Abstract
Background
In most cases of diverticulitis, inflammation is mild, and the only treatment required is a clear liquid diet and antibiotics. Until recently, patients were given this treatment as inpatients with the consequent expenditure of resources. The aim of this study was to assess the safety and efficacy of an outpatient treatment protocol with oral antibiotics in selected patients with uncomplicated acute diverticulitis in comparison with inpatient intravenous treatment.
Methods
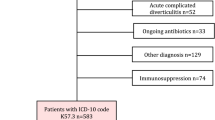
We conducted a prospective non-randomized study between January 2007 and December 2009. We included all patients diagnosed with uncomplicated acute diverticulitis, at the Emergency Department of the University General Hospital of Elche. We compared the efficacy, safety and costs of hospital treatment with intravenous antibiotics and outpatient treatment with oral antibiotics. Seventy-six patients were included in the study. Forty-four of them underwent intravenous treatment with Metronidazole 500 mg/8 h + Ciprofloxacin 400 mg/12 h (hospital treatment group) and 32 took oral antibiotics Metronidazole 500 mg/8 h and Ciprofloxacin 500 mg/12 h (outpatient group).
Results
Outpatient treatment is viable in almost 95 % of those patients suffering from uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Treatment was effective in resolving inflammation, and there were no complications in the majority of cases (94 %). Only 2 patients (6 %) required admission after outpatient treatment. The results further reflect complications and relapse rates similar to those of patients admitted to hospital and treated with intravenous antibiotics. There are no significant statistical differences (p = 0.86) between inpatients and outpatients. It is possible to save approximately 1,600 € per patient with outpatient treatment (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Outpatient treatment has demonstrated a safety and efficiency similar to inpatient treatment, producing an important reduction in expenses and medical resources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sandler RS, Everhart JE, Donowitz M et al (2002) The burden of selected digestive diseases in the United States. Gastroenterology 122:1500–1511
Commane DM, Arasaradnam RP, Mills S, Mathers JC, Bradburn M (2009) Diet, ageing and genetic factors in the pathogenesis of diverticular disease. World J Gastroenterol 15:2479–2488
Kohler L, Sauerland S, Neugebauer E (1999) Diagnosis and treatment of diverticular disease: results of a consensus development conference. The scientific committee of the European association for endoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 13:430–436
Gordon P (1998) Diverticular disease. In: Nicholls RJ, Dozois RR (eds) Surgery of the colon and rectum. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 691–798
Stollman NH, Raskin JB (1999) Diverticular disease of the colon. J Clin Gastroenterol 29:241–252
Ambrosetti P, Jenny A, Becker C, Terrier T, Morel P (2000) Acute left colonic diverticulitis-compared performance of computed tomography and water-soluble contrast enema: prospective evaluation of 420 patients. Dis Colon Rectum 43:1363–1367
Stollman N, Raskin JB (2004) Diverticular disease of the colon. Lancet 363:631–639
Ferrer J, Fondevila C, Bombuy E et al (2006) Controlled, open, parallel-group study of the clinical and microbiological efficacy of piperacillin-tazobactam versus metronidazole + gentamicin in urgent colorectal surgery. Cir Esp 79:365–369
Lombardo L, Lapertosa G (1991) The Ambulatory treatemnt of colonic diverticulitis. An open clinico-endoscopic-histological study with rifaximin, a nonaminoglycoside enteric antibiotic. Recenti Prog Med 82:300–304
Mizuki A, Nagata H, Tatemichi M, Kaneda S, Tsukada N, Ishii H (2005) The outpatient management of patients with acute mild.to-moderate colonic diverticulitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21:889–897
Alonso S, Pera M, Parés D et al (2010) Outpatient treatemnt of patients with uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Colorectal Dis 12:278–282
Ridgway P, Latif A, Shabbir J et al (2009) Randomised controlled trial of oral versus intravenous therapy for clinically diagnosed acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. Colorectal Dis 11:941–946
Kim HU, Kim YH, Choe WH et al (2003) Clinical characteristics of colonic diverticulitis in Koreans. Korean J Gastroenterol 42:363–368
Doringer E (1992) Computerized tomography of colonic diverticulitis. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 33:421–435
Kang JY, Hoare J, Tinto A et al (2003) Diverticular disease of the colon on the rise: a study of hospital admissions in England between 1989/1990 and 1999/2000. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 17:1189–1195
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moya, P., Arroyo, A., Pérez-Legaz, J. et al. Applicability, safety and efficiency of outpatient treatment in uncomplicated diverticulitis. Tech Coloproctol 16, 301–307 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-012-0847-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-012-0847-0