Abstract
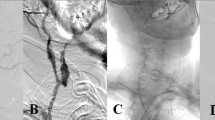
To explore the treatments for and manifestations of carotid blowout syndrome (CBS) and to further explore the critical role of high-flow bypass combined with parent artery isolation. The clinical data of nine patients with radiotherapy-related CBS who were admitted to our hospital from March 2020 to March 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. Relevant literature was reviewed. From March 2020 to March 2023, nine CBS patients were admitted to Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, including eight males and one female. Digital subtraction angiography was performed for all the patients; all the pseudoaneurysms were located at the petrous segment of the internal carotid artery. A balloon occlusion test was performed on four patients, which was tolerated by all patients. CT and MRI scans showed seven cases of osteonecrosis combined with infection and two cases of tumor recurrence. Emergency permanent parent artery occlusion was performed on six patients, aneurysm embolization was completed in one case, covered stent implantation was performed in one patient, and three cases were treated by cerebral bypass surgery (including two patients with failed interventional treatment). Rebleeding was found in two patients, and no rebleeding was found in the bypass group. Paralysis was found in three patients, and asymptomatic cerebral infarction without permanent neurologic impairment was found in three patients. Two patients died due to tumor progression. Emergency occlusion surgery is lifesaving in the acute phase of CBS. Endovascular therapy cannot prevent the progression of pseudoaneurysms or lower the recurrence rate of bleeding events. High-flow bypass combined with parent artery isolation is a safe and effective method that may facilitate further surgical treatment. Further research is warranted.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Lu HJ, Chen KW, Chen MH, Chu PY, Tai SK, Wang LW et al (2013) Predisposing factors, management, and prognostic evaluation of acute carotid blowout syndrome. J Vasc Surg 58(5):1226–1235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2013.04.056
Ketcham AS, Hoye RC (1965) Spontaneous carotid artery hemorrhage after head and neck surgery. Am J Surg 110(4):649–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9610(65)90055-3
Suarez C, Fernandez-Alvarez V, Hamoir M, Mendenhall WM, Strojan P, Quer M et al (2018) Carotid blowout syndrome: modern trends in management. Cancer Manag Res 10:5617–5628. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S180164
Joseph DL, Shumrick DL (1973) Risks of head and neck surgery in previously irradiated patients. Arch Otolaryngol 97(5):381–384. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1973.00780010393005
Sarkar S, Mehta SA, Tiwari J, Mehta AR, Mehta MS (1990) Complications following surgery for cancer of the larynx and pyriform fossa. J Surg Oncol 43(4):245–249. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.2930430411
McDonald MW, Moore MG, Johnstone PA (2012) Risk of carotid blowout after reirradiation of the head and neck: a systematic review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(3):1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.08.029
Zeng L, Wan W, Luo Q, Jiang H, Ye J (2022) Retrospective analysis of massive epistaxis and pseudoaneurysms in nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 279(6):2973–2980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-021-07111-x
Chan JY, Wong ST, Chan RC, Wei WI (2016) Extracranial/intracranial vascular bypass and craniofacial resection: new hope for patients with locally advanced recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1404–E1412. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24234
Witz M, Korzets Z, Shnaker A, Lehmann JM, Ophir D (2002) Delayed carotid artery rupture in advanced cervical cancer—a dilemma in emergency management. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 259(1):37–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00007526
Cao SM, Simons MJ, Qian CN (2011) The prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China. Chin J Cancer 30(2):114–119. https://doi.org/10.5732/cjc.010.10377
Liu F, Luo T, Jin T, Zhang J, Xiang Z, Yan R et al (2019) Advantages of using reduced-volume intensity modulated radiation therapy for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective paired study. BMC Cancer 19(1):554. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5774-2
Zhang S, Lin S, Hu L (2016) Lobaplatin combined with docetaxel neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by concurrent lobaplatin with intensity-modulated radiotherapy increases the survival of patients with high-risk lymph node positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J BUON 21(1):161–167
Wei WI, Kwong DL (2010) Current management strategy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 3(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2010.3.1.1
Mnejja W, Nouri O, Fourati N, Dhouib F, Siala W, Charfeddine I et al (2022) Current management and perspectives for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Radiother 26(5):730–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2021.11.026
Chen HC, Lin CJ, Jen YM, Juan CJ, Hsueh CJ, Lee JC et al (2004) Ruptured internal carotid pseudoaneurysm in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient with skull base osteoradionecrosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130(3):388–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2003.08.010
Hanakita S, Iijima A, Ishikawa O, Kamada K, Saito N (2011) Treatment of a cervical carotid pseudoaneurysm that occurred years after laryngectomy and irradiation of a neck tumor. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51(8):588–591. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.51.588
Lam JW, Chan JY, Lui WM, Ho WK, Lee R, Tsang RK (2014) Management of pseudoaneurysms of the internal carotid artery in postirradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Laryngoscope 124(10):2292–2296. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24721
Wei WI, Sham JS (2005) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 365(9476):2041–2054. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66698-6
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J (2019) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 394(10192):64–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0
Kodani N, Yamazaki H, Tsubokura T, Shiomi H, Kobayashi K, Nishimura T et al (2011) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for head and neck tumor: disease control and morbidity outcomes. J Radiat Res 52(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1269/jrr.10086
Soccorso G, England RJ, Godbole PP, Fisher RM, Marven SS (2012) Mind the gap: delayed diagnosis of oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula due to passage of a nasogastric tube. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 97(6):F463–F464. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2012-301929
Jong MA, Candanedo C, Gross M, Cohen JE (2019) Intervening in the acute phase of postradiation carotid blowout syndrome. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 23(2):172–177. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1676660
Mak CH, Cheng KM, Cheung YL, Chan CM (2013) Endovascular treatment of ruptured internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms after irradiation for nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Hong Kong Med J 19(3):229–36. https://doi.org/10.12809/hkmj133833
Zhan J, Zhang S, Wei X, Fu Y, Zheng J (2019) Etiology and management of nasopharyngeal hemorrhage after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 11:2171–2178. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S183537
Dong F, Li Q, Wu J, Zhang M, Zhang G, Li B et al (2016) Carotid blowout syndrome after nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy: successful treatment by internal carotid artery occlusion after stent implantation failure. Springerplus 5(1):1553. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3209-y
Wu P, Yuan G, Lu Z, Yang S, Zhu H, Zhou R et al (2021) [Extracranial/intracranial vascular bypass to control carotid artery blowout in postirradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 35(5):448-52. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.05.015
Chen YL, Wong HF, Ku YK, Wong AM, Wai YY, Ng SH (2008) Endovascular covered stent reconstruction improved the outcomes of acute carotid blowout syndrome. Experiences at a single institute. Interv Neuroradiol 14(2):23–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/15910199080140S206
Leikensohn J, Milko D, Cotton R (1978) Carotid artery rupture. Management and prevention of delayed neurologic sequelae with low-dose heparin. Arch Otolaryngol 104(6):307–10. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1978.00790060009002
Marchetta FC, Sako K, Maxwell W (1967) Complications after radical head and neck surgery performed through previously irradiated tissues. Am J Surg 114(6):835–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9610(67)90402-3
Herranz J, Sarandeses A, Fernandez MF, Barro CV, Vidal JM, Gavilan J (2000) Complications after total laryngectomy in nonradiated laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinomas. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122(6):892–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0194-59980070020-9
Chen YJ, Wang CP, Wang CC, Jiang RS, Lin JC, Liu SA (2015) Carotid blowout in patients with head and neck cancer: associated factors and treatment outcomes. Head Neck 37(2):265–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.23590
Liu HM, Yang CY, Lee CW, Wang YH, Chen YF (2013) Rapid, sequential bilateral acute carotid blowout syndrome. Neuroradiology 55(4):475–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1151-z
Liang NL, Guedes BD, Duvvuri U, Singh MJ, Chaer RA, Makaroun MS et al (2016) Outcomes of interventions for carotid blowout syndrome in patients with head and neck cancer. J Vasc Surg 63(6):1525–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2015.12.047
Chang FC, Luo CB, Lirng JF, Lin CJ, Lee HJ, Wu CC et al (2015) Endovascular management of post-irradiated carotid blowout syndrome. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0139821. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139821
Manzoor NF, Rezaee RP, Ray A, Wick CC, Blackham K, Stepnick D et al (2017) Contemporary management of carotid blowout syndrome utilizing endovascular techniques. Laryngoscope 127(2):383–390. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26144
Chang FC, Lirng JF, Luo CB, Wang SJ, Wu HM, Guo WY et al (2008) Patients with head and neck cancers and associated postirradiated carotid blowout syndrome: endovascular therapeutic methods and outcomes. J Vasc Surg 47(5):936–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2007.12.030
Patsalides A, Fraser JF, Smith MJ, Kraus D, Gobin YP, Riina HA (2010) Endovascular treatment of carotid blowout syndrome: who and how to treat. J Neurointerv Surg 2(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnis.2009.001131
Chaloupka JC, Putman CM, Citardi MJ, Ross DA, Sasaki CT (1996) Endovascular therapy for the carotid blowout syndrome in head and neck surgical patients: diagnostic and managerial considerations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17(5):843–852
Macdonald S, Gan J, McKay AJ, Edwards RD (2000) Endovascular treatment of acute carotid blow-out syndrome. J Vasc Interv Radiol 11(9):1184–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1051-0443(07)61361-x
Wong DJY, Donaldson C, Lai LT, Coleman A, Giddings C, Slater LA et al (2018) Safety and effectiveness of endovascular embolization or stent-graft reconstruction for treatment of acute carotid blowout syndrome in patients with head and neck cancer: case series and systematic review of observational studies. Head Neck 40(4):846–854. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25018
Hakime A, Khoury E, Hameg A, Liberge R, Deschamps F, Farouil G et al (2013) Polytetrafluoroethylene-covered nitinol stent graft for treatment of carotid artery blowout syndrome in head and neck cancer patients. Laryngoscope 123(7):1670–1675. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24006
Powitzky R, Vasan N, Krempl G, Medina J (2010) Carotid blowout in patients with head and neck cancer. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119(7):476–484. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348941011900709
Simizu Y (2021) Endovascular treatment of carotid blowout syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 30(8):105818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105818
Xu J, Cao Y (2014) Radiation-induced carotid artery stenosis: a comprehensive review of the literature. Interv Neurol 2(4):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1159/000363068
Huvos AG, Leaming RH, Moore OS (1973) Clinicopathologic study of the resected carotid artery. Analysis of sixty-four cases. Am J Surg. 126(4):570–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9610(73)80051-0
Acknowledgements
We express our sincere appreciation to Mrs. Zhirui Liu for the editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XT raised and designed this subject. KG and WG collected and extracted data, and drafted the article. YS, GL, XZ, and HL collected and extracted data. MS commented the content. XT revised the manuscript and approved the version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Clinical College of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Neurorehabilitation, Tianjin Medical University.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, K., Guo, W., Shang, Y. et al. Surgical treatment of carotid blowout syndrome after radiotherapy for head and neck malignant tumors: a single-center experience. Neurosurg Rev 46, 293 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-02193-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-023-02193-z