Abstract
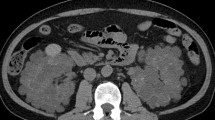
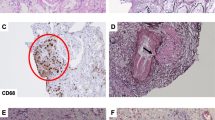
The patient was a 54-year-old woman with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) who developed complicating systemic sarcoidosis. Hypercalcemia and an abrupt increase in serum creatinine levels were observed during the clinical course. Steroid therapy was initiated and produced a distinct improvement in renal function. A kidney biopsy was not feasible because ADPKD is a contraindication for renal needle biopsy. The clinical findings strongly suggested renal disorder secondary to tubulointerstitial nephritis caused by renal sarcoidosis with complicating hypercalcemia. In addition to controlling hypertension and improving the hypercalcemia and dehydration, steroid therapy also improved the renal function in this patient.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman AB. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: time for a change? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1399–407.
Higashihara E, Nutahara K, Kojima M, Tamakoshi A, Yoshiyuki O, Sakai H, et al. Prevalence and renal prognosis of diagnosed autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Japan. Nephron. 1998;80:421–7.
Berliner AR, Haas M, Choi MJ. Sarcoidosis: the Nephrologist’s perspective. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:856–70.
Muther RS, McCarron DA, Bennet WM. Renal manifestations of sarcoidosis. Arch Intern Med. 1981;141:643–5.
Sato A. Renal dysfunction in patients with sarcoidosis. Intern Med. 1996;35:523–4.
Gobel U, Kettritz R, Schneider W, Luft F. The protean face of renal sarcoidosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:616–23.
Cruzado JM, Poveda R, Mana J, Carreras L, Carrera M, Grinyó JM. Interstitial nephritis in sarcoidosis: simultaneous multiorgan involvement. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;26:947–51.
Ohmichi M, Yamada G, Hiraga Y. Clinical usefulness of 67Ga scintigraphy and 67Ga single photon emission computed tomography in sarcoidosis. Nippon Rinsho (Japanese journal of clinical medicine). 1994;52:1516–20.
D’Cruz S, Singh R, Mohan H, Kaur R, Minz RW, Kapoor V, Sachdev A. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis—an unusual association: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2010;29(4):125–9.
Shikata K, Makino H, Ota Z. A membranous nephropathy associated with adult polycystic kidney disease. Clin Nephrol. 1991;36:223–7.
Higashihara E, Aso Y, Shimazaki J, Ito H, Koiso K, Sakai O. Clinical aspects of polycystic kidney disease. J Urol. 1992;147:329–32.
King BF, Reed JE, Bergstralh EJ, Sheedy PF 2nd, Torres VE. Quantification and longitudinal trends of kidney, renal cyst, and renal parenchyma volumes in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11:1505–11.
Ecder T, Chapman AB, Brosnahan GM, Edelstein CL, Johnson AM, Schrier RW. Effect of antihypertensive therapy on renal function and urinary albumin excretion in hypertensive patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35:427–32.
Ong AC, Wagner B. Detection of proximal tubular motile cilia in a patient with renal sarcoidosis associated with hypercalcemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45:1096–9.
Utas C, Dogukan A, Patiroglu TE, Oymak S, Oymak O. Granulomatous interstitial nephritis in extrapulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin Nephrol. 1999;51:252–4.
Mitome J, Kawaguchi Y, Arase S, Horino T, Okada H, Okada N. A case of renal sarcoidosis: a special reference to calcium metabolism as a diagnostic and the therapeutic implications. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2004;8:375–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasa, Y., Arai, J., Mitobe, M. et al. Successful steroid treatment of a patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease complicated by sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 442–447 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0412-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0412-6