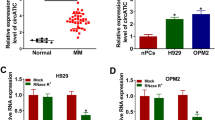
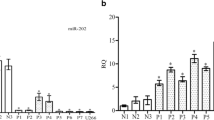
Abstract
Berberine (BBR), a traditional Chinese herbal medicine compound, has emerged as a novel class of anti-tumor agent. Our previous microRNA (miRNA) microarray demonstrated that miR-106b/25 was significantly down-regulated in BBR-treated multiple myeloma (MM) cells. Here, systematic integration showed that miR-106b/25 cluster is involved in multiple cancer-related signaling pathways and tumorigenesis. MiREnvironment database revealed that multiple environmental factors (drug, ionizing radiation, hypoxia) affected the miR-106b/25 cluster expression. By targeting the seed region in the miRNA, tiny anti-mir106b/25 cluster (t-anti-mir106b/25 cluster) significantly induced suppression in cell viability and colony formation. Western blot validated that t-anti-miR-106b/25 cluster effectively inhibited the expression of P38 MAPK and phospho-P38 MAPK in MM cells. These findings indicated the miR-106b/25 cluster functioned as oncogene and might provide a novel molecular insight into MM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi J, Qiu L, Chang H (2014) Micro-RNAs, new performers in multiple myeloma bone marrow microenvironment. Biomarker Res 2:10
Bi C, Chng WJ (2014) MicroRNA: important player in the pathobiology of multiple myeloma. Biomed Res Int 2014:521586
Brett JO, Renault VM, Rafalski VA, Webb AE, Brunet A (2011) The microRNA cluster miR-106b ∼25 regulates adult neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Aging 3(2):108–124
Chen FL, Yang ZH, Liu Y, Li LX, Liang WC, Wang XC, Zhou WB, Yang YH, Hu RM (2008) Berberine inhibits the expression of TNFalpha, MCP-1, and IL-6 in AcLDL-stimulated macrophages through PPARgamma pathway. Endocrine 33(3):331–337
Cheng CJ, Saltzman WM, Slack FJ (2013) Canonical and non-canonical barriers facing antimiR cancer therapeutics. Curr Med Chem 20(29):3582–3593
de Mel S, Lim SH, Tung ML, Chng WJ (2014) Implications of heterogeneity in multiple myeloma. Biomed Res Int 2014:232546
Di Martino MT, Gulla A, Gallo Cantafio ME, Altomare E, Amodio N, Leone E, Morelli E, Lio SG, Caracciolo D, Rossi M, Frandsen NM, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P (2014) In vitro and in vivo activity of a novel locked nucleic acid (LNA)-inhibitor-miR-221 against multiple myeloma cells. PLoS One 9(2):e89659
Fabre C, Mimura N, Bobb K, Kong SY, Gorgun G, Cirstea D, Hu Y, Minami J, Ohguchi H, Zhang J, Meshulam J, Carrasco RD, Tai YT, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2012) Dual inhibition of canonical and noncanonical NF-kappaB pathways demonstrates significant antitumor activities in multiple myeloma. Clin Can Res 18(17):4669–4681
Feng M, Luo X, Gu C, Fei J (2015a) Seed targeting with tiny anti-miR-155 inhibits malignant progression of multiple myeloma cells. J Drug Target 23(1):59–66
Feng M, Luo X, Gu C, Li Y, Zhu X, Fei J (2015b) Systematic analysis of berberine-induced signaling pathway between miRNA clusters and mRNAs and identification of miR-99a approximately 125b cluster function by seed-targeting inhibitors in multiple myeloma cells. RNA Biol 12(1):82–91
Guaman Ortiz LM, Tillhon M, Parks M, Dutto I, Prosperi E, Savio M, Arcamone AG, Buzzetti F, Lombardi P, Scovassi AI (2014) Multiple effects of berberine derivatives on colon cancer cells. Biomed Res Int 2014:924585
Glushkova OV, Khrenov MO, Novoselova TV, Lunin SM, Parenyuk SB, Alekseev SI, Fesenko EE, Novoselova EG (2015) The role of the NF-kappaB, SAPK/JNK, and TLR4 signalling pathways in the responses of RAW 264.7 cells to extremely low-intensity microwaves. Int J Radiat Biol 91(4):321–328
Hata A, Lieberman J (2015) Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis and gene silencing in cancer. Sci Signal 8(368):re3
He J, Liu Z, Zheng Y, Qian J, Li H, Lu Y, Xu J, Hong B, Zhang M, Lin P, Cai Z, Orlowski RZ, Kwak LW, Yi Q, Yang J (2012) p38 MAPK in myeloma cells regulates osteoclast and osteoblast activity and induces bone destruction. Cancer Res 72(24):6393–6402
Hebraud B, Magrangeas F, Cleynen A, Lauwers-Cances V, Chretien ML, Hulin C, Leleu X, Yon E, Marit G, Karlin L, Roussel M, Stoppa AM, Belhadj K, Voillat L, Garderet L, Macro M, Caillot D, Mohty M, Facon T, Moreau P, Attal M, Munshi N, Corre J, Minvielle S, Avet-Loiseau H (2015) Role of additional chromosomal changes in the prognostic value of t (4;14) and del(17p) in multiple myeloma: the IFM experience. Blood 125(13):2095–2100
Hideshima T, Akiyama M, Hayashi T, Richardson P, Schlossman R, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2003) Targeting p38 MAPK inhibits multiple myeloma cell growth in the bone marrow milieu. Blood 101(2):703–705
Jantova SCL, Cernakova M, Kost’alova D (2003) Effect of berberine on proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in HeLa and L1210 cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 55:1143–1149
Jin P, Zhang C, Li N (2015) Berberine exhibits antitumor effects in human ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 15(4):511–516
Kim S, Kim Y, Kim JE, Cho KH, Chung JH (2008) Berberine inhibits TPA-induced MMP-9 and IL-6 expression in normal human keratinocytes. Phytomedicine 15(5):340–347
Kluiver J, Kroesen BJ, Poppema S, van den Berg A (2006) The role of microRNAs in normal hematopoiesis and hematopoietic malignancies. Leukemia 20(11):1931–1936
Kobayashi T, Kuroda J, Ashihara E, Oomizu S, Terui Y, Taniyama A, Adachi S, Takagi T, Yamamoto M, Sasaki N, Horiike S, Hatake K, Yamauchi A, Hirashima M, Taniwaki M (2010) Galectin-9 exhibits anti-myeloma activity through JNK and p38 MAP kinase pathways. Leukemia 24(4):843–850
Li Q, Zou C, Zou C, Han Z, Xiao H, Wei H, Wang W, Zhang L, Zhang X, Tang Q, Zhang C, Tao J, Wang X, Gao X (2013) MicroRNA-25 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in colon cancer by targeting Smad7. Cancer Lett 335(1):168–174
Li Y, Zhu X, Gu J, Dong D, Yao J, Lin C, Huang K, Fei J (2010) Anti-miR-21 oligonucleotide sensitizes leukemic K562 cells to arsenic trioxide by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Sci 101(4):948–954
Murphy BL, Obad S, Bihannic L, Ayrault O, Zindy F, Kauppinen S, Roussel MF (2013) Silencing of the miR-17 ∼92 cluster family inhibits medulloblastoma progression. Cancer Res 73(23):7068–7078
Nguyen AN, Stebbins EG, Henson M, O’Young G, Choi SJ, Quon D, Damm D, Reddy M, Ma JY, Haghnazari E, Kapoun AM, Medicherla S, Protter A, Schreiner GF, Kurihara N, Anderson J, Roodman GD, Navas TA, Higgins LS (2006) Normalizing the bone marrow microenvironment with p38 inhibitor reduces multiple myeloma cell proliferation and adhesion and suppresses osteoclast formation. Exp Cell Res 312(10):1909–1923
Pan ST, Qin Y, Zhou ZW, He ZX, Zhang X, Yang T, Yang YX, Wang D, Qiu JX, Zhou SF (2015) Plumbagin induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK- and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:1601–1626
Peng H, Peng T, Wen J, Engler DA, Matsunami RK, Su J, Zhang L, Chang CC, Zhou X (2014) Characterization of p38 MAPK isoforms for drug resistance study using systems biology approach. Bioinformatics 30(13):1899–1907
Petrocca F, Vecchione A, Croce CM (2008) Emerging role of miR-106b-25/miR-17-92 clusters in the control of transforming growth factor beta signaling. Cancer Res 68(20):8191–8194
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Riccardi L, Fornari A, Song MS, Hobbs RM, Sportoletti P, Varmeh S, Egia A, Fedele G, Rameh L, Loda M, Pandolfi PP (2010) Identification of the miR-106b ∼25 microRNA cluster as a proto-oncogenic PTEN-targeting intron that cooperates with its host gene MCM7 in transformation. Sci Signal 3(117):ra29
Rocci A, Hofmeister CC, Pichiorri F (2014) The potential of miRNAs as biomarkers for multiple myeloma. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 14(8):947–959
Röllig C, Knop S, Bornhäuser M (2014) Multiple myeloma. Lancet 385(9983):2197–2208
Schmid CA, Craig VJ, Muller A, Flori M (2013) The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of hematopoietic malignancies. Curr Pharm Des 19(7):1201–1210
Smith AL, Iwanaga R, Drasin DJ, Micalizzi DS, Vartuli RL, Tan AC, Ford HL (2012) The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-beta signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer. Oncogene 31(50):5162–5171
Staedel C, Varon C, Nguyen PH, Vialet B, Chambonnier L, Rousseau B, Soubeyran I, Evrard S, Couillaud F, Darfeuille F (2015) Inhibition of gastric tumor cell growth using seed-targeting LNA as specific, long-lasting microRNA inihibitor. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 4:e246
Steinbrunn T, Stühmer T, Sayehli C, Chatterjee M, Einsele H, Bargou RC (2012) Combined targeting of MEK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signalling in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 159(4):430–440
Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E, Kai M (2013) Epigenetic alteration and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Front Genet 4:258
Tang Q, Zhong H, Xie F, Xie J, Chen H, Yao G (2014) Expression of miR-106b-25 induced by salvianolic acid B inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in HK-2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 741:97–103
Xu P, Cai F, Liu X, Guo L (2015) Sesamin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced proliferation and invasion through the p38-MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep 33(6):3117–3123
Yang J, He J, Wang J, Cao Y, Ling J, Qian J, Lu Y, Li H, Zheng Y, Lan Y, Hong S, Matthews J, Starbuck MW, Navone NM, Orlowski RZ, Lin P, Kwak LW, Yi Q (2012) Constitutive activation of p38 MAPK in tumor cells contributes to osteolytic bone lesions in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 26(9):2114–2123
Zhang BJ, Xu D, Guo Y, Ping J, Chen LB, Wang H (2008) Protection by and anti-oxidant mechanism of berberine against rat liver fibrosis induced by multiple hepatotoxic factors. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 35(3):303–309
Zhao ZN, Bai JX, Zhou Q, Yan B, Qin WW, Jia LT, Meng YL, Jin BQ, Yao LB, Wang T, Yang AG (2012) TSA Suppresses miR-106b-93-25 cluster expression through downregulation of MYC and inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human EMC. PLoS One 7(9):e45133
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81170496), Research Project for Practice Development of National TCM Clinical Research Bases (no. JDZX2015119), and Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province (no. 2012B031800474, 2013B021800151, 2014A020212729).
Authors’ contributions
JF conceived and designed the experiments. CG, TL, and ZY performed the experiments. JF and SC analyzed the data. JS and JF contributed reagents, materials, and analytical tools. JF and YZ wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
This article forms part of a special issue of Functional and Integrative Genomics entitled “miRNA in model and complex organisms” (Issue Editors: Hikmet Budak and Baohong Zhang)
Chunming Gu, Tianfu Li and Zhao Yin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, C., Li, T., Yin, Z. et al. Integrative analysis of signaling pathways and diseases associated with the miR-106b/25 cluster and their function study in berberine-induced multiple myeloma cells. Funct Integr Genomics 17, 253–262 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0519-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0519-7