Abstract
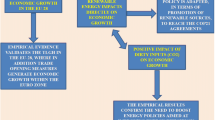
Due to urbanization and the need for people to go from one country to another either for commercial purpose or tourism, it is therefore important to determine the extent to which tourism contributes to growth. This article aims to investigate the tourism-led growth hypothesis in a sample of 34 European countries utilizing the yearly data from 1995 to 2015. The research work makes use of 8 tourism indicators, which cover different dimensions of tourism sector development such as foreign visitors' spending, and international tourist arrival. For empirical analysis, the study accounts key determinants of growth such as capital, labor and energy (renewable and non-renewable) consumption. The results from common correlated effects (CCE) augmented mean group (AMG) and groped-mean estimators confirms that there is a positive relationship between tourism, labour, capital and GDP insinuating the presence of tourism-led growth hypothesis in the European countries. Also, findings from the FMOLS show that changes in the variables leads to a proportional change in GDP. Specifically, the evidence shows that the tourism indicators play an indispensable role in promoting economic development, along with energy consumption, capital, and labor. Sustainable Combating environmental issues associated with foreign arrivals, renewable energy consumption should be encouraged to reduce environmental externalities to ensure sustainable environments for businesses and tourists’ arrivals.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Economic growth and income level might be improved through the reallocation of resources from the least efficient domestic sectors of the economy towards the tourism sector.
The total final energy consumption includes energy from renewable and non-renewable sources and data is available at Sustainable energy for all. https://databank.worldbank.org/source/sustainable-energy-for-all.
References
Adedoyin FF, Bekun FV (2020) Modelling the interaction between tourism, energy consumption, pollutant emissions and urbanization: renewed evidence from panel VAR. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09869-9
Adedoyin FF, Nathaniel S, Adeleye N (2020a) An investigation into the anthropogenic nexus among consumption of energy, tourism, and economic growth: do economic policy uncertainties matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13
Adedoyin FF, Bekun FV, Driha OM, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2020b) The effects of air transportation, energy, ICT and FDI on economic growth in the industry 4.0 era: Evidence from the United States. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 160(August):120297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120297
Andereck KL, Valentine KM, Knopf RC, Vogt CA (2005) Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. AnnTour Res 32(4):1056–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2005.03.001
Antonakakis N, Dragouni M, Filis G (2015) Tourism and growth: The times they are a-changing. Ann Tour Res 50:165–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2014.11.008
Aratuo DN, Etienne XL (2019) Industry level analysis of tourism-economic growth in the United States. Tour Manage 70(September 2018), 333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.09.004
Aslan A (2016) Current Issues in Tourism Does tourism cause growth? Evidence from Turkey 3500. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2015.1015970
Balaguer J, Cantavella-Jordá M (2002) Tourism as a long-run economic growth factor: The Spanish case. Appl Econ 34(7):877–884. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036840110058923
Balli E, Sigeze C, Manga M, Birdir S, Birdir K (2019) The relationship between tourism, CO 2 emissions and economic growth: a case of Mediterranean countries. Asia Pac J Tourism Res 24(3):219–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2018.1557717
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Adedoyin FF (2020) The asymmetric impact of air transport on economic growth in Spain: fresh evidence from the tourism-led growth hypothesis. Curr Issue Tour 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2020.1720624
Bassil C, Hamadeh M, Samara N (2015) The tourism led growth hypothesis: the Lebanese case. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-05-2014-0022
Bhorat H, Cassim A, Tseng D (2016) Higher education, employment and economic growth: Exploring the interactions. Dev South Afr 33(3):312–327. https://doi.org/10.1080/0376835X.2016.1161501
Bourne R (2016) Why did the British Brexit? and What are the Implications for Classical Liberals? Econ Aff 36(3):356–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecaf.12205
Brida JG, Lanzilotta B, Pizzolon F (2016) Dynamic relationship between tourism and economic growth in MERCOSUR countries: A nonlinear approach based on asymmetric time series models. Econ Bull 36(2):879–894
Chiu FP, Kuo HI, Chen CC, Hsu CS (2015) The energy price equivalence of carbon taxes and emissions trading-Theory and evidence. Appl Energy 160:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.09.022
Chou MC (2013) Does tourism development promote economic growth in transition countries? A panel data analysis. Econ Model 33:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2013.04.024
Gengenbach C, Urbain JP, Westerlund J (2016) Error correction testing in panels with common stochastic trends. J Appl Econom 31(6):982–1004
Corbet S, O’Connell JF, Efthymiou M, Guiomard C, Lucey B (2019) The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Ann Tour Res 75(December 2018), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2018.12.012
Cui L, Li R, Song M, Zhu L (2019a) Can China achieve its 2030 energy development targets by fulfilling carbon intensity reduction commitments? Energy Econ 83(2019):61–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.06.016
Cui L, Sun Y, Melnikiene R, Song M, Mo J (2019b) Exploring the impacts of Sino–US trade disruptions with a multi-regional CGE model. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istrazivanja 32(1):4015–4032. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2019.1679211
Cui L, Sun Y, Song M, Zhu L (2020) Co-financing in the green climate fund: lessons from the global environment facility. Clim Pol 20(1):95–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/14693062.2019.1690968
Dogru T, Bulut U (2018) Is tourism an engine for economic recovery? Theory and empirical evidence. Tour Manag 67:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.06.014
Durbarry R (2004) Tourism and economic growth: the case of. Tour Econ 10(4):389–401
Eberhardt M, Teal F (2010) Productivity Analysis in Global Manufacturing Production
Fahimi A, Akadiri S, Saint, Seraj M, Akadiri AC (2018) Testing the role of tourism and human capital development in economic growth. A panel causality study of micro states. Tour Manag Perspect 28(August):62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2018.08.004
Fatima T, Shahzad U, Cui L (2020) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, trade and CO2 emissions in high emitter countries: does the income level matter? J Environ Plan Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2020.1816532
Fauzel S, Sannassee RV (2016) Growth: Evidence from a small island developing state Analyzing the impact of tourism foreign direct investment on economic growth: Evidence from a small island developing state, (August). https://doi.org/10.1177/1354816616664249
Gibson HD, Hall SG, Tavlas GS (2012) Journal of International Money The Greek financial crisis: Growing imbalances and sovereign spreads. J Int Money and Financ 31(3):498–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimonfin.2011.10.009
Gunter U, Ceddia MG, Tröster B (2018) Contribution of international ecotourism to comprehensive economic development and convergence in the Central American and Caribbean region. Appl Econ 00(00):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2018.1430339
Hatemi-J A (2011) ACTEST: AUSS module to apply asymmetric causality tests statistical software components G00014, Boston College Department of Economics.
Hatemi-J A, Ajmi AN, el Montasser G, Inglesi-Lotz R, Gupta R (2016) Research output and economic growth in G7 countries: new evidence from asymmetric panel causality testing. Appl Econ 48(24):2301–2308
Hatemi-J A, Gupta R, Kasongo A, Mboweni T, Netshitenzhe N (2018) Does tourism cause growth asymmetrically in a panel of G-7 countries? A short note Empirical 45(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10663-016-9345-3
Hsu MK, Zhang J, Ahmad Y (2017) Government digital information discovery and exploration: the case of unraveling tourism-led-growth paradox in China. Information Discovery and Delivery 45(4):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1108/IDD-10-2016-0036
Ivanov S, Webster C (2013) Tourism’s impact on growth: The Role of Globalization. Ann Tour Res 41:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2012.12.008
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for Error Correction in Panel Data. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics 69(6):709–748
Jones C, Li SN (2015) The economic importance of meetings and conferences: A satellite account approach. Ann Tour Res 52:117–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2015.03.004
Dolado JJ, Lütkepohl H (1996) Making wald tests work for cointegrated VAR systems. Econometric Reviews 15(4):369–386
Kožić I (2019) Can tourism development induce deterioration of human capital? Ann Tour Res 77(December 2018):168–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2018.12.018
Kristo J (2014) Evaluating the Tourism-Led Economic Growth Hypothesis in a Developing Country: The Case of Albania 5(8):39–51. https://doi.org/10.5901/mjss.2014.v5n8p39
Lanouar C, Goaied M (2019) Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tour Manag 70(September):404–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.09.002
Lee CC, Chang CP (2008) Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tour Manag 29(1):180–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2007.02.013
Li KX, Jin M, Shi W (2018) Tourism as an important impetus to promoting economic growth: A critical review. Tour Manag Perspect 26(April 2016):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.10.002
Liu A, Wu DC (2019) Tourism productivity and economic growth. Ann Tour Res 76(April):253–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2019.04.005
Liu A, Wu DC, Pablo-Romero MDP, Molina JA, Tang CF, Tan EC, Lin D (2015) How strong is the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe? Ann Tour Res 61(1):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2013.05.006
Matarrita-Cascante D (2010) Beyond growth. Reaching tourism-led development. Ann Tour Res 37(4):1141–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2010.05.004
Merida A, Golpe AA (2016) The Formation of the Tourist’s Loyalty How Does It Affect Price Discounts? Int J Tour Res 9(August):453–464. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr
Mitra SK (2019) Is tourism-led growth hypothesis still valid? Int J Tou Res (September 2018):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.2285
Ohlan R (2017) The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Business Journal 3(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbj.2017.01.003
Ongan S (2016) The Contribution of Tourism to the Long-run Turkish Economic Growth The Contribution of Tourism to the Long-Run Turkish Economic Growth Assistant Professor Dr . Serdar Ongan Department of Economics Department of Economics, (January 2005).
Pablo-Romero MDP, Molina JA (2013) Tourism and economic growth: A review of empirical literature. Tour Manag Perspect 8:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2013.05.006
Perles-Ribes JF, Ramón-Rodríguez AB, Rubia A, Moreno-Izquierdo L (2017) Is the tourism-led growth hypothesis valid after the global economic and financial crisis? The case of Spain 1957–2014. Tour Manag 61:96–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.01.003
Pesaran MH (2004) General Diagnostic Tests for Cross Section Dependence in Panels. University of Cambridge, Working paper.
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22:265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae
Pipike JK (2012) Comparative Study between Fiji and Papua New Guinea Tourism Development: Lessons to Learn from Fiji. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 65:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.11.110
Severn AK (1968) Exports and Economic Growth. Kyklos 21(3):546–548. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6435.1968.tb00132.x
Simon F (2019) Energy consumption continues to rise in Europe: Eurostat. [Online] Available at: https://www.euractiv.com/section/energy/news/energy-consumption-continues-to-rise-in-europeeurostat/#targetText=Energy%20consumption%20in%20the%20EU,the%20previous%20year%2C%20Eurostat%20said. [Accessed 29 September 2019].
Shahbaz M, Sarwar S, Chen W, Malik MN (2017) Dynamics of electricity consumption, oil price and economic growth: Global perspective. Energy Policy 108(May):256–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.06.006
Shahzad SJH, Shahbaz M, Ferrer R, Kumar RR (2017) Tourism-led growth hypothesis in the top ten tourist destinations: New evidence using the quantile-on-quantile approach. Tour Manag 60:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.12.006
Shahzad U, Ferraz D, Doğan B, Aparecida do Nascimento Rebelatto, D. (2020) Export Product Diversification and CO2 Emissions: Contextual evidences from Developing and Developed Economies. J Cleaner Prod 276:124146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124146
Shahzad U, Hussain M, Qin F, Muhamadi S (2019) Role of FDI and Foreign Remittances in Boosting and Economic Growth: Evidence from Brazil. European Online Journal of Natural and Social Sciences 8(1):118–127
Shahzad U, Lv Y, Dogan B, Xia W (2021) Unveiling the heterogeneous impacts of export product diversi fi cation on renewable energy consumption: New evidence from G-7 and E-7 countries. Renewable Energy Journal 164:1457–1470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.10.143
Smith H (2016) A year after the crisis was declared over, Greece is still spiraling down. [Online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/aug/13/greek-economy-still-spiralling-down-year-after-crisis-declared-over [Accessed 29 August 2019]
Solarin SA (2014) Current Issues in Tourism Global financial crisis and stationarity of tourist arrivals: evidence from Mauritius, (July 2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2014.985639
Tang CF, Ozturk I (2017) Is tourism a catalyst of growth in Egypt? Evidence from Granger non-causality and the generalized variance decomposition analysis. Anatolia 2917(May):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2017.1283635
Tang CF, Tan EC (2013) How stable is the tourism-led growth hypothesis in Malaysia? Evidence from disaggregated tourism markets. Tour Manag 37:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2012.12.014
Tang CF, Tan EC (2015) Does tourism effectively stimulate Malaysia’s economic growth? Tour Manag 46(2015):158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2014.06.020
Tang CF, Tiwari AK, Shahbaz M (2016) Dynamic inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India. Geosystem Eng 9328:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/12269328.2016.1162113
Toda HY, Yamamoto T (1995) Statistical inference in vector autoregressions with possibly integrated processes. J Econom 66(1–2):225–250
Trang M (2015) Research note: Empirical assessment of the tourism-led growth hypothesis – the case of, (August 2014). https://doi.org/10.5367/te.2013.0307
UNWTO (2018) UNWTO Tourism Highlights. International Tourism Trends 2017. United Nations World Tourism Organization, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284419876
UNWTO (2019) International Tourist Arrivals Reach 1.4 billion Two Years Ahead of Forecasts. [Online] Available at: http://www2.unwto.org/press-release/2019-01-21/international-tourist-arrivals-reach-14-billion-two-years-ahead-forecasts [Accessed 30 August 2019].
World Development Bank (2020) World Development Indicators. [Online] Available at: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?source=world-development-indicators# [Accessed 15 July 2019].
WTTS (2011) Annual Reports, Progress and Priorities 2011. [Online] Available at: https://www.wttc.org/economic-impact/country-analysis/country-reports [Accessed 29 August 2019].
Yang Y, Fik T (2014) Spatial effects in regional tourism growth. Ann Tour Res 46:144–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2014.03.007
Yu-chi S, Lin H (2018) Causality Relationship Between Tourism, Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Taiwan. Asian J Econ Model 6(3):287–293. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.8.2018.63.287.293
Funding
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, W., Doğan, B., Shahzad, U. et al. An empirical investigation of tourism-led growth hypothesis in the European countries: evidence from augmented mean group estimator. Port Econ J 21, 239–266 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10258-021-00193-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10258-021-00193-9