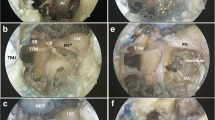
Abstract
A better understanding of the surgical anatomy of the cerebellar peduncles in different surgical approaches and their relationship with other neural structures are delineated through cadaveric dissections. We aimed to revisit the surgical anatomy of the cerebellar peduncles to describe their courses along the brain stem and the cerebellum and revise their segmental classification in surgical areas exposed through different approaches. Stepwise fiber microdissection was performed along the cerebellar tentorial and suboccipital surfaces. Multiple surgical approaches in each of the cerebellar peduncles were compared in eight silicone-injected cadaveric whole heads to evaluate the peduncular exposure areas. From a neurosurgical point of view, the middle cerebellar peduncle (MCP) was divided into a proximal cisternal and a distal intracerebellar segments; the inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) into a ventricular segment followed by a posterior curve and a subsequent intracerebellar segment; the superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP) into an initial congregated, an intermediate intraventricular, and a distal intramesencephalic segment. Retrosigmoid and anterior petrosectomy approaches exposed the junction of the MCP segments; telovelar, supratonsillar, and lateral ICP approaches each reached different segments of ICP; paramedian supracerebellar infratentorial, suboccipital transtentorial, and combined posterior transpetrosal approaches displayed the predecussation SCP within the cerbellomesencephalic fissure, whereas the telovelar approach revealed the intraventricular SCP within the superolateral recess of the fourth ventricle. Better understanding of the microsurgical anatomy of the cerebellar peduncles in various surgical approaches and their exposure limits constitute the most critical aspect for the prevention of surgical morbidity during surgery in and around the pons and the upper medulla. Our findings help in evaluating radiological data and planning an operative procedure for cerebellar peduncles.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abe H, Rhoton AL (2006) Microsurgical anatomy of the cochlear nuclei. Neurosurgery 58:728–739. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000204870.83778.A1
Akakin A, Peris-Celda M, Kilic T, Seker A, Gutierrez-Martin A, Rhoton A (2014) The Dentate nucleus and its projection system in the human cerebellum. Neurosurgery 74:401–425. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000293
Akiyama O, Matsushima K, Nunez M, Matsuo S, Kondo A, Arai H, Rhoton AL, Matsushima T (2018) Microsurgical anatomy and approaches around the lateral recess with special reference to entry into the pons. J Neurosurg 129:740–751. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.5.JNS17251
van Baarsen KM, Kleinnijenhuis M, Jbabdi S, Sotiropoulos SN, Grotenhuis JA, van Cappellen van Walsum AM (2016) A probabilistic atlas of the cerebellar white matter. Neuroimage 124:724–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.014
Bähr M, Frotscher M, Duus P (2005) Duus’ topical diagnosis in neurology: anatomy, physiology, signs, symptoms. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York
Bammer R, Acar B, Moseley ME (2003) In vivo MR tractography using diffusion imaging. Eur J Radiol 45:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0720-048X(02)00311-X
Brazis PW (1981) Cerebellar degeneration with Hodgkin’s disease: computed tomographic correlation and literature review. Arch Neurol 38:253. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1981.00510040079015
Catani M, Howard RJ, Pajevic S, Jones DK (2002) Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. Neuroimage 17:77–94. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2002.1136
Chan-Palay V, Palay SL, Brown JT, Van Itallie C (1977) Sagittal organization of olivocerebellar and reticulocerebellar projections: autoradiographic studies with 35S-methionine. Exp Brain Res 30:561–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237645
Creutzfeldt O (1995) Cortex cerebri: performance, structural, and functional organization of the cortex. Oxford University Press
Dailey AT, McKhann GM, Berger MS (1995) The pathophysiology of oral pharyngeal apraxia and mutism following posterior fossa tumor resection in children. J Neurosurg 83:467–475. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.83.3.0467
Danner H, Pfister C (1973) The development of the cerebellum in Salmo irideus (Gibbons 1855). Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 87:637–652
Deshmukh VR, Rangel-Castilla L, Spetzler RF (2014) Lateral inferior cerebellar peduncle approach to dorsolateral medullary cavernous malformation: clinical article. JNS 121:723–729. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.5.JNS132276
Dimancescu MD, Schwartzman RJ (1973) Cerebellopontine influence on the motor system: a functional and anatomical study following section of the brachium pontis in trained macaque monkeys. Trans Am Neurol Assoc 98:33–36
Duvernoy HM (1995) The human brain stem and cerebellum: surface, structure, vascularization, and threedimensional sectional anatomy, with MRI. Springer-Verlag, Wien, New York.
Fujii K, Lenkey C, Rhoton AL (1980) Microsurgical anatomy of the choroidal arteries fourth ventricle and cerebellopontine angles. J Neurosurg 52:504–524. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1980.52.4.0504
Glasser MF, Sotiropoulos SN, Wilson JA, Coalson TS, Fischl B, Andersson JL, Xu J, Jbabdi S, Webster M, Polimeni JR, Van Essen DC, Jenkinson M (2013) The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 80:105–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.127
Gocht A, Zeunert G, Laas R, Löhler J (1992) The carbohydrate epitope 3-fucosyl-N acetyllactosamine is developmentally regulated in the human cerebellum. Anat Embryol 186(6):543–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186977
Hebb MO, Spetzler RF (2010) Lateral transpeduncular approach to intrinsic lesions of the rostral pons. Oper Neurosurg 66:ons-26-ons-29. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000350865.85697.18
Hendelman W (2006) Atlas of functional neuroanatomy, 2nd edn. CRC Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Hirsch JF, Renier D, Czernichow P, Benveniste L, Pierre-Kahn A (1979) Medulloblastoma in childhood. Survival and functional results. Acta Neurochir 48:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406016
Hitotsumatsu T, Matsushima T, Inoue T (2003) Microvascular decompression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: three surgical approach variations: technical note. Neurosurgery 53:1436–1443. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000093431.43456.3B
Holmes G (1922) The Croonian lectures on the clinical symptoms of cerebellar disease and their interpretation. Lancet (London, England) ii: 59-65, 111–115
Hoover JE, Strick PL (1999) The organization of cerebellar and basal ganglia outputs to primary motor cortex as revealed by retrograde transneuronal transport of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Neurosci 19:1446–1463. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01446.1999
Kawase T, Toya S, Shiobara R, Mine T (1985) Transpetrosal approach for aneurysms of the lower basilar artery. J Neurosurg 63:857–861. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1985.63.6.0857
Kirino TFT (2000) Combined transhorizontal-supracerebellar approach for microvascular decompression of trigeminal neuralgia. Br J Neurosurg 14:531–534. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690020005536
Klingler J (1935) Erleichterung der makrokopischen Präparation des Gehirns durch den Gefrierprozess. Orell Füssli.
Law N, Greenberg M, Bouffet E, Taylor MD, Laughlin S, Strother D, Fryer C, McConnell D, Hukin J, Kaise C, Wang F, Mabbott DJ (2012) Clinical and neuroanatomical predictors of cerebellar mutism syndrome. Neuro Oncol 14:1294–1303. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos160
Lawton MT, Quiñones-Hinojosa A, Jun P (2006) The supratonsillar approach to the inferior cerebellar peduncle: anatomy, surgical technique, and clinical application to cavernous malformations. Oper Neurosurg 59:ONS244–ONS252. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000232767.16809.68
Leonetti JP, Anderson DE, Newell DJ, Smith PG (1993) Posterior internal auditory canal closure following the retrosigmoid approach to the cerebellopontine angle. Am J Otol 14:31–33
Martins C, Yasuda A, Campero A, Ulm AJ, Tanriover N, Rhoton A (2005) Microsurgical anatomy of the dural arteries. Oper Neurosurg 56:ONS-211-2ONS-251. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000144823.94402.3D
Matsushima K, Yagmurlu K, Kohno M, Rhoton AL (2016) Anatomy and approaches along the cerebellar-brainstem fissures. JNS 124:248–263. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.2.JNS142707
Matsushima T, Abe H, Kawashima M, Inoue T (2012) Exposure of the wide interior of the fourth ventricle without splitting the vermis: importance of cutting procedures for the tela choroidea. Neurosurg Rev 35:563–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0384-3
Matsushima T, Rhoton AL, Lenkey C (1982) Microsurgery of the fourth ventricle: Part 1. Neurosurgery 11:631–667. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198211000-00008
Mussi ACM, Rhoton AL (2000) Telovelar approach to the fourth ventricle: microsurgical anatomy. J Neurosurg 92:812–823. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.92.5.0812
Naidich TP, Duvernoy HM, Delman BN, Sorensen AG, Kollias SS, Haacke EM (2009) Duvernoy’s atlas of the human brain stem and cerebellum: high-field MRI, surface anatomy, internal structure, vascularization and 3D sectional anatomy. Springer, Wien, New York.
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, van Huijzen C (2008) The human central nervous system. Springer, Berlin
Ogata N, Yonekawa Y (1997) Paramedian supracerebellar approach to the upper brain stem and peduncular lesions. Neurosurgery 40:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199701000-00023
Ohue S, Fukushima T, Friedman AH, Kumon Y, Ohnishi T (2010) Retrosigmoid suprafloccular transhorizontal fissure approach for resection of brainstem cavernous malformation. Oper Neurosurg 66:ons306–ons313. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000369703.67562.BB
Palesi F, Tournier J-D, Calamante F, Muhlert N, Castellazzi G, Chard D, D’Angelo E, Wheeler-Kingshott CAM (2015) Contralateral cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathways with prominent involvement of associative areas in humans in vivo. Brain Struct Funct 220:3369–3384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0861-2
Perrini P, Tiezzi G, Castagna M, Vannozzi R (2013) Three-dimensional microsurgical anatomy of cerebellar peduncles. Neurosurg Rev 36:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0417-y
Rodríguez-Mena R, Piquer-Belloch J, Llácer-Ortega JL, Riesgo-Suárez P, Rovira-Lillo V (2017) Anatomía de los pedúnculos cerebelosos en 3D basada en microdisección de fibras y demostración a través de tractografía. Neurocirugía 28:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucir.2016.10.001
Salamon N, Sicotte N, Drain A, Frew A, Alger JR, Jen J, Perlman S, Salamon G (2007) White matter fiber tractography and color mapping of the normal human cerebellum with diffusion tensor imaging. J Neuroradiol 34:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2007.03.002
Samii M, Draf W, Lang J (1989) Surgery of the skull base: an interdisciplinary approach. Springer, Berlin
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN (1995) Prefrontal cortex projections to the basilar pons in rhesus monkey: implications for the cerebellar contribution to higher function. Neurosci Lett 199:175–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3940(95)12056-A
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN (1997) The cerebrocerebellar system. In: Bradley RJ, Harris RA, Jenner P (eds) International Review of Neurobiology, 1st edn. Elsevier, USA, pp 31–60
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN (2006) Fiber pathways of the brain. Oxford University Press, New York
Shimizu S, Tanaka R, Rhoton AL, Fukushima Y, Osawa S, Kawashima M, Oka H, Fujii K (2006) Anatomic dissection and classic three-dimensional documentation: a unit of education for neurosurgical anatomy revisited. Neurosurgery 58:E1000–E1000. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000210247.37628.43
Shimoji K, Miyajima M, Karagiozov K, Yatomi K, Matsushima T, Arai H (2009) Surgical considerations in fourth ventricular ependymoma with the transcerebellomedullary fissure approach in focus. Childs Nerv Syst 25:1221–1228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-0835-5
Shin H-J, Cho B-K, Jung H-W, Wang K-C (1998) Pediatric pineal tumors: need for a direct surgical approach and complications of the occipital transtentorial approach. Child’s Nervous System 14:174–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003810050206
Shirane R, Kumabe T, Yoshida Y, Su C, Jokura H, Umezawa K, Yoshimoto T (2001) Surgical treatment of posterior fossa tumors via the occipital transtentorial approach: evaluation of operative safety and results in 14 patients with anterosuperior cerebellar tumors. J Neurosurg 94:927–935. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.94.6.0927
Snell RS (2014) Neuroanatomía clínica. Wolters Kluwer, Barcelona
Standring S, Gray H (2009) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice, 40. ed., reprinted. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Edinburgh
Suzuki L, Coulon P, Sabel-Goedknegt EH, Ruigrok TJH (2012) Organization of cerebral projections to identified cerebellar zones in the posterior cerebellum of the rat. J Neurosci 32:10854–10869. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0857-12.2012
Tanriover N, Ulm AJ, Rhoton AL, Yasuda A (2004) Comparison of the transvermian and telovelar approaches to the fourth ventricle. J Neurosurg 101:484–498. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2004.101.3.0484
Tayebi Meybodi A, Lawton MT, Tabani H, Benet A (2017) Tonsillobiventral fissure approach to the lateral recess of the fourth ventricle. J Neurosurg 127:768–774. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.JNS16855
Ulm AJ, Tanriover N, Kawashima M, Campero A, Bova FJ, Rhoton AL (2004) Microsurgical approaches to the perimesencephalic cisterns and related segments of the posterior cerebral artery: comparison using a novel application of image guidance. Neurosurgery 54:1313–1328. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000126129.68707.E7
Watson C, Paxinos G, Puelles L (2012) The mouse nervous system. Academic Press, Amsterdam
Yagmurlu K, Middlebrooks EH, Tanriover N, Rhoton AL (2016) Fiber tracts of the dorsal language stream in the human brain. J Neurosurg 124:1396–1405. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.5.JNS15455
Yagmurlu K, Rhoton AL, Tanriover N, Bennett JA (2014) Three-dimensional microsurgical anatomy and the safe entry zones of the brainstem. Operative Neurosurgery 10:602–620. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000466
Yaşargil MG, Adamson TE, Yaşargil MG (1994) CNS tumors: surgical anatomy, neuropathology, neuroradiology, neurophysiology, clinical considerations, operability, treatment options. Georg Thieme Verlag ; Thieme Medical Publishers, Stuttgart ; New York : New York
Acknowledgements
We thank Stryker Medical Technology Co and company’s country representation in Turkey, for providing the electrically powered instruments, including the drills, to the Microsurgical Neuroanatomy Laboratory in Istanbul University—Cerrahpasa, Department of Neurosurgery.
We also thank Ufuk Köse for providing artwork.
Data were provided in part by the Human Connectome Project, WU-Minn Consortium (Principal Investigators: David Van Essen and Kamil Ugurbil; 1U54MH091657) funded by the 16 NIH Institutes and Centers that support the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research; and by the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience at Washington University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OB: cadaver dissections, conducted study method, literature search, collected data, writing of the manuscript, revised the manuscript and final approval; SB: cadaver dissections, literature search, revised the manuscript and final approval; MM: some cadaveric dissections, revised the manuscript and final approval; NB: some cadaveric dissections, revised the manuscript and final approval; BB: some cadaveric dissections, revised the manuscript and final approval; EM: 3D radiologic figures, revised the manuscript and final approval; FO: study supervision, revised the manuscript and final approval; NT: conceived the idea, study supervision, revised the manuscript and final approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethics committee approval is not required as it is an anatomical study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baran, O., Baydin, S., Mirkhasilova, M. et al. Microsurgical anatomy and surgical exposure of the cerebellar peduncles. Neurosurg Rev 45, 2095–2117 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01701-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01701-3