Abstract
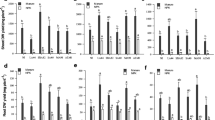
The effects of inoculation with Bacillus and Azospirillum strains on growth and cesium accumulation of five plant species, Komatsuna, Amaranth, sorghum, common millet and buckwheat, grown on cesium-spiked soil were assessed for potential use in cesium remediation. Pot experiments were performed using “artificially” Cs-contaminated soil. Three treatments were applied based on Cs location in the soil. For a soil height of 15 cm in the pots, Cs was added as follows: in the top five cm to imitate no ploughing condition; in the bottom five cm simulating inverted ploughing; and uniformly distributed Cs reproducing normal plowing. Generally, inoculation of Cs-exposed plants significantly enhanced growth and tolerance to this element. Transfer factor (ratio of Cs concentration in the plant tissues to that in surrounding soil) was strongly influenced by Cs distribution, with higher values in the top-Cs treatment. Within this treatment, inoculation of Komatsuna with Bacillus and Azospirillum strains resulted in the greatest transfer factors of 6.55 and 6.68, respectively. Cesium content in the shoots was high in the Azospirillum-inoculated Komatsuna, Amaranth, and buckwheat, i.e., 1,830, 1,220, and 1,030 µg per pot, respectively (five plants were grown in each pot). Therefore, inoculation of Komatsuna and Amaranth with the strains tested here could be effective in enhancing Cs accumulation. The decrease of Cs transfer under uniform- and bottom-Cs treatments would suggest that countermeasures aiming at decreasing the transfer of Cs could rely on ploughing practices.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askbrant S, Melin J, Sandalls J, Rauret G, Vallejo R, Hinton T, Cremers A, Vandecastelle C, Lewyckyj N, Ivanov YA, Firsakova SK, Arkhipov NP, Alexakhin RM (1996) Mobility of radionuclides in undisturbed and cultivated soils in Ukraine, Belarus and Russia six years after the Chernobyl fallout. J Environ Radioact 31:287–312. doi:10.1016/0265-931X(95)00054-E
Berreck M, Haselwandter K (2001) Effect of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis upon uptake of cesium and other cations by plants. Mycorrhiza 10:275–280
Borghei M, Arjmandi R, Moogouei R (2011) Potential of Calendula alata for phytoremediation of stable cesium and lead from solutions. Environ Monit Assess 181:63–68. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1813-9
Broadley MR, Willey NJ, Mead A (1999) A method to assess taxonomic variation in shoot caesium concentration among flowering plants. Environ Pollut 106:341–349. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00105-0
Camps M, Rigol A, Hillier S, Vidal M, Rauret G (2004) Quantitative assessment of the effects of agricultural practices designed to reduce 137Cs and 90Sr soil-plant transfer in meadows. Sci Total Environ 332:23–38. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.04.008
Chiang PN, Wang MK, Wang JJ, Chiu CY (2005) Low-molecular-weight organic acid exudation of rape (Brassica campestris) roots in cesium-contaminated soils. Soil Sci 170:726–733
Cook LL, Inouye RS, McGonigle TP, White GJ (2007) The distribution of stable cesium in soils and plants of the eastern Snake River Plain in southern Idaho. J Arid Environ 69:40–64. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2006.08.014
Cook LL, Inouye RS, McGonigle TP (2009) Evaluation of four grasses for use in phytoremediation of Cs-contaminated arid land soil. Plant Soil 324:169–184. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-9942-z
De Boulois H, Voets L, Delvaux B, Jakobsen I, Declerck S (2006) Transport of radiocaesium by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to Medicago truncatula under in vitro conditions. Environ Microbiol 8:1926–1934
De Micco V, Arena C, Pignalosa D, Durante M (2011) Effects of sparsely and densely ionizing radiation on plants. Radiat Environ Biophys 50:1–19. doi:10.1007/s00411-010-0343-8
Dushenkov S (2003) Trends in phytoremediation of radionuclides. Plant Soil 249:167–175. doi:10.1023/A:1022527207359
Entry JA, Watrud LS, Reeves M (1999) Accumulation of 137Cs and 90Sr from contaminated soil by three grass species inoculated with mycorrhizal fungi. Environ Pollut 104:449–457
Fuhrmann M, Lasat MM, Ebbs SD, Kochian LV, Cornish J (2002) Uptake of cesium-137 and strontium-90 from contaminated soil by three plant species; application to phytoremediation. J Environ Qual 31:904–909
Fuhrmann M, Lasat M, Ebbs S, Cornish J, Kochian L (2003) Uptake and release of cesium-137 by five plant species as influenced by soil amendments in field experiments. J Environ Qual 32:2272–2279
Gaspar L, Navas A (2013) Vertical and lateral distributions of 137Cs in cultivated and uncultivated soils on Mediterranean hillslopes. Geoderma 207–208:131–143. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.04.034
Glick BR (2003) Phytoremediation: synergistic use of plants and bacteria to clean up the environment. Biotechnol Adv 21:383–393. doi:10.1016/S0734-9750(03)00055-7
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28:367–374. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.02.001
Jones HE, West HM, Chamberlain PM, Parekh NR, Beresford NA, Crout NM (2004) Effects of gamma irradiation on Holcus lanatus (Yorkshire fog grass) and associated soil microorganisms. J Environ Radioact 74:57–71. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2004.01.027
Kang DJ, Seo YJ, Saito T, Suzuki H, Ishii Y (2012) Uptake and translocation of cesium-133 in napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum.) under hydroponic conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:122–126. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.05.017
Kim JH, Back MH, Chuang BY, Wi SG, Kim JS (2004) Alterations in photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant machineries of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) seedlings from gamma-irradiated seeds. J Plant Biol 74:314–321
Kobatashi D, Okouchi T, Yamagami M, Shinano T (2014) Verification of radiocesium decontamination from farmlands by plants in Fukushima. J Plant Res 127:51–56. doi:10.1007/s10265-013-0607-x
Kumar DP, Chaturvedi A, Sreedhar M, Aparna M, Venu-babu P, Singhal RK (2013) Impact of gamma radiation on plant height and pollen fertility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian J Exp Biol Sci 4:129–133
Kuwahara C, Fukumoto A, Ohsone A, Furuya N, Shibata H, Sugiyama H, Kato F (2005) Accumulation of radiocesium in wild mushrooms collected from a Japanese forest and cesium uptake by microorganisms isolated from the mushroom-growing soils. Sci Total Environ 345:165–173. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.10.022
Kuwahara C, Fukumoto A, Nishina M, Sugiyama H, Anzai Y, Kato F (2011) Characteristics of cesium accumulation in the filamentous soil bacterium Streptomyces sp. K202. J Environ Radioact 102:138–144. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.11.004
Le Lay P, Isaure MP, Sarry JE, Kuhn L, Fayard B, Le Bail JL, Bastien O, Garin J, Roby C, Bourguignon J (2006) Metabolomic, proteomic, and biophysical analyses of Arabidopsis thaliana cells exposed to a caesium stress. Influence of potassium supply. Biochimie 88:1533–1547. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2006.03.013
Leung HM, Wang ZW, Ye ZH, Yung KL, Peng XL, Cheung KC (2013) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizae and plants in phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils: a Review. Pedosphere 23:549–563
McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2003) Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:277–282. doi:10.1016/S0958-1669(03)00060-0
Meunchang S, Panichsakpatana S, Ando S, Yokoyama T (2004) Phylogenetic and physiological characterization of indigenous Azospirillum isolates in Thailand. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50:413–421
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) of Japan (2013) http://www.maff.go.jp/mobile/kinkyu/tohoku_saigai/08/2011/1109/110914/110914_gijutu_betu01.html and http://www.s.affrc.go.jp/docs/press/pdf/110914-09.pdf, In Japanese
Ohno T, Muramatsu Y, Miura Y, Oda K, Inagawa N, Ogawa H, Yamazaki A, Toyama C, Sato M (2012) Depth profiles of radioactive cesium and iodine released from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant in different agricultural fields and forests. Geochem J 46:287–295
Pinheiro JC, Marques CR, Pinto G, Bouguerra S, Mendo S, Gomes NC, Gonçalves F, Rocha-Santos T, Duarte AC, Roembke J, Sousa JP, Ksibi M, Haddioui A, Pereira R (2013) The performance of Fraxinus angustifolia as a helper for metal phytoremediation programs and its relation to the endophytic bacterial communities. Geoderma 202–203:171–182. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.03.014
Rogers RD, Williams SE (1986) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza: influence on plant uptake of cesium and cobalt. Soil Biol Biochem 18:371–376. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(86)90040-4
Smolders E, Tsukada H (2011) The transfer of radiocesium from soil to plants: mechanisms, data, and perspectives for potential countermeasures in Japan. Integr Environ Assess Manag 7:379–381
Soudek P, Valenova S, Vavrikova Z, Vanek T (2006) 137Cs and 90Sr uptake by sunflower cultivated under hydroponic conditions. J Environ Radioact 88:236–250
Tang S, Liao S, Guo J, Song Z, Wang R, Zhou X (2011) Growth and cesium uptake responses of Phytolacca americana Linn. and Amaranthus cruentus L. grown on cesium contaminated soil to elevated CO2 or inoculation with a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp. D54, or in combination. J Hazard Mater 198:188–197. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.029
Tomioka N, Uchiyama H, Yagi O (1992) Isolation and characterization of cesium accumulating bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1019–1023
Tsukada H, Hasegawa H, Hisamatsu S, Yamasaki S (2002) Transfer of 137Cs and stable Cs from paddy soil to polished rice in Aomori Japan. J Environ Radioact 59:351–363. doi:10.1016/S0265-931X(01)00083-2
Varskog P, Naeumann R, Steinnes E (1994) Mobility and plant availability of radioactive Cs in natural soil in relation to stable Cs, other alkali elements and soil fertility. J Environ Radioact 22:43–53
Vinichuk M, Mårtensson A, Ericsson T, Rosén K (2013) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi on 137Cs uptake by plants grown on different soils. J Environ Radioact 115:151–156. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2012.08.004
Wang D, Wen F, Xu C, Tang Y, Luo X (2012) The uptake of Cs and Sr from soil to radish (Raphanus sativus L.)-potential for phytoextraction and remediation of contaminated soils. J Environ Radioact 110:78–83. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2012.01.028
Wensling LA, Harsh JB, Ward TE, Palmer CD, Hamilton MA, Boyle JS, Flury M (2005) Cesium desorption from illite as affected by exudates from rhizosphere bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 39:4505–4512
White PJ, Broadley MR (2000) Mechanisms of caesium uptake by plants. New Phytol 147:241–256. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00704.x
Willey NJ, Martin MH (1995) Annual patterns of Cs-133 concentration in British upland vegetation. Chemosphere 30:717–724. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(94)00437-Y
Willey NJ, Tang S, Watt NR (2005) Predicting inter-taxa differences in plant uptake of cesium-134/137. J Environ Qual 34:1478–1489. doi:10.2134/jeq2004.0454
Wu HB, Tang SR, Zhang XM, Guo JK, Song ZG, Tian S, Smith DL (2009) Using elevated CO2 to increase the biomass of Sorghum vulgare × Sorghum vulgare var. sudanense hybrid and Trifolium pratense L. and to trigger hyperaccumulation of cesium. J Hazard Mater 170:861–870. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.069
Yamaguchi N, Eguchi S, Fujiwara H, Hayashi K, Tsukada H (2012) Radiocesium and radioiodine in soil particles agitated by agricultural particles: field observation after the Fukushima nuclear accident. Sci Total Environ 425:128–134. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.037
Yoshida S, Muramatsu Y, Dvornik AM, Zhuchenko TA, Linkov I (2004) Equilibrium of radiocesium with stable cesium within the biological cycle of contaminated forest ecosystems. J Environ Radioact 75:301–313. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2003.12.008
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Special Research Fund of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan titled “Research and development of security and safe crop production to reconstruct agricultural lands in Fukushima prefecture based on novel techniques to remove radioactive compounds using advanced bio-fertilizer and plant protection strategies”. This work was also supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B):24380176 from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS). The authors are also grateful for Dr. Haruo Tanaka from soil science laboratory at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology for providing soil analysis data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djedidi, S., Kojima, K., Yamaya, H. et al. Stable cesium uptake and accumulation capacities of five plant species as influenced by bacterial inoculation and cesium distribution in the soil. J Plant Res 127, 585–597 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-014-0647-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-014-0647-x