Abstract
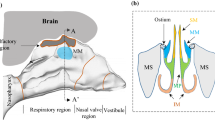
The present study aims to investigate the effect of swirling flow on particle deposition in a realistic human airway. A computational fluid dynamic (CFD) model was utilized for the simulation of oral inhalation and particle transport patterns, considering the k-ω turbulence model. Lagrangian particle tracking was used to track the particles’ trajectories. A normal breathing condition (30 L/min) was applied, and two-micron particles were injected into the mouth, considering swirling flow to the oral inhalation airflow. Different cases were considered for releasing the particles, which evaluated the impacts of various parameters on the deposition efficiency (DE), including the swirl intensity, injection location and pattern of the particle. The work's novelty is applying several injection locations and diameters simultaneously. The results show that the swirling flow enhances the particle deposition efficiency (20–40%) versus no-swirl flow, especially in the mouth. However, releasing particles inside the mouth, or injecting them randomly with a smaller injection diameter (dinj) reduced DE in swirling flow condition, about 50 to 80%. Injecting particles inside the mouth can decrease DE by about 20%, and releasing particles with smaller dinj leads to 50% less DE in swirling flow. In conclusion, it is indicated that the airflow condition is an important parameter for a reliable drug delivery, and it is more beneficial to keep the inflow uniform and avoid swirling flow.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- d p :
-
Particle diameter (m)
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg/m s)
- d inj :
-
Injection diameter (m)
- ρ f :
-
Fluid density (kg/m3)
- f :
-
Drag coefficient
- ρ p :
-
Particle density (kg/m3)
- F D :
-
Drag force (N)
- τ ij :
-
Reynolds stress tensor
- m p :
-
Particle mass (kg)
- τ p :
-
Particle relaxation (response) time (s)
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- υ f :
-
Kinetic molecular viscosity (µf/ρf)
- R 0 :
-
Inlet radius (m)
- υ t :
-
Kinetic eddy viscosity (µf/ρf)
- SN:
-
Swirl number
- t :
-
Time (s)
- V a :
-
Axial velocity (m/s)
- V f :
-
Fluid velocity (m/s)
- V f :
-
Fluid volume (m3)
- V p :
-
Particle volume (m3
- DE:
-
Deposition efficiency
- V p :
-
Particle velocity (m/s)
- DPM:
-
Discrete phase model
- V t :
-
Tangential velocity (m/s)
- EsE:
-
Escaped efficiency
- TDD:
-
Targeted drug delivery
References
Ahookhosh K, Pourmehran O, Aminfar H, Mohammadpourfard M, Sarafraz MM, Hamishehkar H (2020a) Development of human respiratory airway models: a review. Eur J Pharm Sci 145:105233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105233
Ahookhosh K, Saidi M, Aminfar H, Mohammadpourfard M, Hamishehkar H, Yaqoubi S (2020b) Dry powder inhaler aerosol deposition in a model of tracheobronchial airways: validating CFD predictions with in vitro data. Int J Pharm 587:119599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119599
Ahookhosh K, Saidi M, Mohammadpourfard M, Aminfar H, Hamishehkar H, Farnoud A, Schmid O (2021) Flow structure and particle deposition analyses for optimization of a pressurized metered dose inhaler (pMDI) in a model of tracheobronchial airway. Euro J Pharm Sci 164:105911
Ahookhosh K, Yaqoubi S, Mohammadpourfard M, Hamishehkar H, Aminfar H (2019) Experimental investigation of aerosol deposition through a realistic respiratory airway replica: an evaluation for MDI and DPI performance. Int J Pharm 566:157–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.058
Arsalanloo A, Abbasalizadeh M (2017) Numerical study on deposition of particles in a 90° bend in the presence of swirling flow using Eulerian-Lagrangian method. Powder Technol 320:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.07.050
Chandel A, Goyal AK, Ghosh G, Rath G (2019) Recent advances in aerosolised drug delivery. Biomed Pharmacother 112:108601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108601
Childress E, Kleinstreuer C (2014) Computationally efficient particle release map determination for direct tumor-targeting in a representative hepatic artery system. J Biomech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1115/14025881
Elghobashi S (1991) Particle-laden turbulent flows: direct simulation and closure models Computational fluid dynamics for the petrochemical process industry. Springer, Berlin, pp 91–104
Fan Y, Dong J, Tian L, Inthavong K, Tu J (2020) Numerical and experimental analysis of inhalation airflow dynamics in a human pharyngeal airway. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5):1556
Farnoud A, Baumann I, Rashidi MM, Schmid O, Gutheil E (2020a) Simulation of patient-specific bi-directional pulsating nasal aerosol dispersion and deposition with clockwise 45° and 90° nosepieces. Comput Biol Med 123:103816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103816
Farnoud A, Cui X, Baumann I, Gutheil E (2017) Numerical simulation of the dispersion and deposition of a spray carried by a pulsating airflow in a patient-specific human nasal cavity. Atom Sprays 27(11):913–928. https://doi.org/10.1615/AtomizSpr.2017020782
Farnoud A, Tofighian H, Baumann I, Garcia GJM, Schmid O, Gutheil E, Rashidi MM (2020b) Large eddy simulations of airflow and particle deposition in pulsating bi-directional nasal drug delivery. Phys Fluids 32(10):101905. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0024264
Feng Y, Chen X, Yang M (2018) An In Silico Investigation of a Lobe-Specific Targeted Pulmonary Drug Delivery Method. Paper presented at the 2018 Design of Medical Devices Conference.
Finlay WH (2001) The mechanics of inhaled pharmaceutical aerosols an introduction. Academic press, USA
Frank-Ito DO, Wofford M, Schroeter JD, Kimbell JS (2016) Influence of mesh density on airflow and particle deposition in sinonasal airway modeling. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 29(1):46–56
Ghosh A, Islam MS, Saha SC (2020) Targeted drug delivery of magnetic nano-particle in the specific lung region. Computation 8(1):10
Goodarzi M, Tlili I, Moria H, Alkanhal TA, Ellahi R, Anqi AE, Safaei MR (2020) Boiling heat transfer characteristics of graphene oxide nanoplatelets nano-suspensions of water-perfluorohexane (C6F14) and water-n-pentane. Alex Eng J 59(6):4511–4521
Guo J, Chen Z, Shen B, Wang J, Yang L (2020) Numerical study on characteristics of particle deposition efficiency on different walls of 90° square bend. Powder Technol 364:572–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.01.059
Gurumurthy A, Kleinstreuer C (2021) Helical fluid-particle flow dynamics for controlling micron-particle deposition in a representative human upper lung-airway model. J Aerosol Sci 151:105656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2020.105656
Hreiz R, Gentric C, Midoux N (2011) Numerical investigation of swirling flow in cylindrical cyclones. Chem Eng Res Des 89(12):2521–2539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2011.05.001
Inthavong K, Choi L-T, Tu J, Ding S, Thien F (2010) Micron particle deposition in a tracheobronchial airway model under different breathing conditions. Med Eng Phys 32(10):1198–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.08.012
Inthavong K, Ma J, Shang Y, Dong J, Chetty ASR, Tu J, Frank-Ito D (2019) Geometry and airflow dynamics analysis in the nasal cavity during inhalation. Clin Biomech 66:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2017.10.006
Islam MS, Saha S, Sauret E, Gu Y, Ristovski Z (2015). Numerical investigation of aerosol particle transport and deposition in realistic lung airway. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computational Methods, Volume 2, 2015
Islam MS, Saha SC, Sauret E, Gemci T, Gu YT (2017) Pulmonary aerosol transport and deposition analysis in upper 17 generations of the human respiratory tract. J Aerosol Sci 108:29–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2017.03.004
Islam MS, Saha SC, Sauret E, Ong H, Young P, Gu Y (2019) Euler-Lagrange approach to investigate respiratory anatomical shape effects on aerosol particle transport and deposition. Toxicol Res Appl 3:2397847319894675. https://doi.org/10.1177/2397847319894675
Kannan RR, Przekwas A, Singh N, Delvadia R, Tian G, Walenga R (2017) Pharmaceutical aerosols deposition patterns from a Dry Powder Inhaler: Euler Lagrangian prediction and validation. Med Eng Phys 42:35–47
Kenjereš S, Tjin JL (2017) Numerical simulations of targeted delivery of magnetic drug aerosols in the human upper and central respiratory system: a validation study. Royal Soc Open Sci 4(12):170873
Kleinstreuer C, Zhang Z, Li Z (2008) Modeling airflow and particle transport/deposition in pulmonary airways. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 163(1–3):128–138
Koullapis PG, Stylianou FS, Sznitman J, Olsson B, Kassinos SC (2020) Towards whole-lung simulations of aerosol deposition: a model of the deep lung. J Aerosol Sci 144:105541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2020.105541
Longest PW, Bass K, Dutta R, Rani V, Thomas ML, El-Achwah A, Hindle M (2019a) Use of computational fluid dynamics deposition modeling in respiratory drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 16(1):7–26
Longest PW, Hindle M, Choudhuri SD, Xi J (2008) Comparison of ambient and spray aerosol deposition in a standard induction port and more realistic mouth–throat geometry. J Aerosol Sci 39(7):572–591
Longest PW, Holbrook LT (2012) In silico models of aerosol delivery to the respiratory tract—development and applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64(4):296–311
Longest W, Spence B, Hindle M (2019b) Devices for improved delivery of nebulized pharmaceutical aerosols to the lungs. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 32(5):317–339
Lueshen E, Venugopal I, Kanikunnel J, Soni T, Alaraj A, Linninger A (2014) Intrathecal magnetic drug targeting using gold-coated magnetite nanoparticles in a human spine model. Nanomedicine 9(8):1155–1169
Menter FR (1994) Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J 32(8):1598–1605. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12149
Mortazavy Beni H, Mortazavi H, Aghaei F, Kamalipour S (2021) Experimental tracking and numerical mapping of novel coronavirus micro-droplet deposition through nasal inhalation in the human respiratory system. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 20(3):1087–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-021-01434-8
Nazari S, Ellahi R, Sarafraz M, Safaei MR, Asgari A, Akbari OA (2020) Numerical study on mixed convection of a non-Newtonian nanofluid with porous media in a two lid-driven square cavity. J Therm Anal Calorim 140(3):1121–1145
Rahimi-Gorji M, Gorji TB, Gorji-Bandpy M (2016) Details of regional particle deposition and airflow structures in a realistic model of human tracheobronchial airways: two-phase flow simulation. Comput Biol Med 74:1–17
Saha S, Islam M, Rahimi-Gorji M, Molla M (2019) Aerosol particle transport and deposition in a CT-scan based mouth-throat model. Paper presented at the AIP conference proceedings
Sarafraz MM, Pourmehran O, Yang B, Arjomandi M, Ellahi R (2020) Pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of iron oxide nano-suspension under constant magnetic field. Int J Thermal Sci 147:106131
Sodagar H, Shakiba A, Niazmand H (2020) Numerical investigation of drug delivery by using magnetic field in a 90-degree bent vessel: a 3D simulation. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 19(6):2255–2269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-020-01337-0
Walters DK, Luke WH (2011) Computational fluid dynamics simulations of particle deposition in large-scale, multigenerational lung models. J Biomech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1115/14002936
Wilcox, D. C. (1998). Turbulence modeling for CFD (Vol. 2): DCW industries La Canada, CA.
Yousefi M, Inthavong K, Tu J (2015) Microparticle transport and deposition in the human oral airway: toward the smart spacer. Aerosol Sci Technol 49(11):1109–1120. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2015.1101052
Yousefi M, Inthavong K, Tu J (2017a) Effect of pressurized metered dose inhaler spray characteristics and particle size distribution on drug delivery efficiency. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 30(5):359–372. https://doi.org/10.1089/jamp.2016.1299
Yousefi M, Pourmehran O, Gorji-Bandpy M, Inthavong K, Yeo L, Tu J (2017b) CFD simulation of aerosol delivery to a human lung via surface acoustic wave nebulization. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 16(6):2035–2050
Zhang Z, Kleinstreuer C (2004) Airflow structures and nano-particle deposition in a human upper airway model. J Comput Phys 198(1):178–210
Funding
The authors received no financial support for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taheri, M.H., Pourmehran, O., Sarafraz, M.M. et al. Effect of swirling flow and particle-release pattern on drug delivery to human tracheobronchial airways. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 20, 2451–2469 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-021-01518-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-021-01518-5