Abstract
Background
Cancer cachexia, a catabolic state characterized by weight loss, occurs frequently in patients with terminal-stage neoplastic diseases. Gastrointestinal hormones and cytokines may be associated with anorexia and wasting in cancer cachexia.
Methods
This study aimed to examine the mechanism of anorexia in cachectic patients through a prospective investigation of plasma cytokines, ghrelin, and leptin in 16 cachectic patients with cancer of the digestive organs and 10 healthy volunteers.
Results
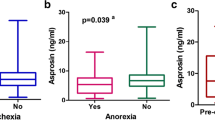
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), and ghrelin levels were significantly higher in cachectic cancer patients than in the healthy volunteers, whereas leptin was significantly lower in the cachectic cancer patients. Plasma leptin levels and cytokine levels (TNF-α and IL-6) correlated significantly with body mass index (BMI), but plasma ghrelin levels did not correlate with BMI or with the grade of symptoms.
Conclusion
Neither weight loss nor the grade of symptoms seemed to be directly associated with the increase in ghrelin levels. Hence, it is considered that the increase in ghrelin levels cannot simply be explained by an increase in ghrelin secretion, suggesting that other mechanisms, such as the decreased inactivation of ghrelin, may also play a role. Further studies are needed to clarify the mechanisms of the increase in ghrelin levels. Additionally, the changes in plasma cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) and leptin in cachectic cancer patients suggest that these molecules may be useful markers for the evaluation of cancer cachexia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li WG, Gavrila D, Liu X, et al. (2004) Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappa B activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation 109:2221–2226
Nelson KA (2001) Modern management of the cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep 5:250–256
Pfitzenmaier J, Vessella R, Higano CS, et al. (2003) Elevation of cytokine levels in cachectic patients with prostate carcinoma. Cancer 97:1211–1216
Dixit VD, Schaffer EM, Pyle RS, et al. (2004) Ghrelin inhibits leptin- and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J Clin Invest 114: 57–66
Asakawa A, Inui A, Kaga T, et al. (2001) Ghrelin is an appetitestimulatory signal from stomach with structural resemblance to motilin. Gastroenterology 120:337–345
Zhang, Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al. (1994) Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372:425–432
Shimizu Y, Nagaya N, Isobe T, et al. (2003) Increased plasma ghrelin level in lung cancer cachexia. Clin Cancer Res 9:774–778
Waelput W, Brouckaert P, Broekaert D, Tavernier J (2002) A role for leptin in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and in immune response. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 1:277–289
Aleman MR, Santolaria, F, Batista N, et al. (2002) Leptin role in advanced lung cancer. A mediator of the acute phase response or a marker of the status of nutrition? Cytokine 19:21–26
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, et al. (1999) Ghrelin is a growthhormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402: 656–660
Tschop M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML (2000) Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 407:908–913
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, et al. (2002) Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 346:1623–1630
Inui A (2001) Ghrelin: an orexigenic and somatotrophic signal from the stomach. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:551–560
Hanada T, Toshinai K, Kajimura N, et al. (2003) Anti-cachectic effect of ghrelin in nude mice bearing human melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:275–279
Sobin LH, Wittekind Ch (2002) TNM classification of Malignant Tumors, 6th edn. Wiley
Common Toxicity Criteria (CTC) version 2.0/Revised March 23, 1998
Noguchi Y, Yoshikawa T, Matsumoto A, et al. (1996) Are cytokines possible mediators of cancer cachexia? Surg Today 26:467–475
Keller U (1993) Pathophysiology of cancer cachexia. Support Care Cancer 1:290–294.
Mantovani G, Maccio A, Lai P, et al. (1998) Cytokine activity in cancer-related anorexia/cachexia: role of megestrol acetate and medroxyprogesterone acetate. Semin Oncol 25(2 Suppl 6): 45–52
Mantovani G, Maccio A, Mura L, et al. (2000) Serum levels of leptin and proinflammatory cytokines in patients with advancedstage cancer at different sites. J Mol Med 78:554–561
Meier U, Gressner AM (2004) Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism: review of pathobiochemical and clinical chemical aspects of leptin, ghrelin, adiponectin, and resistin. Clin Chem 50:1511–1525
Wolf I, Sadetzki S, Kanety H, et al. (2006) Adiponectin, ghrelin, and leptin in cancer cachexia in breast and colon cancer patients. Cancer 106:966–973
Simons JP, Schols AM, Campfield LA, et al. (1997) Plasma concentration of total leptin and human lung-cancer-associated cachexia. Clin Sci (Lond) 93:273–277
Brown DR, Berkowitz DE, Breslow MJ (2001) Weight loss is not associated with hyperleptinemia in humans with pancreatic cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:162–166
Hanada T, Toshinai K, Date Y, et al. (2004) Upregulation of ghrelin expression in cachectic nude mice bearing human melanoma cells. Metabolism 53:84–88
Garcia JM, Garcia-Touza M, Hijazi RA, et al. (2005) Active ghrelin levels and active to total ghrelin ratio in cancer-induced cachexia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:2920–2926
Jeon TY, Lee S, Kim HH, et al. (2004) Changes in plasma ghrelin concentration immediately after gastrectomy in patients with early gastric cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5392–5396
Crown AL, Cottle K, Lightman SL, et al. (2002) What is the role of the insulin-like growth factor system in the pathophysiology of cancer cachexia, and how is it regulated? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56:723–733
Neary NM, Small CH, Wren AM, et al. (2004) Ghrelin increases energy intake in cancer patients with impaired appetite: acute, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2832–2836
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Terashima, M., Takagane, A. et al. Ghrelin and leptin levels in cachectic patients with cancer of the digestive organs. Int J Clin Oncol 14, 315–320 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-008-0856-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-008-0856-1