Abstract
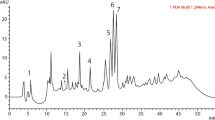
To identify phytoalexins of adzuki bean elicited in response to attempted infection of Phytophthora vignae f. sp. adzukicola, we isolated compounds from adzuki bean and evaluated their antifungal activity. Seven flavonoids (daidzein, genistein, 2′-hydroxygenistein, coumestrol, dalbergioidin, kievitone, and phaseol) were identified from epicotyls wound-inoculated with a mycelial suspension of an avirulent race of P. vignae f. sp. adzukicola. Of those compounds, kievitone and dalbergioidin accumulated to higher levels in incompatible interactions compared to compatible interactions 48 h after inoculation. Kievitone strongly inhibited the germination of encysted zoospores, and dalbergioidin were slightly suppressive. From these results, we concluded that kievitone and dalbergioidin are phytoalexins in adzuki bean.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe N, Sato H, Sakamura S (1987) Antifungal stress compounds from adzuki bean, Vigna angularis, treated with Cephalosporium gregatum type B. Agric Biol Chem 51:349–353
Brooks CJW, Watson DG (1985) Phytoalexins. Nat Prod Rep 2:427–459
Burden RS, Bailey JA, Dawson GW (1972) Structures of three new isoflavanoids from Phaseolus vulgaris infected with tobacco necrosis virus. Tetrahedron Lett 41:4175–4178
Deverall BJ (1972) Phytoalexins and disease resistance. Proc R Soc Lond B 181:233–246
Fujita S (2007) Studies on the breeding of adzuki bean cultivars resistant to adzuki bean brown stem rot (BSR) and Phytophthora stem rot (PSR). Rep Hokkaido Pref Agric Exp Sta No. 115
Fujita S, Murata K, Shimada H, Aoyama S, Chiba I, Matsukawa I, Shirai S, Miura T, Kondo N (2002) A new adzuki bean variety “Syumari” with soil-borne disease resistance and excellent processing quality. Bull Hokkaido Pref Agric Exp Stn 82:31–40
Grisebach H, Ebel J (1978) Phytoalexins, chemical defense substances of higher plants? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 17:635–647
Harada G, Kondo N (2009) Adzuki bean leaf infection by Phytophthora vignae f. sp. adzukicola and resistance evaluation using detached leaves inoculated with zoospores. J Gen Plant Pathol 75:52–55
Ingham JL (1972) Phytoalexins and other natural products as factors in plant disease resistance. Bot Rev 38:343–424
Ingham JL (1977) Phytoalexins of hyacinth bean (Lablab niger). Z Naturforsh 32c:1018–1020
Ingham JL (1990) Systematic aspects of phytoalexin formation within tribe Phaseoleae of the Leguminosae (Subfamily Papilionoideae). Biochem Syst Ecol 18:329–343
Iwashina T (2003) Flavonoid function and activity to plants and other organisms. Biol Sci Space 17:24–44
Kitazawa K, Tsuchiya S, Kodama F, Kamjaipai W, Ogoshi A, Yanagita K (1978) Phytophthora stem rot of adzuki-bean (Phaseolus angularis) caused by Phytophthora vignae Purss. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 44:528–531
Kitazawa K, Suzui T, Yanagita K (1979) Pathogenicity of Phytophthora vignae Purss to adzuki-bean and cowpea. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 45:406–408
Kondo N, Notsu A, Naito S (2004) Distribution of Phytophthora vignae f. sp. adzukicola races in adzuki bean fields in Hokkaido, Japan. Plant Dis 88:875–877
Mohr PG, Cahill DM (2001) Relative roles of glyceollin, lignin and the hypersensitive response and the influence of ABA in compatible and incompatible interactions of soybeans with Phytophthora sojae. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 58:31–41
Notsu A, Kondo N, Fujita S, Murata K, Naito S (2003) New race of Phytophthora vignae f. sp. adzukicola, the causal agent of Phytophthora stem rot of the adzuki bean. J Gen Plant Pathol 69:39–41
O’Neill MJ, Adesanya SA, Roberts MF (1983) Antifungal phytoalexins in Phaseolus aureus Roxb. Z Naturforsh 38c:693–697
Ogura R (2008) New race of Phytophthora vignae f. sp. adzukicola, causal agent of Phytophthora stem rot of adzuki bean. Jpn J Phytopathol (Abstract in Japanese) 74:79
Partridge JE, Keen NT (1976) Association of the phytoalexin kievitone with single-gene resistance of cowpeas to Phytophthora vignae. Phytopathology 66:426–429
Paxton JD (1980) A new working definition of the term “Phytoalexin”. Plant Dis 64:734
Seneviratne GI, Harborne JB (1992) Constitutive flavonoids and induced isoflavonoids as taxonomic markers in the genus Vigna. Biochem Syst Ecol 20:459–467
Tsuchiya S (1982) Studies on Phytophthora stem rot and its control. PhD dissertation, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
Tsuchiya S, Yanagawa M, Ogoshi A (1986) Forma speciales differentiation of Phytophthora vignae isolates from cowpea and adzuki bean. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 52:577–584
Woodward MD (1979) Phaseoluteone and other 5-hydroxyisoflavonoids from Phaseolus vulgaris. Phytochemistry 18:363–365
Yamamoto H (1994) Studies on taxonomy of the causal fungus of brown stem rot of adzuki bean and soybean, Phialophora gregata (Allington et Chamberlain) Gams. Mem Fac Agric Hokkaido Univ 19:57–98
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Eri Fukushi and Mr. Kenji Watanabe (GC-MS & MNR Laboratory, Graduate School of Agriculture, Hokkaido University) for MS measurements. This study was supported by the Japan Beans Fund Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada, G., Kondo, N. Induction of phytoalexins in adzuki bean after inoculation with Phytophthora vignae f. sp. adzukicola . J Gen Plant Pathol 75, 432–436 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-009-0203-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-009-0203-z