Abstract
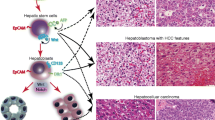
This review describes the pathological classification of pediatric liver cancer types and subtypes proposed at the recent international symposium (March 2011, Los Angeles, USA) and meetings involving pathologists serving as central reviewers for the Children’s Oncology Group, Société Internationale d’Oncologie Pédiatrique, Gesellschaft für Pädiatrische Onkologie und Hämatologie, or Japanese Study Group for Pediatric Liver Tumors, and pediatric oncologists/surgeons specializing in liver cancers, as well as immunohistochemical panels, recommendations for submission, sampling and evaluation of diagnostic specimens. The pathological classification is intended to be standardized and clinically meaningful, thus improving future patient management and prognosis. The most common pediatric liver cancer is hepatoblastoma (HBL). HBL has two types, the wholly epithelial type and the mixed epithelial and mesenchymal (MEM) type. The wholly epithelial type was subdivided into well-differentiated fetal (pure fetal with low mitotic activity), crowded fetal (mitotically active), embryonal, epithelial mixed, small cell undifferentiated, and cholangioblastic. A macrotrabecular pattern and a pleomorphic epithelial pattern were recognized as supplemental features of epithelial components. The MEM type was subdivided into MEM without teratoid features and MEM with teratoid features. Other liver cancers in children were divided into hepatocellular carcinoma (classic hepatocellular carcinoma and fibrolamellar carcinoma) and hepatocellular malignant tumor not otherwise specified. This classification is basically applied to pretreatment specimens; the evaluation of post-chemotherapy specimens will be the subject of further studies.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finegold MJ (2004) Hepatic tumors in childhood. In: Russo P, Ruchelli E, Piccoli DA (eds) Pathology of Pediatric Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. Springer, New York
Weinberg AG, Finegold MJ (1983) Primary hepatic tumors of childhood. Hum Pathol 14:512–537
Stocker JT (2001) Hepatic tumors in children. Clin Liver Dis 5:259–281, viii–ix
Haas JE, Muczynski KA, Krailo M et al (1989) Histopathology and prognosis in childhood hepatoblastoma and hepatocarcinoma. Cancer 64:1082–1095
Ishak KG, Glunz PR (1967) Hepatoblastoma and hepatocarcinoma in infancy and childhood. Report of 47 cases. Cancer 20:396–422
Finegold MJ, Bowen J, Lopez-Terrada DH et al (2011) Protocol for the examination of specimens from pediatric patients with hepatoblastoma. Protocol applies to hepatoblastoma. Other malignant primary hepatic tumors are not included. http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2012/Hepatoblast_12protocol.pdf#search=‘Protocol+for+the+Examination+of+Specimens+From+Pediatric+Patients+With+Hepatoblastoma.+Protocol+applies+to+hepatoblastoma.+Other+malignant+primary+hepatic+tumors+are+not+included.’
Ismail H, Broniszczak D, Kaliciński P et al (2012) Changing treatment and outcome of children with hepatoblastoma: analysis of a single center experience over the last 20 years. J Pediatr Surg 47:1331–1339
Kasai M, Watanabe I (1970) Histologic classification of liver-cell carcinoma in infancy and childhood and its clinical evaluation. A study of 70 cases collected in Japan. Cancer 25:551–563
Hishiki T, Matsunaga T, Horie H et al (2006) Histopathology and its significance in clinical behavior of hepatoblastoma. Jpn J Pediatr Surg 38:627–631
Malogolowkin MH, Katzenstein HM, Meyers RL et al (2011) Complete surgical resection is curative for children with hepatoblastoma with pure fetal histology: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 29:3301–3306
Libbrecht L, Desmet V, Roskams T (2003) Stages of normal and aberrant intrahepatic bile duct development in a mixed hepatoblastoma. Histopathology 42:618–620
Zimmermann A (2002) Hepatoblastoma with cholangioblastic features (‘cholangioblastic hepatoblastoma’) and other liver tumors with bimodal differentiation in young patients. Med Pediatr Oncol 39:487–491
De Ioris M, Brugieres L, Zimmermann A et al (2008) Hepatoblastoma with a low serum alpha-fetoprotein level at diagnosis: the SIOPEL group experience. Eur J Cancer 44:545–550
Trobaugh-Lotrario AD, Tomlinson GE et al (2009) Small cell undifferentiated variant of hepatoblastoma: adverse clinical and molecular features similar to rhabdoid tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 52:328–334
Haas JE, Feusner JH, Finegold MJ (2001) Small cell undifferentiated histology in hepatoblastoma may be unfavorable. Cancer 92:3130–3134
Meyers RL, Rowland JR, Krailo M et al (2009) Predictive power of pretreatment prognostic factors in children with hepatoblastoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53:1016–1022
Gadd S, Sredni ST, Huang CC et al (2010) Rhabdoid tumor: gene expression clues to pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets. Lab Invest 90:724–738
Russo P, Biegel JA (2009) SMARCB1/INI1 alterations and hepatoblastoma: another extrarenal rhabdoid tumor revealed? Pediatr Blood Cancer 52:312–313
Zimmermann A (2005) The emerging family of hepatoblastoma tumours: from ontogenesis to oncogenesis. Eur J Cancer 41:1503–1514
González-Crussi F, Upton MP, Maurer HS (1982) Hepatoblastoma. Attempt at characterization of histologic subtypes. Am J Surg Pathol 6:599–612
Zimmermann A, Lopez-Terrada D (2011) Pathology of pediatric liver tumors. In: Zimmermann A, Perilongo G, Malogolowkin M et al (eds) Pediatric Liver Tumors. Springer, Berlin, pp 83–112
Ward SC, Waxman S (2011) Fibrolamellar carcinoma: a review with focus on genetics and comparison to other malignant primary liver tumors. Semin Liver Dis 31:61–70
Prokurat A, Kluge P, Kościesza A et al (2002) Transitional liver cell tumors (TLCT) in older children and adolescents: a novel group of aggressive hepatic tumors expressing beta-catenin. Med Pediatr Oncol 39:510–518
Dezso K, Halász J, Bisgaard HC et al (2008) Delta-like protein (DLK) is a novel immunohistochemical marker for human hepatoblastomas. Virchows Arch 452:443–448
Yanai H, Nakamura K, Hijioka S et al (2010) Dlk-1, a cell surface antigen on foetal hepatic stem/progenitor cells, is expressed in hepatocellular, colon, pancreas and breast carcinomas at a high frequency. J Biochem 148:85–92
Finegold MJ, Lopez-Terrada DH, Bowen J et al (2007) Protocol for the examination of specimens from pediatric patients with hepatoblastoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 131:520–529
Wang LL, Filippi RZ, Zurakowski D et al (2010) Effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on hepatoblastoma: a morphologic and immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol 34:287–299
Vujanić GM, Sandstedt B (2010) The pathology of Wilms’ tumour (nephroblastoma): the International Society of Paediatric Oncology approach. J Clin Pathol 63:102–109
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, Y., Inoue, T. & Horie, H. International pediatric liver cancer pathological classification: current trend. Int J Clin Oncol 18, 946–954 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0624-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0624-8