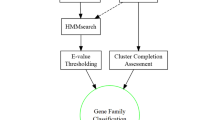
Abstract
Cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) is comprised of two subspecies: japonica and indica. Polymorphism levels between putative homologues were determined for genes whose japonica homologue had been classified into functional categories using the Gene Ontology (GO) system. Genes were partitioned into below-average and above-average polymorphism groups, and then the set of genes having each GO term was checked for the randomness of its distribution into these polymorphism groups using a series of False Discovery Rate (FDR) tests. The robustness of the conclusions was enhanced by employing different cutoff values and sequence samplings in the FDR tests. Significant nonrandom polymorphism distributions were found for protein-coding sequences in many GO categories. In contrast, a random distribution for nearly all GO terms was seen with intron sequences. These results were extended by measuring the nonsynonymous to synonymous codon usage ratio (dN/dS) using a permutation test, which showed that some above-average polymorphism GO categories also had a high proportion of genes with a dN/dS ratio greater than one, suggesting positive selection on these GO categories during indica–japonica differentiation. An analysis of predominant gene names in the significant GO categories divided them into four functional classes: production of defense-related compounds, cell wall, cell signaling, and transcription factors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JV, Davis DG (2004) Abiotic stress alters transcript profiles and activity of glutathione S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in Euphorbia esula. Physiol Plant 1203:421–433
Andreasson E, Jenkins T, Brodersen P, Thorgrimsen S, Petersen NH, Zhu S, Qiu JL, Micheelsen P, Rocher A, Petersen M, Newman MA, Bjorn Nielsen H, Hirt H, Somssich I, Mattsson O, Mundy J (2005) The MAP kinase substrate MKS1 is a regulator of plant defense responses. EMBO J 24:2579–2589
Aris-Brosou S (2005) Determinants of adaptive evolution at the molecular level: the extended complexity hypothesis. Mol Biol Evol 22:200–209
Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Sato S, Tabata S (2004) Characteristics of the Lotus japonica gene repertoire deduced from large-scale expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis. Plant Mol Biol 54:405–414
Ayliffe MA, Lagudah ES (2004) Molecular genetics of disease resistance in cereals. Ann Bot 94:765–773
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Benjamini Y, Hocheberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Bennetzen JL, Coleman C, Liu R, Ma J, Ramakrishna W (2004) Consistent over-estimation of gene number in complex plant genomes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:732–736
Bergelson J, Kreitman M, Stahl EA, Tian D (2001) Evolutionary dynamics of plant R-genes. Science 292:2281–2285
Breslin T, Eden P, Krogh M (2004) Comparing functional annotation analyses with Catmap. BMC Bioinformatics 5:193
Buchanan CD, Lim S, Salzman RA, Kagiampakis I, Morishige DT, Weers BD, Klein RR, Pratt LH, Cordonnier-Pratt MM, Klein PE, Mullet JE (2005) Sorghum bicolor's transcriptome response to dehydration, high salinity and ABA. Plant Mol Biol 85: 99–720
The Carbohydrate-Active enZYmes server (2006). http://www.afmb.cnrs-rs.fr/%7Ecazy/CAZY/index.html
Cheng CY, Motohashi R, Ohtsuo E (2003) Polyphyletic origin of cultivated rice: based on the interspersion pattern of SINEs. Mol Biol Evol 20:67–75
Coberly LC, Rausher MD (2003) Analysis of a chalcone synthase mutant in Ipomoea purpurea reveals a novel function for flavonoids: amelioration of heat stress. Mol Ecol 12:1113–1124
Cruveiller S, Jabbari K, Clay O, Bernardi G (2004) Incorrectly predicted genes in rice? Gene 333:187–188
Feltus FA, Wan J, Schulze SR, Estill JC, Jiang N, Paterson AH (2004) An SNP resource for rice genetics and breeding based on subspecies indica and japonica genome alignments. Genome Res 14:1812–1819
Gamas P, de Carvalho Niebel F, Lescure N, Cullimore J (1996) Use of a subtractive hybridization approach to identify new Medicago truncatula genes induced during root nodule development. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:233–242
García-Olmedo F, Molina A, Alamillo JM, Rodríguez-Palenzuela P (1998) Plant defense peptides. Biopolymers 47:479–491
Gene Ontology Consortium (2000) Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Glaszmann JC (1987) Isozymes and classification of Asian rice varieties. Theor Appl Genet 74:21–30
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296:92–100
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JDG (1996) Resistance gene-dependent plant defense responses. Plant Cell 8:1773–1779
Han B, Xue Y (2003) Genome-wide intraspecific DNA-sequence variations in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:134–138
Ikehashi H, Araki H (1986) Genetics of F1 sterility in rice. In: Rice genetics. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, The Philippines, pp 119–132
Ina Y (1996) Patterns of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions: an indicator of mechanisms of molecular evolution. J Genet 75:91–115
Jabbari K, Cruveiller S, Clay O, Le Saux J, Bernardi G (2004) The new genes of rice: a closer look. Trends Plant Sci 9:281–285
Jia L, Clegg MT, Jiang T (2004) Evolutionary dynamics of the DNA-binding domains in putative R2R3-MYB genes identified from rice subspecies indica and japonica. Plant Physiol 134:575–585
Kato S, Kosaka H, Hara S (1928) On the affinity of rice varieties as shown by fertility of hybrid plants. Bull Sci Fac Agric Kyushu Univ, Fukuoka, Japan, 3:132–147
Khush GS (1997) Origin, dispersal, cultivation, and variation of rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:25–34
Kikuchi S, Satoh K, Nagata T, Kawagashira N, Doi K, Kishimoto N, Yazaki J, Ishikawa M, Yamada H, Ooka H, Hotta I, Kojima K, Namiki T, Ohneda E, Yahagi W, Suzuki K, Li CJ, Ohtsuki K, Shishiki T, Otomo Y, Murakami K, Iida Y, Sugano S, Fujimura T, Suzuki Y, Tsunoda Y, Kurosaki T, Kodama T, Masuda H, Kobayashi M, Xie Q, Lu M, Narikawa R, Sugiyama A, Mizuno K, Yokomizo S, Niikura J, Ikeda R, Ishibiki J, Kawamata M, Yoshimura A, Miura J, Kusumegi T, Oka M, Ryu R, Ueda M, Matsubara K, Kawai J, Carninci P, Adachi J, Aizawa K, Arakawa T, Fukuda S, Hara A, Hashizume W, Hayatsu N, Imotani K, Ishii Y, Itoh M, Kagawa I, Kondo S, Konno H, Miyazaki A, Osato N, Ota Y, Saito R, Sasaki D, Sato K, Shibata K, Shinagawa A, Shiraki T, Yoshino M, Hayashizaki Y, Yasunishi A (2003) Collection, mapping, and annotation of over 28,000 cDNA clones from japonica rice. Science 301:376–9. (http://cdna01.dna.affrc.go.jp/cDNA/)
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kranz H, Scholz K, Weisshaar B (2000) c-MYB oncogene-like genes encoding three MYB repeats occur in all major plant lineages. Plant J 21:231–235
Kroymann J, Donnerhacke S, Schnabelrauch D, Mitchell-Olds T (2003) Evolutionary dynamics of an Arabidopsis insect resistance quantitative trait locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(Suppl 2):14587–14592
Lehmann P (2002) Structure and evolution of plant disease resistance genes. J Appl Genet 43:403–414
Ma J, Bennetzen JL (2004) Rapid recent growth and divergence of rice nuclear genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12404–12410
Mackill DJ (1995) Classifying japonica rice cultivars with RAPD markers. Crop Sci 35:885–894
Minglin L, Yuxiu Z, Tuanyao C (2005) Identification of genes up-regulated in response to Cd exposure in Brassica juncea L. Gene 363:151–158
Misako K, Kouichi M (2004) Caffeine synthase and related methyltransferases in plants. Front Biosci 9:1833–1842
Morishima H, Oka HI (1981) Phylogenetic differentiation of cultivated rice, XXII. Numerical evaluation of the indica–japonica differentiation. Jpn J Breed 31:402–413
Nielsen R, Bustamante C, Clark AG, Glanowski S, Sackton TB, Hubisz MJ, Fledel-Alon A, Tanenbaum DM, Civello D, White TJ, Sninsky JJ, Adams MD, Cargill M (2005) A scan for positively selected genes in the genomes of humans and chimpanzees. PLoS Biol 3:e170
Ni J, Colowit PM, Mackill DJ (2002) Evaluation of genetic diversity in rice subspecies using microsatellite markers. Crop Sci 42:6001–6007
Oh IS, Park AR, Bae MS, Kwon SJ, Kim YS, Lee JE, Kang NY, Lee S, Cheong H, Park OK (2005) Secretome analysis reveals an Arabidopsis lipase involved in defense against Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Cell 17:2832–2847
Oka HI (1988) Origin of cultivated rice. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo
Passardi F, Cosio C, Penel C, Dunand C (2005) Peroxidases have more functions than a Swiss army knife. Plant Cell Rep 24:255–265
Rowland O, Ludwig AA, Merrick CJ, Baillieul F, Tracy FE, Durrant WE, Fritz-Layl L, Nekrasov V, Sjolander K, Yoshioka H, Jones JD (2005) Functional analysis of Avr9/Cf-9 rapidly elicited genes identifies a protein kinase, ACIK1, that is essential for full Cf-9-dependent disease resistance in tomato. Plant Cell 171:295–310
Ruepp A, Zollner A, Maier D, Albermann K, Hani J, Mokrejs M, Tetko I, Guldener U, Sakai T, Wada T, Ishiguro S, Okada K (2000) RPT2, a signal transducer of the phototropic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:225–236
Sandhu D, Gao H, Cianzio S, Bhattacharyya MK (2004) Deletion of a disease resistance nucleotide-binding-site leucine-rich- repeat-like sequence is associated with the loss of the Phytophthora resistance gene Rps4 in soybean. Genetics 168:2157–2167
Shen YJ, Jiang H, Jin JP, Zhang ZB, Xi B, He YY, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu QB, Liu HJ, Chen DH, Gao JH, Huang H, Shi TL, Yang ZN (2004) Development of genome-wide DNA polymorphism database for map-based cloning of rice genes. Plant Physiol 135:1198–1205
Smith TF, Waterman MS (1981) Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol 147:195–197. http://www.phrap.org/phredphrap/swat.html
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9440–9445
Takemoto D, Hayashi M, Doke N, Nishimura M, Kawakita K (1999) Molecular cloning of a defense-response-related cytochrome P450 gene from tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol 40:1232–1242
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
van der Biezen EA, Jones JD (1998) The NB-ARC domain: a novel signaling motif shared by plant resistance gene products and regulators of cell death in animals. Curr Biol 26:R226–R227
Verica JA, Chae L, Tong H, Ingmire P, He ZH (2003) Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression of a cluster of tandemly arrayed cell wall-associated kinase-like kinase genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1732–1746
Weisstein EW (1999) Bonferroni correction. From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. (http://www.mathworld.wolfram.com/BonferroniCorrection.html)
Yamanaka S, Nakamura I, Nakai H, Sato YI (2003) Dual origin of the cultivated rice based on molecular markers of newly collected annual and perennial accessions of wild rice species, Oryza nivara and O. rufipogon. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50:529–538
Yamanaka S, Nakamura I, Watanabe KN, SatoY (2004) Identification of SNPs in the waxy gene among glutinous rice cultivars and their evolutionary significance during the domestication process of rice. Theor Appl Genet 108:1200–1204
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci 13:555–556
Yang Z, Nielsen R (1998) Synonymous and nonsynonymous rate variation in nuclear genes of mammals. J Mol Evol 46:409–418
Yang GX, Jan A, Shen SH, Yazaki J, Ishikawa M, Shimatani Z, Kishimoto N, Kikuchi S, Matsumoto H, Komatsu S (2004) Microarray analysis of brassinosteroids- and gibberellin-regulated gene expression in rice seedlings. Mol Genet Genomics 27:468–478
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Cao M, Liu J, Sun J, Tang J, Chen Y, Huang X, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong L, Geng J, Han Y, Li L, Li W, Hu G, Huang X, Li W, Li J, Liu Z, Li L, Liu J, Qi Q, Liu J, Li L, Li T, Wang X, Lu H, Wu T, Zhu M, Ni P, Han H, Dong W, Ren X, Feng X, Cui P, Li X, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai W, Xu Z, Zhang J, He S, Zhang J, Xu J, Zhang K, Zheng X, Dong J, Zeng W, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren X, Chen X, He J, Liu D, Tian W, Tian C, Xia H, Bao Q, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao W, Li P, Chen W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Hu J, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang G, Xiong Y, Li Z, Mao L, Zhou C, Zhu Z, Chen R, Hao B, Zheng W, Chen S, Guo W, Li G, Liu S, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu L, Yuan L, Yang H (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Yu J, Wang J, Lin W, Li S, Li H, Zhou J, Ni P, Dong W, Hu S, Zeng C, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Li R, Xu Z, Li S, Li X, Zheng H, Cong L, Lin L, Yin J, Geng J, Li G, Shi J, Liu J, Lv H, Li J, Wang J, Deng Y, Ran L, Shi X, Wang X, Wu Q, Li C, Ren X, Wang J, Wang X, Li D, Liu D, Zhang X, Ji Z, Zhao W, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Bao J, Han Y, Dong L, Ji J, Chen P, Wu S, Liu J, Xiao Y, Bu D, Tan J, Yang L, Ye C, Zhang J, Xu J, Zhou Y, Yu Y, Zhang B, Zhuang S, Wei H, Liu B, Lei M, Yu H, Li Y, Xu H, Wei S, He X, Fang L, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Huang X, Su Z, Tong W, Li J, Tong Z, Li S, Ye J, Wang L, Fang L, Lei T, Chen C, Chen H, Xu Z, Li H, Huang H, Zhang F, Xu H, Li N, Zhao C, Li S, Dong L, Huang Y, Li L, Xi Y, Qi Q, Li W, Zhang B, Hu W, Zhang Y, Tian X, Jiao Y, Liang X, Jin J, Gao L, Zheng W, Hao B, Liu S, Wang W, Yuan L, Cao M, McDermott J, Samudrala R, Wang J, Wong GK, Yang H (2005) The genomes of Oryza sativa: a history of duplications. PLoS Biol 3:e38
Yuan Q, Ouyang S, Wang A, Zhu W, Maiti R, Lin H, Hamilton J, Haas B, Sultana R, Cheung F, Wortman J, Buell CR (2005) The Institute for Genomic Research Osa1 Rice Genome Annotation Database. Plant Physiol 138:18–26
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Zhang QF, Maroof MAS, Lu TY, Shen BZ (1992) Genetic diversity and differentiation of indica and japonica rice detected by RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 83:495–499
Zhang W, Peumans WJ, Barre A, Astoul CH, Rovira P, Rouge P, Proost P, Truffa-Bachi P, Jalali AA, Van Damme EJ (2000a) Isolation and characterization of a jacalin-related mannose-binding lectin from salt-stressed rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Planta 2106:970–978
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000b) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7:203–214
Zhong S, Tian L, Storch KF, Wong WH (2004) Comparative analysis of gene sets in the Gene Ontology space under the multiple hypothesis testing framework. Proc IEEE Comput Syst Bioinform Conf 3:425–435
Zhu Q, Ge S (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among A-genome species of the genus Oryza revealed by intron sequences of four nuclear genes. New Phytol 167:249–265
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by The National Institutes of Health, grant number 1 R15 GM069408-01. We thank Jacqueline E. Roach for editorial and coaching services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below are the links to the electronic supplementary materials:
Supplementary Fig. 1
Summary of FDR experiments for CDS data. GO term numbers and their corresponding names can be found in Table 2. A + above the bar indicates a significant (q-value < = 0.05) excess of genes in the above-average polymorphism group; a - indicates an excess of genes in the below-average- polymorphism group; a 0 indicates a random distribution of genes; a blank symbol indicates that this GO category did not exist or had fewer than 10 genes for the given FDR experiment. Height of bar is proportional to the rank of the q-value for that GO term. Bar shading indicates q-value: solid: q-value <.001; diagonal lines: q-value <.01; vertical lines: q-value <.05; empty: q-value <=.05. From left to right: Bar 1: third level terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for CDS (3.49/kb); Bar 2: SWAT-aligned genes, third level terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for CDS (3.28/kb); Bar 3: cDNA-derived genes: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for CDS (3.19/kb); Bar 4: complete GO terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for CDS (3.49/kb); Bar 5: original plant GO_slim terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for CDS (3.49/kb); Bar 6: cutoff = 1.00 polymorphisms/kb; Bar 7: cutoff = 3.00 polymorphisms/kb; Bar 8: cutoff = 5.00 polymorphisms/kb; Bar 9: cutoff = 10.00 polymorphisms/kb ; Bar 10: all CDS (including those without introns); cutoff = 3.49; Bar 11: gene families reduced to 1 member; cutoff = 3.49; Bar 12: all gene family members removed; cutoff = 3.49 (GIF 46 867 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Summary of FDR experiments for intron data. GO term numbers and their corresponding names can be found in Table 2. A + above the bar indicates a significant (q-value <=0.05) excess of genes in the above-average -polymorphism group; a - indicates an excess of genes in the below-average- polymorphism group; a 0 indicates a random distribution of genes; a blank symbol indicates that this GO category did not exist or had fewer than 10 genes for the given FDR experiment. Height of bar is proportional to the rank of the q-value for that GO term. Bar shading indicates q-value: solid: q-value <.001; diagonal lines: q-value <.01; vertical lines: q-value <.05; empty: q-value >=.05. From left to right: Bar 1: third level terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for introns (3.49/kb); Bar 2: SWAT-aligned genes, third level terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for introns (4.82/kb); Bar 3: cDNA-derived genes: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for introns (3.88/kb); Bar 4: complete GO terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for introns (3.11/kb); Bar 5: original plant GO_slim terms: cutoff = mean polymorphisms for introns (3.11/kb); Bar 6: cutoff = 1.00 polymorphisms/kb; Bar 7: cutoff = 3.00 polymorphisms/kb; Bar 8: cutoff = 5.00 polymorphisms/kb; Bar 9: cutoff = 10.00 polymorphisms/kb ; Bar 10: all CDS (including those without introns); cutoff = 3.11; Bar 11: gene families reduced to 1 member; cutoff = 3.11; Bar 12: all gene family members removed; cutoff = 3.11 (GIF 47 239 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johns, M.A., Mao, L. Differentiation of the two rice subspecies indica and japonica: a Gene Ontology perspective. Funct Integr Genomics 7, 135–151 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-006-0036-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-006-0036-1