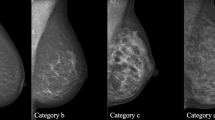
Abstract
A rapid and highly accurate diagnostic tool for distinguishing benign tumors from malignant ones is required owing to the high incidence of breast cancer. Although various computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems have been developed to interpret ultrasound images of breast tumors, feature selection and the setting of parameters are still essential to classification accuracy and the minimization of computational complexity. This work develops a highly accurate CAD system that is based on a support vector machine (SVM) and the artificial immune system (AIS) algorithm for evaluating breast tumors. Experiments demonstrate that the accuracy of the proposed CAD system for classifying breast tumors is 96.67 %. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of the proposed CAD system are 96.67, 96.67, 95.60, and 97.48 %, respectively. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) area index A z is 0.9827. Hence, the proposed CAD system can reduce the number of biopsies and yield useful results that assist physicians in diagnosing breast tumors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63(1):11–30, 2013
Sivaramakrishna R, Gordon R: Detection of breast cancer at a smaller size can reduce the likelihood of metastatic spread: a quantitative analysis. Acad Radiol 4(1):8–12, 1997
Chen DR, Hsiao YH: Computer-aided diagnosis in breast ultrasound. J Med Ultrasound 16(1):46–56, 2008
Zhou Y: Ultrasound diagnosis of breast cancer. J Med Imaging Health Inform 3(2):157–170, 2013
Lodwick GS: Computer diagnosis in radiology. J Mich State Med Soc 61:1239–1242, 1962
Drukker K, Sennett CA, Giger ML: Automated method for improving system performance of computer-aided diagnosis in breast ultrasound. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(1):122–128, 2009
Chang RF, Wu WJ, Moon WK, Chen DR: Automatic ultrasound segmentation and morphology based diagnosis of solid breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 89(2):179–185, 2005
Chen DR, Huang YL, Lin SH: Computer-aided diagnosis with textural features for breast lesions in sonograms. Comput Med Imaging Graph 35(3):220–226, 2011
Moon WK, Chang SC, Huang CS, Chang RF: Breast tumor classification using fuzzy clustering for breast elastography. Ultrasound Med Biol 37(5):700–708, 2011
Chen ST, Hsiao YH, Huang YL, Kuo SJ, Tseng HS, Wu HK, Chen DR: Comparative analysis of logistic regression, support vector machine and artificial neural network for the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant solid breast tumors by the use of three-dimensional power Doppler imaging. Korean J Radiol 10(5):464–471, 2009
Tseng HS, Wu HK, Chen ST, Kuo SJ, Huang YL, Chen DR: Speckle reduction imaging of breast ultrasound does not improve the diagnostic performance in morphology-based CAD System. J Clin Ultrasound 40(1):1–6, 2012
Tan T, Platel B, Huismam H, Sánchez CI, Mus R, Karssemeijer N: Computer-aided lesion diagnosis in automated 3-D breast ultrasound using coronal spiculation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(5):1034–1042, 2012
Wu WJ, Lin SW, Moon WK: Combining support vector machine with genetic algorithm to classify ultrasound breast tumor images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 36(8):627–633, 2012
Han J, Kamber M: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, 2007
Montani S: Exploring new roles for case based reasoning in heterogeneous AI system for medical decision support. Appl Intell 28(3):275–285, 2008
Andrews PS, Timmis J: Inspiration for the next generation of artificial immune systems. Artificial Immune Systems. Springer, Berlin, 2005
Latifoǧlu F, Kodaz H, Kara S, Güneş S: Medical application of artificial immune recognition system (AIRS): diagnosis of atherosclerosis from carotid artery Doppler signals. Comput Biol Med 37(8):1092–1099, 2007
Lin SW, Chen SC: Parameter tuning, feature selection and weight assignment of features for case-based reasoning by artificial immune system. Appl Soft Comput 11(8):5042–5052, 2011
Kuo RJ, Tseng WL, Tien FC, Warren L: Application of an artificial immune system-based fuzzy neural network to a RFID-based positioning system. Comput Ind Eng 63(4):943–956, 2012
Chen GY, Xie WF: Pattern recognition with SVM and dual-tree complex wavelets. Image Vis Comput 25(6):960–966, 2007
Huang YL, Wang KL, Chen DR: Diagnosis of breast tumors with ultrasonic analysis using support vector machines. Neural Comput & Applic 15(2):164–169, 2006
Chang RF, Wu WJ, Moon WK, Chou YH, Chen DR: Support vector machines for diagnosis of breast tumors on US images. Acad Radiol 10(2):189–197, 2003
Wang XY, Yang HY, Cui CY: An SVM-based robust digital image watermarking against desynchronization attacks. Signal Process 88(9):2193–2205, 2008
Wong WT, Hsu SH: Application of SVM and ANN for image retrieval. Eur J Oper Res 173(3):938–950, 2006
Vapnik VN: The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer, New York, 1995
Deguchi K, Izumitani T, Hontani H: Detection and enhancement of line structures in an image by anisotropic diffusion. Pattern Recogn Lett 23(12):1399–1405, 2002
Czerwinski RN, Jones DL, O’Brien WD: Detection of lines and boundaries in speckle images—application to medical ultrasound. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(2):126–136, 1999
Blayvas I, Bruckstein A, Kimmel R: Efficient computation of adaptive threshold surfaces for image binarization. Pattern Recognit 39(1):89–101, 2006
Zhou H, Yuan Y, Lin F, Liu: Level set image segmentation with Bayesian analysis. Neurocomputing 71(10):1994–2000,2008
Fabiszewska E, Grabska I, Jankowska K, Wesolowska E, Bulski W: Comparison of results from quality control of physical parameters and results from clinical evaluation of mammographic images for the mammography screening facilities in Poland. Radiat Prot Dosim 147(1–2):206–209, 2011
Liao Y, Fang SC, Nuttle HLW: A neural network model with bounded-weights for pattern classification. Comput Oper Res 31(9):1411–1426, 2004
Lin HT, Lin CJ: A study on sigmoid kernels for SVM and the training of non-PSD kernels by SMO-type methods. Neural Comput 3:1–32, 2003
Müller KR, Mike S, Rätsch G, Tsuda K, Schölkopf B: An introduction to kernel-based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(2):181–201, 2001
Chang YW, Hsieh CJ, Chang KW, Ringgaard M, Lin CJ: Training and testing low-degree polynomial data mappings via linear SVM. J Mach Learn Res 11:1471–1490, 2010
Pardo M, Sberveglieri G: Classification of electronic nose data with support vector machines. Sensors Actuators B Chem 107(2):730–737, 2005
Bergstra J, Bengio Y: Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 13(1):281–305, 2012
Li Z, He C: Optimal scheduling-based RFID reader-to-reader collision avoidance method using artificial immune system. Appl Soft Comput 13(5):2557–2568, 2013
Lin SW, Ying KC: Minimizing makespan in a blocking flowshop using a revised artificial immune system algorithm. Omega 41(2):383–389, 2013
Shang R, Qi L, Jiao L, Stolkin R, Li Y: Change detection in SAR images by artificial immune multi-objective clustering. Eng Appl Artif Intell 31:53–67, 2014
Ying KC, Lin SW: Efficient wafer sorting scheduling using a hybrid artificial immune system. J Oper Res Soc 65(2):169–179, 2014
Chang CC, Lin CJ: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 2(3):1–27, 2011
Salzberg SL: On comparing classifiers: pitfalls to avoid and a recommended approach. Data Min Knowl Disc 1(3):317–328, 1997
Acknowledgements
The first author of this paper is grateful to the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China (Taiwan) for financially supporting this research [grant number NSC99-2221-E-182-041]. The second author is grateful to the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China (Taiwan) and the Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital for financially supporting this research [grant numbers MOST103-2410-H-182-006 and CARPD3B0012].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, WJ., Lin, SW. & Moon, W.K. An Artificial Immune System-Based Support Vector Machine Approach for Classifying Ultrasound Breast Tumor Images. J Digit Imaging 28, 576–585 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-014-9757-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-014-9757-1