Abstract
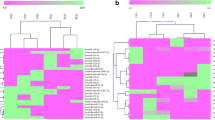
To investigate the roles of microRNAs (miRNA) of Cynoglossus semilaevis in response to Vibrio anguillarum that were previously identified using high-throughput sequencing, microarray analyses was performed on three small RNA libraries (CG, NOSG, and HOSG) prepared from C. semilaevis immune tissues. In total, of 1279 designed probes, 739 (57.78 %) were detectable. The expression levels of these miRNAs were analyzed using pairwise comparisons among the three libraries, and a total of 99 miRNAs were observed to be significantly differentially expressed. The expression patterns of 10 differentially expressed miRNAs were validated by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). In addition, expression of miR-142-5p, miR-223, and miR-181a in response to V. anguillarum at numerous time-points in four tissues, as well as the responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C), peptidoglycan (PGN), and red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) in head kidney cells, were studied by qRT-PCR. Taken together, all of the expression profiles showed significant differences compared to the control group; both similarities and differences in the expression responses to the same pathogen were observed. Collectively, these findings highlighted the putative roles for miRNAs in the context of the innate immune response of C. semilaevis exposing to pathogens and that further studies are needed to understand the molecular mechanisms of miRNA regulation in C. semilaevis host–pathogen interactions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anglicheau D, Sharma VK, Ding R, Hummel A, Snopkowski C, Dadhania D, Seshan SV, Suthanthiran M (2009) MicroRNA expression profiles predictive of human renal allograft status. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:5330–5335
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Basso K, Sumazin P, Morozov P, Schneider C, Maute RL, Kitagawa Y, Mandelbaum J, Haddad J Jr, Chen C-Z, Califano A (2009) Identification of the human mature B cell miRNome. Immunity 30:744–752
Ben-Dov IZ, Muthukumar T, Morozov P, Mueller FB, Tuschl T, Suthanthiran M (2012) MicroRNA sequence profiles of human kidney allografts with or without tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Transplantation 94:1086–94
Benson, E.A., Skaar, T.C. (2013). Incubation of Whole Blood at Room Temperature Does Not Alter the Plasma Concentrations of MicroRNA-16 and -223. Drug Metab Dispos 41:1778–1781
Berezikov E, Guryev V, Van De Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E (2005) Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 120:21–24
Bizuayehu TT, Babiak I (2014) MicroRNA in teleost fish. Genome Biol Evol 6:1911–1937
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Strand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19:185–193
Borsani O, Zhu J, Verslues PE, Sunkar R, Zhu J-K (2005) Endogenous siRNAs derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell 123:1279–1291
Carrington JC, Ambros V (2003) Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301:336–338
Chen G, Zhu W, Shi D, Lv L, Zhang C, Liu P, Hu W (2010) MicroRNA-181a sensitizes human malignant glioma U87MG cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep 23:997–1003
Chen S-Y (2014) MicroRNA-223: a double-edged sword in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 34:285–286
Chen X, Li Q, Wang J, Guo X, Jiang X, Ren Z, Weng C, Sun G, Wang X, Liu Y (2009) Identification and characterization of novel amphioxus microRNAs by Solexa sequencing. Genome Biol 10:R78
Cichocki F, Felices M, Mccullar V, Presnell SR, Al-Attar A, Lutz CT, Miller JS (2011) Cutting edge: microRNA-181 promotes human NK cell development by regulating Notch signaling. J Immunol 187:6171–6175
Danger R, Pallier A, Giral M, Martínez-Llordella M, Lozano JJ, Degauque N, Sanchez-Fueyo A, Soulillou J-P, Brouard S (2012) Upregulation of miR-142-3p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of operationally tolerant patients with a renal transplant. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:597–606
Gao X, Gulari E, Zhou X (2004) In situ synthesis of oligonucleotide microarrays. Biopolymers 73:579–596
Ghosh Z, Mallick B, Chakrabarti J (2009) Cellular versus viral microRNAs in host–virus interaction. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1035–1048
He Q, Zhou X, Li S, Jin Y, Chen Z, Chen D, Cai Y, Liu Z, Zhao T, Wang A (2013) MicroRNA-181a suppresses salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma metastasis by targeting MAPK–Snai2 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1830:5258–5266
Huang S, Wu S, Ding J, Lin J, Wei L, Gu J, He X (2010) MicroRNA-181a modulates gene expression of zinc finger family members by directly targeting their coding regions. Nucleic Acids Res 38:7211–7218
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, Magnus JF, Kibukawa M, Schelter JM, Kobayashi SV, Lim L, Burchard J, Jackson AL (2008) MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and promote cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 28:2167–2174
Jiao Y, Zheng Z, Du X, Wang Q, Huang R, Deng Y, Shi S, Zhao X (2014) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in pearl oyster Pinctada martensii by solexa deep sequencing. Mar Biotechnol 16:54–62
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kaur S, Spillane C (2014) Reduction in carotenoid levels in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum by artificial microRNAs targeted against the endogenous phytoene synthase gene. Mar Biotechnol 17:1–7
Kim D-J, Linnstaedt S, Palma J, Park JC, Ntrivalas E, Kwak-Kim JY, Gilman-Sachs A, Beaman K, Hastings ML, Martin JN (2012) Plasma components affect accuracy of circulating cancer-related microRNA quantitation. J Mol Diagnostics 14:71–80
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, Tewari M (2010) Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods 50:298–301
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M (2007) A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 129:1401–1414
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Li Q-J, Chau J, Ebert PJ, Sylvester G, Min H, Liu G, Braich R, Manoharan M, Soutschek J, Skare P (2007) miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 129:147–161
Li YT, Chen SY, Wang CR, Liu MF, Lin CC, Jou I, Shiau AL, Wu CL (2012) Brief report: amelioration of collagen‐induced arthritis in mice by lentivirus‐mediated silencing of microRNA‐223. Arthritis Rheum 64:3240–3245
Lorenzen J, Volkmann I, Fiedler J, Schmidt M, Scheffner I, Haller H, Gwinner W, Thum T (2011) Urinary miR‐210 as a mediator of acute T‐cell mediated rejection in renal allograft recipients. Am J Transplant 11:2221–2227
Ma J, Cheng L, Liu H, Zhang J, Shi Y, Zeng F, Miele L, Sarkar FH, Xia J, Wang Z (2013) Genistein down-regulates miR-223 expression in pancreatic cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets 14:1150–1156
Naeem A, Zhong K, Moisá S, Drackley J, Moyes K, Loor J (2012) Bioinformatics analysis of microRNA and putative target genes in bovine mammary tissue infected with Streptococcus uberis. J Dairy Sci 95:6397–6408
Nelson JS (2006) Fishes of the world. Wiley-Interscience, New York, p 416
Ou J, Meng Q, Li Y, Xiu Y, Du J, Gu W, Wu T, Li W, Ding Z, Wang W (2012) Identification and comparative analysis of the Eriocheir sinensis microRNA transcriptome response to Spiroplasma eriocheiris infection using a deep sequencing approach. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:345–352
Ren Y, Gao J, Liu J-Q, Wang X-W, Gu J-J, Huang H-J, Gong Y-F, Li Z-S (2012) Differential signature of fecal microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer. Mol Med Rep 6:201–209
Salem M, Xiao C, Womack J, Rexroad Iii CE, Yao J (2010) A microRNA repertoire for functional genome research in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mar Biotechnol 12:410–429
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D (2005) Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell 8:517–527
Sha Z-X, Wang Q-L, Liu Y, Chen S-L (2012) Identification and expression analysis of goose-type lysozyme in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:914–921
Sha Z, Gong G, Wang S, Lu Y, Wang L, Wang Q, Chen S (2014) Identification and characterization of Cynoglossus semilaevis microRNA response to Vibrio anguillarum infection through high-throughput sequencing. Dev Comparative Immunol 44:59–69
Shibuya H, Nakasa T, Adachi N, Nagata Y, Ishikawa M, Deie M, Suzuki O, Ochi M (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-223 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium controls osteoclast differentiation. Mod Rheumatol 23:674–685
Streppel MM, Pai S, Campbell NR, Hu C, Yabuuchi S, Canto MI, Wang JS, Montgomery EA, Maitra A (2013) MicroRNA 223 is upregulated in the multistep progression of Barrett’s esophagus and modulates sensitivity to chemotherapy by targeting PARP1. Clin Cancer Res 19:4067–4078
Sugatani T, Hruska KA (2009) Impaired micro-RNA pathways diminish osteoclast differentiation and function. J Biol Chem 284:4667–4678
Teleman AA, Cohen SM (2006) Drosophila lacking microRNA miR-278 are defective in energy homeostasis. Genes Dev 20:417–422
Tili E, Michaille J-J, Calin GA (2008) Expression and function of micro RNAs in immune cells during normal or disease state. Int J Med Sci 5:73
Wang H, Liu S, Cui J, Li C, Qiu X, Chang Y, Liu Z, Wang X (2014) Characterization and expression analysis of microRNAs in the tube foot of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. PLoS One 9:e111820
Wang Y, Yu Y, Tsuyada A, Ren X, Wu X, Stubblefield K, Rankin-Gee EK, Wang SE (2010) Transforming growth factor-β regulates the sphere-initiating stem cell-like feature in breast cancer through miRNA-181 and ATM. Oncogene 30:1470–1480
Wei Z, Liu X, Feng T, Chang Y (2011) Novel and conserved micrornas in Dalian purple urchin (Strongylocentrotus nudus) identified by next generation sequencing. Int J Biol Sci 7:180
Wu C, Gong Y, Yuan J, Zhang W, Zhao G, Li H, Sun A, Zou Y, Ge J (2012) microRNA-181a represses ox-LDL-stimulated inflammatory response in dendritic cell by targeting c-Fos. J Lipid Res 53:2355–2363
Xu Z, Chen M, Ren Z, Zhang N, Xu H, Liu X, Tian G, Song L, Yang H (2013) Deep sequencing identifies regulated small RNAs in Dugesia japonica. Mol Biol Rep 40:4075–4081
Yang CC, Hung PS, Wang PW, Liu CJ, Chu TH, Cheng HW, Lin SC (2011) miR‐181 as a putative biomarker for lymph‐node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 40:397–404
Zhang X, Guan G, Chen J, Naruse K, Hong Y (2014) Parameters and efficiency of direct gene disruption by zinc finger nucleases in medaka embryos. Mar Biotechnol 16:125–134
Zhao P, Zhao L, Zhang K, Feng H, Wang H, Wang T, Xu T, Feng N, Wang C, Gao Y (2012a) Infection with street strain rabies virus induces modulation of the microRNA profile of the mouse brain. Virol J 9:159
Zhao P, Zhao L, Zhang T, Wang H, Qin C, Yang S, Xia X (2012b) Changes in microRNA expression induced by rabies virus infection in mouse brains. Microb Pathog 52:47–54
Zheng Y, Wang N, Xie M-S, Sha Z-X, Chen S-L (2012) Establishment and characterization of a new fish cell line from head kidney of half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Physiol Biochem 38:1635–1643
Zhou Q, Li M, Wang X, Li Q, Wang T, Zhu Q, Zhou X, Wang X, Gao X, Li X (2012a) Immune-related microRNAs are abundant in breast milk exosomes. Int J Biol Sci 8:118
Zhou X, Zhu Q, Eicken C, Sheng N, Zhang X, Yang L, Gao X (2012b) MicroRNA profiling using m paraflo microfluidic array technology. Series Editor John M Walker School of Life Sciences University of Hertfordshire Hatfield, Hertfordshire, AL10 9AB, UK: 153
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, G., Sha, Z., Chen, S. et al. Expression Profiling Analysis of the microRNA Response of Cynoglossus semilaevis to Vibrio anguillarum and Other Stimuli. Mar Biotechnol 17, 338–352 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-015-9623-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-015-9623-2