Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to assess the long-term outcomes of combining high-dose-rate intraluminal brachytherapy (IBT) with external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) for superficial esophageal cancer (SEC).
Methods
From 1992 to 2002, 87 patients with T1N0M0 thoracic esophageal cancer received IBT in combination with EBRT. Of these, 44 had mucosal cancer and 43 had submucosal cancer. For patients with tumor invasion within the lamina propria mucosa, IBT alone was performed (n = 27). IBT boost following EBRT was performed for patients with tumor invasion in the muscularis mucosa or deeper (n = 60). No patient received chemotherapy.
Results
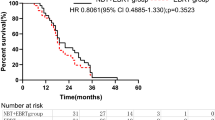
The median follow-up time was 94 months. For mucosal cancer, the 5-year locoregional control (LRC), cause-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 75, 97 and 84%, respectively, and 49, 55 and 31%, respectively, for submucosal cancer. Tumor depth was a significant factor associated with LRC (p = 0.02), CSS (p < 0.001) and OS (p < 0.001) by univariate analysis. Multivariate analysis revealed that tumor depth was the only significant predictor for OS (p = 0.003). Late toxicities of grade 3 or higher in esophagus, pneumonitis, pleural effusion and pericardial effusion were observed in 5, 0, 0 and 1 patients, respectively. Grade ≥3 events of cardiac ischemia and heart failure after radiotherapy were observed in 9 patients, and history of heart disease before radiotherapy was the only significant factor (p = 0.002).
Conclusion
There was a clear difference in outcomes of IBT combined with EBRT between mucosal and submucosal esophageal cancers. More intensive treatment should be considered for submucosal cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okawa T, Tanaka M, Kita M et al (1995) Superficial esophageal cancer: multicenter analysis of results of definitive radiation therapy in Japan. Radiology 196:271–274
(2002) Comprehensive registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan (1998, 1999) and long term results of esophagectomy in Japan (1988–1997), 3rd edn. The Japanese Society for Esophageal Disease
Murakami Y, Kenjo M, Uno T et al (2007) Results of the 1999–2001 Japanese patterns of care study for patients receiving definitive radiation therapy without surgery for esophageal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 37:493–500
Kodama M, Kakegawa T (1998) Treatment of superficial cancer of the esophagus: a summary of responses to a questionnaire on superficial cancer of the esophagus in Japan. Surgery 123:432–439
Endo M, Yoshino K, Kawano T et al (2000) Clinicopathologic analysis of lymph node metastasis in surgically resected superficial cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Dis Esophagus 13:125–129
Bollschweiler E, Baldus SE, Schröder W et al (2006) High rate of lymph-node metastasis in submucosal esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Endoscopy 38:149–156
Makuuchi H, Shimada H, Mizutani K et al (1997) Clinical pathological analysis of surgically resected superficial esophageal carcinoma to determine criteria for deciding on treatment strategy. Diagn Ther Endosc 3:211–220
Nishimaki T, Tanaka O, Suzuki T et al (1993) Tumor spread in superficial esophageal cancer: histopathologic basis for rational surgical treatment. World J Surg 17:766–772
Tachibana M, Yoshimura H, Kinugasa S et al (1997) Clinicopathological features of superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Am J Surg 174:49–53
Nemoto K, Yamada S, Mitsuhashi N et al (2001) Radiation therapy for superficial esophageal cancer: a comparison of radiotherapy methods. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50:639–644
Nemoto K, Yamada S, Nishio M et al (2006) Results of radiation therapy for superficial esophageal cancer using the standard radiotherapy method recommended by the Japanese Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (JASTRO) Study Group. Anticancer Res 26:1507–1512
Shioyama Y, Nakamura K, Sasaki T et al (2005) Clinical results of radiation therapy for stage I esophageal cancer A single institutional experience. Am J Clin Oncol 28:75–80
Ishikawa H, Sakurai H, Yamakawa M et al (2005) Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with definitive radiation therapy alone. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:495–500
Sai H, Mitsumori M, Araki N et al (2005) Long-term results of definitive radiotherapy for stage I esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62:1339–1344
Hareyama M, Nishio M, Kagami Y et al (1992) Intracavitary brachytherapy combined with external-beam irradiation for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 24:235–240
Okawa T, Dokiya T, Nishio M et al (1999) Multi-institutional randomized trial of external radiotherapy with or without intraluminal brachytherapy for esophageal cancer in Japan. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:623–628
Yorozu A, Dokiya T, Oki Y (1999) High-dose-rate brachytherapy boost following concurrent chemoradiotherapy for esophageal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50:271–275
Maingon P, Hombres A, Truc G et al (2000) High dose rate brachytherapy for superficial cancer of the esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:71–76
Ishikawa H, Nonaka T, Sakurai H et al (2010) Usefulness of intraluminal brachytherapy combined with external beam radiation therapy for submucosal esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:452–459
Takahashi H, Arimura Y, Hosokawa M et al (2010) Endoscopic submucosal dissection is superior to conventional endoscopic resection as a curative treatment for early squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72:255–264
Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A et al (1999) Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA 281:1623–1627
Al-Sarraf M, Martz K, Herskovic A et al (1997) Progress report of combined chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with esophageal cancer: an intergroup study. J Clin Oncol 15:277–284
Herskovic A, Martz K, al-Sarraf M et al (1992) Combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in patients with cancer of the esophagus. N Engl J Med 326:1593–1598
Yamada K, Murakami M, Okamoto Y et al (2006) Treatment results of chemoradiotherapy for clinical stage I (T1N0M0) esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:1106–1111
Kato H, Sato A, Fukuda H et al (2009) A phase II trial of chemoradiotherapy for stage I esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group study (JCOG9708). Jpn J Clin Oncol 39:638–643
Akagi A, Hirokawa Y, Ito K et al (1999) Optimum fractionation for high-dose-rate endoesophageal brachytherapy following external irradiation of early stage esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:525–530
Stewart JR, Fajardo LF, Gillette SM et al (1995) Radiation injury to the heart. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1205–1211
Veinot JP, Edwards WD (1996) Pathology of radiation-induced heart disease: a surgical and autopsy study of 27 cases. Hum Pathol 27:766–773
Adams MJ, Hardenbergh PH, Constine LS et al (2003) Radiation-associated cardiovascular disease. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 45:55–75
Ishikura S, Nihei K, Ohtsu A et al (2003) Long-term toxicity after definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J Clin Oncol 21:2697–2702
Conflict of interest
No author has any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, Y., Nagata, Y., Nishibuchi, I. et al. Long-term outcomes of intraluminal brachytherapy in combination with external beam radiotherapy for superficial esophageal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 17, 263–271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-011-0285-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-011-0285-4