51(4): 775–784
Grissom W, Yip C, Zhang Z, Stenger V, Fessler J, Noll D (2006) Spatial domain method for the design of RF pulses in multicoil parallel excitation. Magn Reson Med 56(3): 620–629
Hoult D (2000) Sensitivity and power deposition in a high-field imaging experiment. J Magn Reson Imaging 12(1): 46–67
Ibrahim T, Lee R, Baertlein B, Abduljalil A, Zhu H, Robitaille P (2001) Effect of RF coil excitation on field inhomogeneity at ultra high fields: a field optimized TEM resonator. Magn Reson Imaging 19(10): 1339–1347
International Electrotechnical Commission (2010) International standard, medical equipment—IEC 60601-2-33: particular requirements for the safety of Magnetic resonance equipment, 3rd edn
Wang Z, Lin J, Mao W, Liu W, Smith M, Collins C (2007) SAR and temperature: simulations and comparison to regulatory limits for MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(2): 437–441
Alon L, Deniz C, Lattanzi R, Wiggins G, Brown R, Sodickson D, Zhu Y (2010) An automated method for subject specific global SAR prediction in parallel transmission. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Stockholm, Sweden, p 780
Katscher U, Voigt T, Findeklee C, Vernickel P, Nehrke K, Dössel O (2009) Determination of electric conductivity and local SAR via B1 mapping. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(9): 1365–1374
Seifert F, Wubbeler G, Junge S, Ittermann B, Rinneberg H (2007) Patient safety concept for multichannel transmit coils. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(5): 1315–1321
Collins C, Wang Z, Smith M (2007) A conservative method for ensuring safety within transmit arrays. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Berlin, Germany, p 1092
Graesslin I, Glaesel D, Biederer S, Vernickel P, Katscher U, Schweser F, Annighoefer B, Dingemans H, Mens G, van Yperen G, Harvey P (2008) Comprehensive RF safety concept for parallel transmission systems. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Toronto, Canada, p 74
Brunner D, Paska J, Fröhlich J, Prüssmann K (2009) SAR assessment of transmit arrays: deterministic calculation of worst- and best-case performance. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, p 4803
van den Berg C, van den Bergen B, van den Kamer J, Raaymakers B, Kroeze H, Bartels L, Lagendijk J (2007) Simultaneous B1+ homogenization and specific absorption rate hotspot suppression using a magnetic resonance phased array transmit coil. Magn Reson Med 57(3): 577–586
Cloos M, Luong M, Ferrand G, Amadon A, Le Bihan D, Boulant N (2010) Local SAR reduction in parallel excitation based on channel-dependent Tikhonov parameters. J Magn Reson Imaging 32(5): 1209–1216
Lee J, Gebhardt M, Wald L, Adalsteinsson E (2010) Parallel transmit RF design with local SAR constraints. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Stockholm, Sweden, p 105
Sbrizzi A, Hoogduin H, Lagendijk J, Luijten P, Sleijpen G, van den Berg C (2010) A fast algorithm for local-1gram-SAR optimized parallel-transmit RF-pulse design. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Stockholm, Sweden, p 4931
Brunner D, Prüssmann K (2010) Optimal design of multiple-channel RF pulses under strict power and SAR constraints. Magn Reson Med 63(5): 1280–1291
Zelinski A, Goyal V, Angelone L, Bonmassar G, Wald L, Adalsteinsson E (2007) Designing RF pulses with optimal specific absorption rate (SAR) characteristics and exploring excitation fidelity, SAR and pulse duration tradeoffs. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Berlin, Germany, p 1699
Liu W, Collins C, Smith M (2005) Calculations of B1, distribution, specific energy absorption rate, and intrinsic signal-to-noise ratio for a body-size birdcage coil loaded with different human subjects at 64 and 128 MHz. Appl Magn Reson 29(1): 5–18
Buchenau S, Haas M, Hennig J, Zaitsev M (2009) A comparison of local SAR using individual patient data and a patient template. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, p 4798
Zhai Z, Morich M, DeMeester G, Harvey P (2009) A study of the relationship between B1-field uniformity, body aspect ratio and SAR for whole-body RF Shimming at 3.0T. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, p 3045
van den Bergen B, van den Berg C, Kroeze H, Bartels L, Lagendijk J (2006) The effect of body size and shape on RF safety and B1 field homogeneity at 3T. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Seattle, WA, USA, p 2040
Wang Z, Penney C, Luebbers R, Collins C (2008) Poseable male and female numerical body models for field calculations in MRI. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Toronto, Canada, p 75
Yeo D, Wang Z, Loew W, Vogel M, Hancu I (2011) Local specific absorption rate in high-pass birdcage and transverse electromagnetic body coils for multiple human body models in clinical landmark positions at 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(5): 1209–1217
Homann H, Börnert P, Eggers H, Nehrke K, Dössel O, Graesslin I (2011a) Towards individualized SAR models and in vivo validation. Magn Reson Med (in early view). doi:10.1002/mrm.22948
Yarnykh V (2007) Actual flip-angle imaging in the pulsed steady state: a method for rapid three-dimensional mapping of the transmitted radiofrequency field. Magn Reson Med 57(1): 192–200
Vernickel P, Röschmann P, Findeklee C, Lüdeke K, Leussler C, Overweg J, Katscher U, Grasslin I, Schünemann K (2007) Eight-channel transmit/receive body MRI coil at 3T. Magn Reson Med 58(2): 381–389
Vernickel P, Findeklee C, Eichmann J, Graesslin I (2007b) Active digital decoupling for multi-channel transmit MRI systems. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Berlin, Germany, p 170
IEEE (2008) IEEE standard for safety levels with respect to human exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields, 3 kHz to 300 GHz. IEEE Std C95.3-2002
Bardati F, Borrani A, Gerardino A, Lovisolo G (1995) SAR optimization in a phased array radiofrequency hyperthermia system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 42(12): 1201–1207
Gebhardt M, Diehl D, Adalsteinsson E, Wald L, Eichfelder G (2010) Evaluation of maximum local SAR for parallel transmission (pTx) pulses based on pre-calculated field data using a selected subset of virtual observation points. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Stockholm, Sweden, p 1441
Eichfelder G, Gebhardt M (2011) Local specific absorption rate control for parallel transmission by virtual observation points. Magn Reson Med (in early view). doi:10.1002/mrm.22927
Wang Z, Oh S, Smith M, Collins C (2007b) RF Shimming considering both excitation homogeneity and SAR. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Berlin, Germany, p 1022
Setsompop K, Wald L, Alagappan V, Gagoski B, Adalsteinsson E (2008) Magnitude least squares optimization for parallel radio frequency excitation design demonstrated at 7 Tesla with eight channels. Magn Reson Med 59(4): 908–915
Kassakian P (2006) Convex approximation and optimization with applications in magnitude filter design and radiation pattern synthesis. PhD thesis, University of California at Berkeley
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2009) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Caputa K, Okoniewski M, Stuchly M (1999) An algorithm for computations of the power deposition in human tissue. IEEE Antennas Propag Mag 41(4): 102–107
Oh S, Carluccio G, Collins C (2011) Method and tool for improved, rapid N-gram average SAR determination. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Montreal, Canada, p 3868
Bottomley P, Redington R, Edelstein W, Schenck J (1985) Estimating radiofrequency power deposition in body NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med 2(4): 336–349
Homann H, Graesslin I, Voigt T, Börnert P, Dössel O (2009) The influence of body size on the specific absorption rate (SAR). In: Proceedings of the ESMRMB (Magma 22, Suppl 1), p 522
Harvey P, Zhai Z, Morich M, Mens G, van Yperen G, DeMeester G, Graesslin I, Hoogeveen R (2009) SAR behavior during whole-body multitransmit RF Shimming at 3.0T. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, p 4786
Homann H, Börnert P, Dössel O, Graesslin I (2011b) A robust concept for real-time SAR calculation in parallel transmission. In: Proceedings of the ISMRM, Montreal, Canada, p 3843
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homann, H., Graesslin, I., Eggers, H. et al. Local SAR management by RF Shimming: a simulation study with multiple human body models. Magn Reson Mater Phy 25, 193–204 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0281-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0281-8