Abstract
Objective
Immune escape plays an important role in tumor progression. In the present study, the expression of B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3 involved in immune escape in gastric carcinoma was investigated and the corresponding clinical significance was evaluated.
Methods
Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3 in 100 gastric cancer specimens, and 30 paracarcinoma tissues were used as the control.
Results
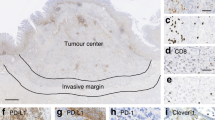
Both B7-H1 and B7-H4 showed high expression levels in gastric cancer tissues (65.0 and 71.0 %, respectively), and the expressions of B7-H1 and B7-H4 were positively correlated with the depth of tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis and American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage (P < 0.05). The number of Foxp3+ Tregs was much higher in gastric cancer tissues than control tissues, which was positively correlated with lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05). Similarly, a positive correlation between B7-H1 or B7-H4 expression and the number of Foxp3+ Tregs was observed. The median overall survival rate of patients with high expression of B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3 was significantly poorer than that of patients with low expression of these proteins (P < 0.05). Cox regression multivariate analysis confirmed that lymph node metastasis, AJCC stage, and B7-H1 and Foxp3 overexpression were independent prognostic factors.
Conclusion
B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3 were overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues. B7-H1 and Foxp3 are negative prognostic factors for patients with gastric cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrone S, Whiteside TL (2007) Tumor microenvironment and immune escape. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16(4):755–774
Zou W, Chen L (2008) Inhibitory B7-family molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 8(6):467–477
Pardoll DM (2002) Spinning molecular immunology into successful immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2(4):227–238
Chen J, Li G, Meng H et al (2012) Upregulation of B7-H1 expression is associated with macrophage infiltration in hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61(1):101–108
Pan XC, Li L, Mao JJ et al (2013) Synergistic effects of soluble PD-1 and IL-21 on antitumor immunity against H22 murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett 5(1):90–96
Zhang L, Wu H, Lu D et al (2013) The costimulatory molecule B7-H4 promote tumor progression and cell proliferation through translocating into nucleus. Oncogene 32(46):5347–5358
Wang S, Chen L (2004) Co-signaling molecules of the B7-CD28 family in positive and negative regulation of T lymphocyte responses. Microbes Infect 6(8):759–766
Zhu G, Augustine MM, Azuma T et al (2009) B7-H4-deficient mice display augmented neutrophil-mediated innate immunity. Blood 113(8):1759–1767
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y et al (2005) Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(8):2947–2953
Zheng X, Li XD, Wu CP et al (2012) Expression of costimulatory molecule B7-H4 in human malignant tumors. Onkologie 35(11):700–705
Gadiot J, Hooijkaas AI, Kaiser AD et al (2011) Overall survival and PD-L1 expression in metastasized malignant melanoma. Cancer 117(10):2192–2201
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J et al (2006) Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Acta Histochem 108(1):19–24
Jiang J, Zhu Y, Wu C et al (2010) Tumor expression of B7-H4 predicts poor survival of patients suffering from gastric cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59(11):1707–1714
Mailloux AW, Young MR (2010) Regulatory T-cell trafficking: from thymic development to tumor-induced immune suppression. Crit Rev Immunol 30(5):435–447
Hori S, Sakaguchi S (2004) Foxp3: a critical regulator of the development and function of regulatory T cells. Microbes Infect 6(8):745–751
Gratz IK, Rosenblum MD, Abbas AK (2013) The life of regulatory T cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1283:8–12
Lu X, Liu J, Li H et al (2011) Conversion of intratumoral regulatory T cells by human gastric cancer cells is dependent on transforming growth factor-beta1. J Surg Oncol 104(6):571–577
Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ et al (2001) Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 61(12):4766–4772
Wang HY, Wang RF (2007) Regulatory T cells and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 19(2):217–223
Association Japanese Gastric Cancer (1998) Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma—2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer 1(1):10–24
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC et al (2009) Gastric cancer. Lancet 374(9688):477–490
Yeh JM, Kuntz KM, Ezzati M et al (2009) Exploring the cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori screening to prevent gastric cancer in China in anticipation of clinical trial results. Int J Cancer 124(1):157–166
Zang X, Allison JP (2007) The B7 family and cancer therapy: costimulation and coinhibition. Clin Cancer Res 13(18 Pt 1):5271–5279
Brown JA, Dorfman DM, Ma FR et al (2003) Blockade of programmed death-1 ligands on dendritic cells enhances T cell activation and cytokine production. J Immunol 170(3):1257–1266
Choi IH, Zhu G, Sica GL et al (2003) Genomic organization and expression analysis of B7-H4, an immune inhibitory molecule of the B7 family. J Immunol 171(9):4650–4654
Kryczek I, Zou L, Rodriguez P et al (2006) B7-H4 expression identifies a novel suppressive macrophage population in human ovarian carcinoma. J Exp Med 203(4):871–881
Krambeck AE, Thompson RH, Dong H et al (2006) B7-H4 expression in renal cell carcinoma and tumor vasculature: associations with cancer progression and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(27):10391–10396
Tringler B, Zhuo S, Pilkington G et al (2005) B7-h4 is highly expressed in ductal and lobular breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(5):1842–1848
Tringler B, Liu W, Corral L et al (2006) B7-H4 overexpression in ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol 100(1):44–52
Zang X, Thompson RH, Al-Ahmadie HA et al (2007) B7-H3 and B7x are highly expressed in human prostate cancer and associated with disease spread and poor outcome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(49):19458–19463
Simon I, Liu Y, Krall KL et al (2007) Evaluation of the novel serum markers B7-H4, Spondin 2, and DcR3 for diagnosis and early detection of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 106(1):112–118
Thompson RH, Zang X, Lohse CM et al (2008) Serum-soluble B7x is elevated in renal cell carcinoma patients and is associated with advanced stage. Cancer Res 68(15):6054–6058
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y et al (2002) Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(19):12293–12297
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR et al (2002) Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med 8(8):793–800
Curiel TJ, Wei S, Dong H et al (2003) Blockade of B7-H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Nat Med 9(5):562–567
Prasad DV, Richards S, Mai XM et al (2003) B7S1, a novel B7 family member that negatively regulates T cell activation. Immunity 18(6):863–873
Sica GL, Choi IH, Zhu G et al (2003) B7-H4, a molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity. Immunity 18(6):849–861
Zang X, Loke P, Kim J et al (2003) B7x: a widely expressed B7 family member that inhibits T cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(18):10388–10392
Strauss L, Bergmann C, Szczepanski M et al (2007) A unique subset of CD4+ CD25highFoxp3+ T cells secreting interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res 13(15 Pt 1):4345–4354
Liu J, Zhang N, Li Q et al (2011) Tumor-associated macrophages recruit CCR6+ regulatory T cells and promote the development of colorectal cancer via enhancing CCL20 production in mice. PLoS One 6(4):e19495
Loser K, Apelt J, Voskort M et al (2007) IL-10 controls ultraviolet-induced carcinogenesis in mice. J Immunol 179(1):365–371
Li Q, Chen J, Liu Y et al (2013) Prevalence of Th17 and Treg cells in gastric cancer patients and its correlation with clinical parameters. Oncol Rep 30(3):1215–1222
Li H, Yu JP, Cao S et al (2007) CD4 +CD25+ regulatory T cells decreased the antitumor activity of cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells of lung cancer patients. J Clin Immunol 27(3):317–326
Bastid J, Cottalorda-Regairaz A, Alberici G et al (2013) ENTPD1/CD39 is a promising therapeutic target in oncology. Oncogene 32(14):1743–1751
Sun X, Wu Y, Gao W et al (2010) CD39/ENTPD1 expression by CD4 + Foxp3 + regulatory T cells promotes hepatic metastatic tumor growth in mice. Gastroenterology 139(3):1030–1040
Acknowledgments
This research project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81171653 and 30972703) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2011246 and BK2011247).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Geng and H. Wang contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, Y., Wang, H., Lu, C. et al. Expression of costimulatory molecules B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3+ Tregs in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Int J Clin Oncol 20, 273–281 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0701-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0701-7