Abstract
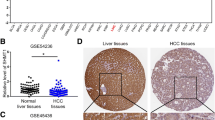
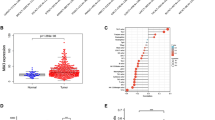
The poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients is mainly due to cancer metastasis. Methionine adenosyltransferase 2β (MAT2B) encodes a regulatory subunit (β) for methionine adenosyltransferase. Previous studies reveal that MAT2B provides a growth advantage for HCC, but its role in metastasis is unknown. This study showed that both in the xenograft zebra fish model and in the lung metastasis model in nude mice, the stable inhibition of MAT2B could suppress the metastasis of HCC cancer cells. Silencing of MAT2B in HCC cell lines could remarkably inhibit migration and invasion. By analysis of human phospho-kinase array membranes, we found several differentially expressed proteins, including phosphor-AKT, phospho-EGFR, phospho-Src family, phospho-FAK, phospho-STAT3 and phospho-ERK. We further confirmed the change of these EGFR pathway-related proteins was in accordance with MAT2B expression pattern through immunoblotting test. Finally, we found that MAT2B was overexpressed in HCC caner tissues and correlated with poor prognosis for HCC patients in clinical manifestation. Our study demonstrated that silencing of MAT2B could suppress liver cancer cell migration and invasion through the inhibition of EGFR signaling, which suggested that MAT2B might serve as a new prognostic marker and therapeutic target for HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86.
Llovet JM, Bruix J. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;48:1312–27.
Feo F, Pascale RM, Simile MM, De Miglio MR, Muroni MR, Calvisi D. Genetic alterations in liver carcinogenesis: implications for new preventive and therapeutic strategies. Crit Rev Oncog. 2000;11:19–62.
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M, Cléries R. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5–16.
Lu SC, Mato JM. S-Adenosylmethionine in cell growth, apoptosis and liver cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23(Suppl 1):S73–7.
Halim AB, LeGros L, Geller A, Kotb M. Expression and functional interaction of the catalytic and regulatory subunits of human methionine adenosyltransferase in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:29720–5.
Lu SC, Mato JM. S-adenosylmethionine in liver health, injury, and cancer. Physiol Rev. 2012;92:1515–42.
Yang H, Cho ME, Li TWH, Peng H, Ko KS, Mato JM, et al. MicroRNAs regulate methionine adenosyltransferase 1A expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Investig. 2013;123:285–98.
Ramani K, Mato JM, Lu SC. Role of methionine adenosyltransferase genes in hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel). 2011;3:1480–97.
Kotb M, Mudd SH, Mato JM, Geller AM, Kredich NM, Chou JY, et al. Consensus nomenclature for the mammalian methionine adenosyltransferase genes and gene products. Trends Genet. 1997;13:51–2.
Halim AB, LeGros L, Chamberlin ME, Geller A, Kotb M. Regulation of the human MAT2A gene encoding the catalytic alpha 2 subunit of methionine adenosyltransferase, MAT II: gene organization, promoter characterization, and identification of a site in the proximal promoter that is essential for its activity. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:9784–91.
LeGros L, Halim AB, Chamberlin ME, Geller A, Kotb M. Regulation of the human MAT2B gene encoding the regulatory beta subunit of methionine adenosyltransferase. MAT II. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:24918–24.
Wang Q, Liu Q, Liu Z-S, Qian Q, Sun Q, Pan D. Inhibition of hepatocelluar carcinoma MAT2A and MAT2beta gene expressions by single and dual small interfering RNA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2008;27:72.
Zhang T, Zheng Z, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Liu Y, et al. Overexpression of methionine adenosyltransferase II alpha (MAT2A) in gastric cancer and induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells by shRNA-mediated silencing of MAT2A gene. Acta Histochem. 2013;115:48–55.
Liu Q, Wu K, Zhu Y, He Y, Wu J, Liu Z. Silencing MAT2A gene by RNA interference inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Hepatol Res. 2007;37:376–88.
Ramani K, Yang H, Kuhlenkamp J, Tomasi L, Tsukamoto H, Mato JM, et al. Changes in the expression of methionine adenosyltransferase genes and S-adenosylmethionine homeostasis during hepatic stellate cell activation. Hepatology. 2010;51:986–95.
Martínez-Chantar ML, García-Trevijano ER, Latasa MU, Martín-Duce A, Fortes P, Caballería J, et al. Methionine adenosyltransferase II beta subunit gene expression provides a proliferative advantage in human hepatoma. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:940–8.
Yang H, Ara AI, Magilnick N, Xia M, Ramani K, Chen H, et al. Expression pattern, regulation, and functions of methionine adenosyltransferase 2beta splicing variants in hepatoma cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:281–91.
Ramani K, Yang H, Xia M, Ara AI, Mato JM, Lu SC. Leptin’s mitogenic effect in human liver cancer cells requires induction of both methionine adenosyltransferase 2A and 2beta. Hepatology. 2008;47:521–31.
Mikol YB, Hoover KL, Creasia D, Poirier LA. Hepatocarcinogenesis in rats fed methyl-deficient, amino acid-defined diets. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4:1619–29.
Ghoshal AK, Farber E. The induction of liver cancer by dietary deficiency of choline and methionine without added carcinogens. Carcinogenesis. 1984;5:1367–70.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76.
Perry JF, Poustchi H, George J, Farrell GC, McCaughan GW, Strasser SI. Current approaches to the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Med. 2005;5:1–13.
Mazzoccoli G, Tarquini R, Valoriani A, Oben J, Vinciguerra M, Marra F. Management strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma: old certainties and new realities. Clin Exp Med. 2016;16:243–56.
Nordenstedt H, White DL, El-Serag HB. The changing pattern of epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42(Suppl 3):S206–14.
Wu F, Yang L-Y, Li Y-F, Ou D-P, Chen D-P, Fan C. Novel role for epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 in metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2009;50:1839–50.
Ye Q-H, Qin L-X, Forgues M, He P, Kim JW, Peng AC, et al. Predicting hepatitis B virus-positive metastatic hepatocellular carcinomas using gene expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med. 2003;9:416–23.
Luedde T. MicroRNA-151 and its hosting gene FAK (focal adhesion kinase) regulate tumor cell migration and spreading of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010;52:1164–6.
Yang F, Yin Y, Wang F, Wang Y, Zhang L, Tang Y, et al. miR-17-5p Promotes migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-heat shock protein 27 pathway. Hepatology. 2010;51:1614–23.
Zandi R, Larsen AB, Andersen P, Stockhausen M-T, Poulsen HS. Mechanisms for oncogenic activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell Signal. 2007;19:2013–23.
Berasain C, Castillo J, Prieto J, Avila MA. New molecular targets for hepatocellular carcinoma: the ErbB1 signaling system. Liver Int. 2007;27:174–85.
Breuhahn K, Longerich T, Schirmacher P. Dysregulation of growth factor signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25:3787–800.
Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:505–16.
Kira S, Nakanishi T, Suemori S, Kitamoto M, Watanabe Y, Kajiyama G. Expression of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver. 1997;17:177–82.
Daveau M, Scotte M, François A, Coulouarn C, Ros G, Tallet Y, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and their receptors as combined markers of prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2003;36:130–41.
Liebmann C. EGF receptor activation by GPCRs: an universal pathway reveals different versions. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;331:222–31.
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TPJ, Ward CW, Burgess AW. Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:31–53.
Peng H, Dara L, Li TWH, Zheng Y, Yang H, Tomasi ML, et al. MAT2B-GIT1 interplay activates MEK1/ERK 1 and 2 to induce growth in human liver and colon cancer. Hepatology. 2013;57:2299–313.
Funding
This work was supported by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China ‘(81401980)’ (to Lijun Wu) and the Development Fund for Shanghai Talents ‘(201660)’ (to Dongqin Yang) and the Natural Science Foundation and Major Basic Research Program of Shanghai ‘(16JC1420104)’ (to Jie Liu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lijun Wu was responsible for manuscript preparation and contributed to study design and experiment process. Ping Chen contributed to the data analysis and experiment process. Dongqin Yang contributed to study design. All co-authors contributed to the data interpretation and manuscript revision. All authors approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Chen, P., Ying, J. et al. MAT2B mediates invasion and metastasis by regulating EGFR signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Med 19, 535–546 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-019-00579-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-019-00579-2