Abstract
Backgound
We retrospectively investigated the clinical characteristics and outcome of pneumothorax after stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for lung tumors.
Methods
Between April 2003 and July 2012, 473 patients with lung tumors were treated with SBRT. We identified 12 patients (2.5 %) with pneumothorax caused by SBRT, and evaluated the clinical features of pneumothorax.
Results
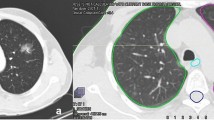
All of the tumors were primary lung cancers. The severity of radiation pneumonitis was grade 1 in 10 patients and grade 2 in two patients. Nine patients had emphysema. The planning target volume and pleura overlapped in 11 patients, and the tumors were attached to the pleura in 7 patients. Rib fractures were observed in three patients before or at the same time as the diagnosis of pneumothorax. The median time to onset of pneumothorax after SBRT was 18.5 months (4–84 months). The severity of pneumothorax was grade 1 in 11 patients and grade 3 in one patient.
Conclusion
Although pneumothorax was a relatively rare late adverse effect after SBRT, some patients demonstrated pneumothorax after SBRT for peripheral lung tumors. Although most pneumothorax was generally tolerable and self-limiting, careful follow-up is needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M et al (2009) Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 27:3290–3296
Yoshitake T, Nakamura K, Shioyama Y et al. (2014) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary lung cancers clinically diagnosed without pathological confirmation: a single-institution experience. Int J Clin Oncol (in press)
Siva S, MacManus M, Ball D (2010) Stereotactic radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol 5:1091–1099
Libshitz HI, Banner MP (1974) Spontaneous pneumothorax as a complication of radiation therapy to the thorax 1. Radiology 112:199–201
Pezner RD, Horak DA, Sayegh HO et al (1990) Spontaneous pneumothorax in patients irradiated for Hodgkin’s disease and other malignant lymphomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 18:193–198
Rowinsky EK, Abeloff MD, Wharam M (1985) Spontaneous pneumothorax following thoracic irradiation. Chest J 88:703–708
Ohnishi K, Shioyama Y, Nomoto S et al (2009) Spontaneous pneumothorax after stereotactic radiotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Jpn J Radiol 27:269–274
Shioyama Y, Nakamura K, Anai S et al (2005) Stereotactic radiotherapy for lung and liver tumors using a body cast system: setup accuracy and preliminary clinical outcome. Radiat Med 23:407–413
Yoshitake T, Shioyama Y, Nakamura K et al (2009) A clinical evaluation of visual feedback-guided breath-hold reproducibility of tumor location. Phys Med Biol 54:7171–7182
Melton L 3rd, Hepper N, Offord K (1979) Incidence of spontaneous pneumothorax in Olmsted County, Minnesota: 1950 to 1974. Am Rev Respir Dis 120:1379–1382
Bense L, Eklund G, Wiman L-G (1987) Smoking and the increased risk of contracting spontaneous pneumothorax. Chest 92:1009–1012
Fiorelli A, Vicidomini G, Napolitano F et al (2011) Spontaneous pneumothorax after chemotherapy for sarcoma with lung metastases: case report and consideration of pathogenesis. J Thorac Dis 3:138–140
Baydur A, Gottlieb LS (1976) Pneumopericardium and pneumothorax complicating bronchogenic carcinoma. West J Med 124:144–146
Lai R-S, Perng R-P, Chang S-C (1992) Primary lung cancer complicated with pneumothorax. Jpn J Clin Oncol 22:194–197
Maniwa T, Nakagawa K, Isaka M et al (2011) Pneumothorax associated with treatment for pulmonary malignancy. Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg 13:257–261
Asai K, Shioyama Y, Nakamura K et al (2012) Radiation-induced rib fractures after hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy: risk factors and dose–volume relationship. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:768–773
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Japan (no. 26670563, 25461917, 26461894, and 24591842).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Asai, K., Nakamura, K., Shioyama, Y. et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of pneumothorax after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors. Int J Clin Oncol 20, 1117–1121 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-015-0833-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-015-0833-4