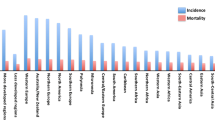
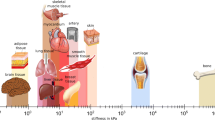
Abstract
This paper reviews the existing literature on the tests used to determine the mechanical properties of women breast tissues (fat, glandular and tumour tissue) as well as the different values of these properties. The knowledge of the mechanical properties of breast tissue is important for cancer detection, study and planning of surgical procedures such as surgical breast reconstruction using pre-surgical methods and improving the interpretation of clinical tests. Based on the data collected from the analysed studies, some important conclusions were achieved: (1) the Young’s modulus of breast tissues is highly dependent on the tissue preload compression level, and (2) the results of these studies clearly indicate a wide variation in moduli not only among different types of tissue but also within each type of tissue. These differences were most evident in normal fat and fibroglandular tissues.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah N, El-khoury M, Kao E (2009) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Lexicon for US: Interobserver Agreement for assessment of breast masses. Radiology 252:665–672. doi:10.1148/radiol.2523080670
Azar FS, Metaxas DN, Schnall MD (2002) Methods for modeling and predicting mechanical deformations of the breast under external perturbations. Med Image Anal 6:1–27. doi:10.1016/S1361-8415(01)00053-6
Azar FS, Metaxas DN, Schnall MD (2001) A deformable finite element model of the breast for predicting mechanical deformations under. Acad Radiol 10:965–975. doi:10.1016/S1076-6332(03)80640-2
Bamber JC, Barbone PE, Bush NL, Cosgrove DO, Doyely MM, Fuechsel FG, Meaney PM, Miller NR, Shiina T, Tranquart F (2002) Progress in freehand elastography of the breast. IEICE Trans Inf Syst 85(1):5–14
Bakic P (2000) Breast tissue description and modeling in mammography. Dissertation, Leigh University, PA, USA
Barr RG, Zhang Z (2012) Effects of precompression on elasticity imaging of the breast: development of a clinically useful semiquantitative method of precompression assessment. J. Ultrasound Med 31:895–902
Bogonoletz W (1986) Elastosis in breast cancer. Pathol Annu, 21(2):347–366. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(197401)33:1<174::AID-CNCR2820330126>3.0.CO;2-X
Buckley A, Hill K, Davidson J (1988) Collagen metabolism. Methods Enzymol 163:674–694
Buijs J, Hansen H, Lopata R, Corte C, Misra S (2011) Predicting target displacements using ultrasound elastography and finite element modeling. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(11):3143–3155. doi:10.1109/TBME.2011.2164917
Burnside E, Hall T, Sommer A, Hesley G, Sisney G, Svensson W, Fine J, Jiang J, Hangiandreou N (2007) Differentiating benign from malignant solid breast masses with US strain imaging. Radiology 245:401–410. doi:10.1148/radiol.2452061805
Butcher DT, Alliston T, Weaver VM (2009) A tense situation: forcing tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 9(2):108–122. doi:10.1038/nrc2544
Carter T, Sermesant M, Cash D, Barratt D, Tanner C, Hawkes D (2005) Application of soft tissue modeling to image-guided surgery. Med Eng Phys 27:893–909. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2005.10.005
Cespedes I, Ophir J, Ponnekanti H, Maklad N (1993) Elastography: elasticity imaging using ultrasound with application to muscle and breast in vivo. Ultrason Imaging 15:73–88. doi:10.1177/016173469301500201
Cheng HD, Shan J, Ju W, Guo Y, Zhang L (2010) Automated breast cancer detection and classification using ultrasound images: a survey. Pattern Recognit 43:299–317. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2009.05.012
Cheng J, Brandt KR, Ghosh K, Grimm RC, Glaser KJ, Kugel JL, et al. (2013) Non compressive MR elastography of breasts. Proceedings of the international society for magnetic resonance in medicine. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Salt Lake City, USA
Cox TR, Erler JT (2011) Remodeling and homeostasis of the extracellular matrix: implications for fibrotic diseases and cancer. Dis Model Mech 4:165–178. doi:10.1242/dmm.004077
Doyley MM, Bamber JC, Fuechsel F, Bush NL (2001) A freehand elastographic imaging approach for clinical breast imaging: system development and performance evaluation. Ultrasound Med Biol 27:1347–1357. doi:10.1016/S0301-5629(01)00429-X
Doyley MM (2013) Model-based elastography: a survey of approaches to the inverse elasticity problem. Phys Med Biol 57(3):R35–R73. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/57/3/R35
Fung YC (1993) Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues. Springer, New York
Garra B, Cespedes E, Ophir J, Spratt S, Zuurbier R, Magnant C, Pennanen M (1997) Elastography of breast lesions: initial clinical results. Radiology 202:79–86. doi:10.1148/radiology.202.1.8988195
Gefen A, Dilmoney B (2007) Mechanics of the normal woman’s breast. Technol Health Care 15(4):259–271
Greenleaf JF, Fatemi M, Insana M (2003) Selected methods for imaging elastic properties of biological tissues. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 5:57–78. doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.5.040202.121623
Han L, Noble JA, Burcher M (2003) A novel ultrasound indentation system for measuring biomechanical properties of in vivo soft tissue. Ultrasound Med Biol 29:813–823. doi:10.1016/S0301-5629(02)00776-7
Harrigan TP, Konofagou EE (2004) Estimation of material elastic moduli in elastography: a local method, and an investigation of Poisson’s ratio sensitivity. J Biomech 37:1215–1221. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2003.12.027
Hiltawsky K, Kruger M, Starke C, Heuser L, Ermert H, Jensen A (2001) Freehand ultrasound elastography of breast lesions: clinical results. Ultrasound Med Biol 27(11):1461–1469. doi:10.1016/S0301-5629(01)00434-3
Housden R, Gee AH, Treece GM, Prager RW (2010) 3-D ultrasonic strain imaging using freehand scanning and a mechanically-swept probe. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 57:501–506. doi:10.1109/TUFFC.2010.1431
Jurvelin J, Buschmann M, Hunziker E (1997) Optical and mechanical determination of Poisson’s ratio of adult bovine humeral articular cartilage. J Biomech 30:235–241. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(96)00133-9
Korte C, Van der Steen A (2002) Intravascular ultrasound elastography: an overview. Ultrasonics 40:859–865. doi:10.1016/S0041-624X(02)00227-5
Kruse S, Smith J, Lawrence A, Dresner M, Manduca A, Greenleaf J, Ehman R (2000) Tissue characterization using magnetic resonance elastography: preliminary results. Phys Med Biol 45:1579–1590. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/45/6/313
Krouskop T, Wheeler T, Kallel F, Garra B (1998) Hall, Elastic moduli of breast and prostate tissues under compression. Ultrason Imaging 20:260–274. doi:10.1177/016173469802000403
Lawrence A, Muthupillai R, Rossman P, Smith J, Manduca A, Ehman R (1998) Magnetic resonance elastography of the breast: preliminary experience. In: Proceedings of the international society for magnetic resonance in medicine. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Sydney, Australia
Lemaitre J (2001) Handbook of materials behavior models: Nonlinear models and properties. Academic Press. ISBN: 978-0-12-443341-0
Lerner RM, Parker KJ (1987) Sono-elasticity images, ultrasonic tissue charactertization and echographic imaging. In: Thijssen J (ed) 7th Eoropean Communities Workshop. Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Lerner RM, Parker KJ, Holen J, Gramiak R, Waag RC (1988) Sono-elasticity: medical elasticity images derived from ultrasound signals in mechanically vibrated targets. In: Kessler LW (ed) Acoustical imaging. Sonoscan Inc. 16, pp 317–27. ISBN 978-1-4613-0725-9
Lopez JI, Kang I, You W-K, McDonald DM, Weaver VM (2011) In situ force mapping of mammary gland transformation. Integr Biol 3:910–921. doi:10.1039/c1ib00043h
Lorenzen J, Sinkus R, Schrader D, Lorenzen M, Leussler C, Dargatz M, Roschmann P (2001) Imaging of breast tumors using MR elastography. Rofo 173(1):12–7. doi:10.1055/s-2001-10233
Lorenzen J, Sinkus R, Biesterfeldt M, Adam G (2003) Menstrual-cycle dependence of breast parenchyma elasticity: estimation with magnetic resonance elastography of breast tissue during the menstrual cycle. Invest Radiol 38(4):236–240
Manduca A, Smith J, Muthupillai R, Rossman P, Greenleaf J, Ehman R (1997) Image analysis techniques for magnetic resonance elastography, Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. In: Proceedings of the 5th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, 2:756-757. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.1996.651961
Manduca A, Dutt V, Borup DT, Muthupillai R, Greenleaf JF, Ehman RL (1998) An inverse approach to the calculation of elasticity maps for magnetic resonance elastography. Proc SPIE - Int Soc Opt Eng 3338:426–436
Mariappan YK, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL (2010) Magnetic resonance elastography: a review. Clin Anat 23:497–511. doi:10.1002/ca.21006
Matsumura T, Umemoto T, Fujihara Y, Ueno E, Yamakawa M, Shiina T, Mitake T (2009) Measurement of elastic property of breast tissue for elasticity imaging. In: Proceedings of IEEE Ultrasonic Symposium, pp 1451–1454. doi:10.1109/ULTSYM.2009.5442044
McKnight AL, Kugel JL, Rossman PJ, Manduca A, Hartmann LC, Ehman RL (2002) MR elastography of breast cancer: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:1411–1417. doi:10.2214/ajr.178.6.1781411
Mehrabian H, Campbell G, Samani A (2010) A constrained reconstruction technique of hyperelasticity parameters for breast cancer assessment. Phys Med Biol 55:7489–7508. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/55/24/007
Muthupillai R, Lomas D, Rossman P, Greenleaf J, Manduca A, Ehman R (1995) Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science 269:1854–1857. doi:10.1126/science.7569924
O’Donnell M, Skovoroda AR, Shapo BM, Emelianov SY (1994) Internal displacement and strain imaging using ultrasonic speckle tracking. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelec Freq Control 41(3):314–325. doi:10.1109/58.285465
O’Hagan JJ, Samani A (2009) Measurement of the hyperelastic properties of tissue slices with tumour inclusion. Phys Med Biol 54:2557–2569. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/54/8/020
Ophir J, Céspedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X (1991) Elastography: a quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging 13:111–134. doi:10.1016/0161-7346(91)90079-W
Ophir J, Garra B, Kallel F, Konofagou E, Krouskop T, Righetti R, Varghese T (2000) Elastographic imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 26(Suppl 1):S23–S29. doi:10.1016/S0301-5629(00)00156-3
Parker KJ, Doyley MM, Rubens DJ (2011) Imaging the elastic properties of tissue: the 20 year perspective. Phys Med Biol 56:R1–R29. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/56/1/R01
Pathmanathan P, Gavaghan D, Whiteley J, Brady SM, Nash M, Nielsen P, Rajagopal V (2004) Predicting tumour location by simulating large deformations of the breast using a 3D finite element model and nonlinear elasticity. Lect Notes Comput Sci 3217:217–224
Pathmanathan P, Gavaghan D, Whiteley J, Chapman S, Brady J (2008) Predicting tumor location by modeling the deformation of the breast. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55:2471–2480. doi:10.1109/TBME.2008.925714
Plewes D, Bishop J, Samani A, Sciarretta J (2000) Visualization and quantification of breast cancer biomechanical properties with magnetic resonance elastography. Phys Med Biol 45(6):1591–1610. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/45/6/314
Price BD, Gibson AP, Tan LT, Royle GJ (2010) An elastically compressible phantom material with mechanical and X-ray attenuation properties equivalent to breast tissue. Phys Med Biol 55:1177–1188. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/55/4/018
Rajagopal V, Lee A, Chung JH, Warren R, Highnam RP, Nash MP, Nielsen PMF (2008) Creating individual-specific biomechanical models of the breast for medical image analysis. Acad Radiol 15:1425–1436. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2008.07.017
Roose L, De Maerteleire W, Mollemans W, Suetens P (2005) Validation of different soft tissue simulation methods for breast augmentation. Int Congr Ser 1281:485–490. doi:10.1016/j.ics.2005.03.126
Ruiter N, Stotzka R, Muller T, Gemmeke H, Reichenbach J, Kaiser W (2006) Model-based registration of X-ray mammograms and MR images of the female breast. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 53(1):204–211. doi:10.1109/TNS.2005.862983
Sadigh G, Carlos RC, Neal CH, Dwamena BA (2012) Accuracy of quantitative ultrasound elastography for differentiation of malignant and benign breast abnormalities: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134(3):923–931. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2020-x
Samani A, Bishop J, Plewes D (2001a) Biomechanical 3-D finite element modeling of the human breast using MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(4):271–279. doi:10.1109/42.921476
Samani A, Bishop J, Plewes D (2001b) A constrained modulus reconstruction technique for breast cancer assessment. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:877–885. doi:10.1109/42.952726
Samani A, Bishop J, Luginbuhl C, Plewes DB (2003) Measuring the elastic modulus of ex vivo small tissue samples. Phys Med Biol 48:2183–2198. PII: S0031-9155(03)60749-9
Samani A, Plewes D (2004) A method to measure the hyperelastic parameters of ex vivo breast tissue samples. Phys Med Biol 49:4395–4405. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/49/18/014
Samani A, Plewes DB (2007) An inverse problem solution for measuring the elastic modulus of intact ex vivo breast tissue tumours Phys. Med Biol 52:1247–1260. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/52/5/003
Samani A, Zubovits J, Plewes D (2007) Elastic moduli of normal and pathological human breast tissues: an inversion-technique-based investigation of 169 samples. Phys Med Biol 52:1565–1576. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/52/6/002
Sarvazyan A, Goukassian D, Maevsky E, Oranskaja G (1994) Elasticity imaging as a new modality of medical imaging for cancer detection. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on Interaction of Ultrasound with Biological Media, pp 69–81
Sarvazyan A, Skovoroda A, Emelianov S, Fowlkes J, Pipe J, Adler R, Buxton R, Carson P (1995) Biophysical bases of elasticity imaging. Acoustical Imaging 21:223–240
Sayed A, Layne G, Abraham J, Mukdadi O (2013) Nonlinear characterization of breast cancer using multi-compression 3D ultrasound elastography in vivo. Ultrasonics 53:979–91. doi:10.1016/j.ultras.2013.01.005
Scaperrotta G, Ferranti C, Costa C, Mariani L, Marchesini M, Suman L, Folini C, Bergonzi S (2008) Role of sonoelastography in non-palpable breast lesions. Eur Radiol 18:2381–2389. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-1032-8
Shiina T (2013) JSUM ultrasound elastography practice guidelines: basics and terminology. J Med Ultrason 40:309–323. doi:10.1007/s10396-013-0490-z
Siegmann KC, Xydeas T, Sinkus R, Kraemer B, Vogel U, Claussen CD (2010) Diagnostic value of MR elastography in addition to contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the breast-initial clinical results. Eur Radiol 20:318–325. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1566-4
Silver FH, Freeman J, Seehra GP (2003) Collagen self-assembly and development of matrix mechanical properties. J Biomech 36:1529–1553. doi:10.1016/S0021-9290(03)00135-0
Silver FH, Landis WJ (2008) Viscoelasticity, energy storage and transmission and dissipation by extracellular matrices in vertebrates. In: Fratzl P (ed) Collagen: structure and mechanics. Spinger, New York, pp 133–154. ISBN: 9780387739052
Sinkus R, Lorenzen J, Schrader D, Lorenzen M, Dargatz M, Holz D (2000) In vivo tensor MR-elastography - anisotropy of mamma-carcinoma. Ismrm 26:493
Sinkus R, Lorenzen J, Schrader D, Lorenzen M, Dargatz M, Holz D (2000a) High-resolution tensor MR elastography for breast tumor detection. Phys Med Biol 45:1649–1664. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/45/6/317
Sinkus R, Tanter M, Catheline S, Lorenzen J, Kuhl C, Sondermann E, Fink M (2005a) Imaging anisotropic and viscous properties of breast tissue by magnetic resonance-elastography. Magn Reson Med 53:372–387. doi:10.1002/mrm.20355
Sinkus R, Tanter M, Xydeas T, Catheline S, Bercoff J, Fink M (2005b) Viscoelastic shear properties of in vivo breast lesions measured by MR elastography. Magn Reson Imaging 23:159–165. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2004.11.060
Society AC (2013) Cancer facts & figures 2013. American Cancer Society, Atlanta
Sommer G, Eder M, Kovacs L, Pathak H, Bonitz L, Mueller C, Regitnig P, Holzapfel GA (2013) Multiaxial mechanical properties and constitutive modeling of human adipose tissue: a basis for preoperative simulations in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Acta Biomater 9:9036–9048. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.06.011
Srivastava A, Verma Y, Rao KD, Gupta PK (2011) Determination of elastic properties of resected human breast tissue samples using optical coherence tomographic elastography. Strain 47:75–87. doi:10.1111/j.1475-1305.2009.00627.x
Stewart ML, Smith LM, Hall N (2011) A numerical investigation of breast compression: a computer-aided design approach for prescribing boundary conditions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58:2876–2884. doi:10.1109/TBME.2011.2162063
Stewart BW, Wild CP (2014) World Cancer Report, International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), ISBN 978-92-832-0429-9
Sudhakar K, Venkatesh R, Ehman L (2014) Magnetic resonance elastography. Springer, New York. Book. ISBN 978-1-4939-1574-3
Thomas A, Fischer T, Frey H, Ohlinger R, Grunwald S, Blohmer JU, Winzer KJ, Weber S, Kristiansen G, Ebert B, Kümmel S (2006) Real-time elastography-an advanced method of ultrasound: first results in 108 patients with breast lesions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 28:335–340. doi:10.1002/uog.2823
Umemoto T, Ueno E, Matsumura T, Yamakawa M, Bando H, Mitake T, Shiina T (2014) Ex vivo and in vivo assessment of the non-linearity of elasticity properties of breast tissues for quantitative strain elastography. Ultrasound Med Biol 40:1755–1768. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2014.02.005
Unlu MZ, Krol A, Magri A, Mandel JA, Lee W, Baum KG, Lipson ED, Coman IL, Feiglin DH (2010) Computerized method for nonrigid MR-to-PET breast-image registration. Comput Biol Med 40:37–53. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.10.010
Van Houten EEW, Doyley MM, Kennedy FE, Weaver JB, Paulsen KD (2003) Initial in vivo experience with steady–state subzone-based MR elastography of the human breast. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:72–85. doi:10.1002/jmri.10232
Wellman PS, Howe RD, Dalton E, Kern KA (1999) Breast tissue stiffness in compression is correlated to histological diagnosis, pp 1–15
Wells PNT, Liang H-D (2011) Medical ultrasound: imaging of soft tissue strain and elasticity. J R Soc Interface 8:1521–1549. doi:10.1098/rsif.2011.0054
Wilson L, Robinson D, Dadd M (2000) Elastography—the movement begins. Phys Med Biol 45:1409–1421. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/45/6/301
World Health Organization (2011) World Report on Disability. Malta: ISBN 978 92 4 068521 5
Xydeas T, Siegmann K, Sinkus R, Krainick-Strobel U, Miller S, Claussen CD (2005) Magnetic resonance elastography of the breast. Invest Radiol 40:412–420. doi:10.1097/01.rli.0000166940.72971.4a
Zhang M, Zheng YP, Mak AFT (1997) Estimating the effective Young ’ s modulus of soft tissues from indentation tests—nonlinear finite element analysis of effects of friction and large deformation. Med Eng Phys 19(6):512–517. doi:10.1016/S1350-4533(97)00017-9
Acknowledgments
The support of Ministério da Ciência Tecnologia e do Ensino Superior and Fundo Social Europeu (MCTES and FSE) under grants SFRH / BD / 85090 / 2012 and SFRH/ BPD/71080/2010 from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT, Portugal) and funding of Laboratório Associado de Energia, Transportes e Aeronáutica (LAETA—UID/EMS/50022/2013) are gratefully acknowledged.
The authors would like to acknowledge the outstanding revision work carried out by the reviewers of the paper. Their constructive criticism was a fundamental contribution to elevate the overall quality of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramião, N.G., Martins, P.S., Rynkevic, R. et al. Biomechanical properties of breast tissue, a state-of-the-art review. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 15, 1307–1323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-016-0763-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-016-0763-8