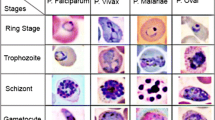
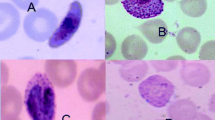
Abstract
Malaria is a serious public health problem in many parts of the world. Early diagnosis and prompt effective treatment are required to avoid anemia, organ failure, and malaria-associated deaths. Microscopic analysis of blood samples is the preferred method for diagnosis. However, manual microscopic examination is very laborious and requires skilled health personnel of which there is a critical shortage in the developing world such as in sub-Saharan Africa. Critical shortages of trained health personnel and the inability to cope with the workload to examine malaria slides are among the main limitations of malaria microscopy especially in low-resource and high disease burden areas. We present a low-cost alternative and complementary solution for rapid malaria screening for low resource settings to potentially reduce the dependence on manual microscopic examination. We develop an image processing pipeline using a modified YOLOv3 detection algorithm to run in real time on low-cost devices. We test the performance of our solution on two datasets. In the dataset collected using a microscope camera, our model achieved 99.07% accuracy and 97.46% accuracy on the dataset collected using a mobile phone camera. While the mean average precision of our model is on par with human experts at an object level, we are several orders of magnitude faster than human experts as we can detect parasites in images as well as videos in real time.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (2018) World malaria report 2018, https://www.who.int/malaria/media/world-malaria-report-2018/en/
White NJ, Ho M: The pathophysiology of malaria. In: Advances in Parasitology, vol 31. Elsevier, 1992, pp 83–173
Kwiatkowski D, Sambou I, Twumasi P, Greenwood B, Hill A, Manogue K, Cerami A, Castracane J, Brewster D: Tnf concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicated plasmodium falciparum malaria. The Lancet 336 (8725): 1201–1204, 1990
Organization W.H. (2016) Malaria microscopy quality assurance manual-version 2. World Health Organization
Petti CA, Polage CR, Quinn TC, Ronald AR, Sande MA: Laboratory medicine in africa: a barrier to effective health care. Clin Infect Dis 42 (3): 377–382, 2006
Moody A: Rapid diagnostic tests for malaria parasites. Clin Microbiol Rev 15 (1): 66–78, 2002
Kim S, Nhem S, Dourng D, Ménard D: Malaria rapid diagnostic test as point-of-care test: study protocol for evaluating the vikia® malaria ag pf/pan. Malar J 14 (1): 114, 2015
Hung J, Carpenter A: Applying faster r-cnn for object detection on malaria images. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, 2017, pp 808–813
Yang D, Subramanian G, Duan J, Gao S, Bai L, Chandramohanadas R, Ai Y: A portable image-based cytometer for rapid malaria detection and quantification. PloS one 12 (6): e0179161, 2017
Pattanaik P, Swarnkar T, Sheet D: Object detection technique for malaria parasite in thin blood smear images. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, 2017, pp 2120–2123
Mehanian C, Jaiswal M, Delahunt C, Thompson C, Horning M, Hu L, McGuire S, Ostbye T, Mehanian M, Wilson B, et al: Computer-automated malaria diagnosis and quantitation using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, pp 116–125
Quinn JA, Andama A, Munabi I, Kiwanuka FN: Automated blood smear analysis for mobile malaria diagnosis. Mobile Point-of-Care Monitors and Diagnostic Device Design 31: 115, 2014
Quinn JA, Nakasi R, Mugagga PK, Byanyima P, Lubega W, Andama A: Deep convolutional neural networks for microscopy-based point of care diagnostics. In: Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, 2016, pp 271–281
Neubeck A, Van Gool L: Efficient non-maximum suppression. In: ICPR 2006. 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2006, vol 3. IEEE, 2006, pp 850–855
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A: You only look once: unified real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, pp 779–788
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C-Y, Berg AC: Ssd: single shot multibox detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2016, pp 21–37
Girshick R (2015) Fast r-cnn, arXiv preprint arXiv:1504.08083
Lin T-Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection, arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.02002
Zhang S, Wen L, Bian X, Lei Z, Li SZ: Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp 4203–4212
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2018) Yolov3: an incremental improvement, arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767
Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams CK, Winn J, Zisserman A: The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int J Comput Vis 88 (2): 303–338, 2010
Lin T-Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick CL: Microsoft coco: common objects in context. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2014, pp 740–755
Chollet F (2016) Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen L-C (2018) Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks: mobile networks for classification, detection and segmentation, arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04381
Hartigan JA, Wong MA: Algorithm as 136: a k-means clustering algorithm. J R Stat Soc: Ser C: Appl Stat 28 (1): 100–108, 1979
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. IEEE, 2009, pp 248–255
Abadi M, et al.: Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16), 2016, pp 265– 283
Chollet F, et al (2015) Keras. https://github.com/fchollet/keras
Tieleman T, Hinton G: Lecture 6.5-rmsprop: divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. COURSERA: Neural Networks for Machine Learning 4 (2): 26–31, 2012
Salton G, McGill MJ: Introduction to modern information retrieval New York: McGraw-Hill Inc., 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chibuta, S., Acar, A.C. Real-time Malaria Parasite Screening in Thick Blood Smears for Low-Resource Setting. J Digit Imaging 33, 763–775 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00284-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00284-2