Abstract
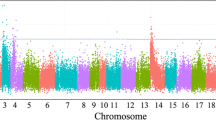
Understanding stress responses is essential for improving animal welfare and increasing agriculture production efficiency. Previously, we reported microsatellite markers associated with quantitative trait loci (QTL) affecting plasma cortisol response to crowding in rainbow trout. In this study, our main objectives were to identify single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers associated with cortisol response to crowding in rainbow trout using both GWAS (genome-wide association studies) and QTL mapping methods and to employ rapidly expanding genomic resources for rainbow trout toward the identification of candidate genes affecting this trait. A three-generation F2 mapping family (2008052) was genotyped using RAD-seq (restriction-site-associated DNA sequencing) to identify 4874 informative SNPs. GWAS identified 26 SNPs associated with cortisol response to crowding whereas QTL mapping revealed two significant QTL on chromosomes Omy8 and Omy12, respectively. Positional candidate genes were identified using marker sequences to search the draft genome assembly of rainbow trout. One of the genes in the QTL interval on Omy12 is a putative serine/threonine protein kinase gene that was differentially expressed in the liver in response to handling and confinement stress in our previous study. A homologue of this gene was differentially expressed in zebrafish embryos exposed to diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and an environmental toxicant. NSAIDs have been shown to affect the cortisol response in rainbow trout; therefore, this gene is a good candidate based on its physical position and expression. However, the reference genome resources currently available for rainbow trout require continued improvement as demonstrated by the unmapped SNPs and the putative assembly errors detected in this study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Aluru N, Vijayan MM (2009) Stress transcriptomics in fish: a role for genomic cortisol signaling. Gen Comp Endocr 164:142–150
Aulchenko YS, Ripke S, Isaacs A, Van Duijn CM (2007) GenABEL: an R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics 23:1294–1296
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA, Selker EU, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. Plos One 3: e3376. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003376
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Berthelot C, Brunet F, Chalopin D, Juanchich A, Bernard M, Noel B, Bento P, Da Silva C, Labadie K, Alberti A, Aury JM, Louis A, Dehais P, Bardou P, Montfort J, Klopp C, Cabau C, Gaspin C, Thorgaard GH, Boussaha M, Quillet E, Guyomard R, Galiana D, Bobe J, Volff JN, Genet C, Wincker P, Jaillon O, Crollius HR, Guiguen Y (2014) The rainbow trout genome provides novel insights into evolution after whole-genome duplication in vertebrates. Nat Commun 5:3657. doi:10.1038/ncomms4657
Bolton JL, Hayward C, Direk N, Lewis JG, Hammond GL, Hill LA, Anderson A, Huffman J, Wilson JF, Campbell H, Rudan I, Wright A, Hastie N, Wild SH, Velders FP, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Lahti J, Raikkonen K, Kajantie E, Widen E, Palotie A, Eriksson JG, Kaakinen M, Jarvelin MR, Timpson NJ, Davey Smith G, Ring SM, Evans DM, St Pourcain B, Tanaka T, Milaneschi Y, Bandinelli S, Ferrucci L, Van Der Harst P, Rosmalen JG, Bakker SJ, Verweij N, Dullaart RP, Mahajan A, Lindgren CM, Morris A, Lind L, Ingelsson E, Anderson LN, Pennell CE, Lye SJ, Matthews SG, Eriksson J, Mellstrom D, Ohlsson C, Price JF, Strachan MW, Reynolds RM, Tiemeier H, Walker BR (2014) Genome wide association identifies common variants at the SERPINA6/SERPINA1 locus influencing plasma cortisol and corticosteroid binding globulin. PLoS Genet 10:e1004474
Brieuc MSO, Waters CD, Seeb JE, Naish KA (2014) A dense linkage map for Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) reveals variable chromosomal divergence after an ancestral whole genome duplication event. G3-Genes Genom Genet 4:447–460
Caldwell CA, Kattesh HG, Strange RJ (1991) Distribution of cortisol among its free and protein-bound fractions in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): evidence of control by sexual maturation. Comp Biochem Physiol-Physiol 99:593–595
Chou CM, Chen YC, Lee MT, Chen GD, Lu IC, Chen ST, Huang CJ (2006) Expression and characterization of a brain-specific protein kinase BSK146 from zebrafish. Biochem Bioph Res Co 340:767–775
Davey JW, Hohenlohe PA, Etter PD, Boone JQ, Catchen JM, Blaxter ML (2011) Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 12:499–510
De Felice B, Copia L, Guida M (2012) Gene expression profiling in zebrafish embryos exposed to diclofenac, an environmental toxicant. Mol Biol Rep 39:2119–2128
Drew RE, Schwabl H, Wheeler PA, Thorgaard GH (2007) Detection of QTL influencing cortisol levels in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 272:S183–S194
Gonen S, Lowe NR, Cezard T, Gharbi K, Bishop SC, Houston RD (2014) Linkage maps of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) genome derived from RAD sequencing. BMC Genomics 15:166
Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Williams TD, Nagaraj SH, Nueda MJ, Robles M, Talon M, Dopazo J, Conesa A (2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3420–3435
Gravel A, Vijayan MM (2006) Salicylate disrupts interrenal steroidogenesis and brain glucocorticoid receptor expression in rainbow trout. Toxicol Sci 93:41–49
Gravel A, Vijayan MM (2007) Salicylate impacts the physiological responses to an acute handling disturbance in rainbow trout. Aquat Toxicol 85:87–95
Gravel A, Wilson JM, Pedro DFN, Vijayan MM (2009) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs disturb the osmoregulatory, metabolic and cortisol responses associated with seawater exposure in rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol C-Toxicol Pharmacol 149:481–490
Hecht BC, Thrower FP, Hale MC, Miller MR, Nichols KM (2012) Genetic architecture of migration-related traits in rainbow and steelhead trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. G3-Genes Genom Genet 2:1113–1127
Hecht BC, Campbell NR, Holecek DE, Narum SR (2013) Genome-wide association reveals genetic basis for the propensity to migrate in wild populations of rainbow and steelhead trout. Mol Ecol 22:3061–3076
Houston RD, Davey JW, Bishop SC, Lowe NR, Mota-Velasco JC, Hamilton A, Guy DR, Tinch AE, Thomson ML, Blaxter ML, Gharbi K, Bron JE, Taggart JB (2012) Characterisation of QTL-linked and genome-wide restriction site-associated DNA (RAD) markers in farmed Atlantic salmon. BMC Genomics 13:244
Houston RD, Taggart JB, Cezard T, Bekaert M, Lowe NR, Downing A, Talbot R, Bishop SC, Archibald AL, Bron JE, Penman DJ, Davassi A, Brew F, Tinch AE, Gharbi K, Hamilton A (2014) Development and validation of a high density SNP genotyping array for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC Genomics 15:90
Liu S, Gao G, Palti Y, Cleveland BM, Weber GM, Rexroad CE 3rd (2014) RNA-seq analysis of early hepatic response to handling and confinement stress in rainbow trout. Plos One 9:e88492
Margarido GRA, Souza AP, Garcia AAF (2007) OneMap: software for genetic mapping in outcrossing species. Hereditas 144:78–79
Miller MR, Dunham JP, Amores A, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2007) Rapid and cost-effective polymorphism identification and genotyping using restriction site associated DNA (RAD) markers. Genome Res 17:240–248
Miller MR, Brunelli JP, Wheeler PA, Liu SX, Rexroad CE, Palti Y, Doe CQ, Thorgaard GH (2012) A conserved haplotype controls parallel adaptation in geographically distant salmonid populations. Mol Ecol 21:237–249
Moisan MP (2010) Genotype-phenotype associations in understanding the role of corticosteroid-binding globulin in health and disease animal models. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316:35–41
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fisher 9:211–268
Narum SR, Campbell NR, Meyer KA, Miller MR, Hardy RW (2013) Thermal adaptation and acclimation of ectotherms from differing aquatic climates. Mol Ecol 22:3090–3097
Ousova O, Guyonnet-Duperat V, Iannuccelli N, Didanel JP, Milan D, Genet C, Llamas B, Yerle M, Gellin J, Chardon P, Emptoz-Bonneton A, Pugeat M, Mormede P, Moisan MP (2004) Corticosteroid binding globulin: a new target for cortisol-driven obesity. Mol Endocrinol 18:1687–1696
Palti Y, Genet C, Gao GT, Hu YQ, You FM, Boussaha M, Rexroad CE, Luo MC (2012) A second generation integrated map of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) genome: analysis of conserved synteny with model fish genomes. Mar Biotechnol 14:343–357
Palti Y, Gao G, Liu S, Kent M.P., Lien S, Miller M.R., Rexroad C.E., 3rd & Moen T. (2014a). The development and characterization of a 57K SNP array for rainbow trout. Mol Ecol Resour. doi:10.1111/1755-0998.12337
Palti Y, Gao G, Miller MR, Vallejo RL, Wheeler PA, Quillet E, Yao J, Thorgaard GH, Salem M, Rexroad CE 3rd (2014b) A resource of single-nucleotide polymorphisms for rainbow trout generated by restriction-site associated DNA sequencing of doubled haploids. Mol Ecol Resour 14:588–596
Quillet E, Krieg F, Dechamp N, Hervet C, Berard A, Le Roy P, Guyomard R, Prunet P, Pottinger TG (2014) Quantitative trait loci for magnitude of the plasma cortisol response to confinement in rainbow trout. Anim Genet 45:223–234
Rexroad CE 3rd, Palti Y, Gahr SA, Vallejo RL (2008) A second generation genetic map for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). BMC Genet 9:74
Rexroad CE 3rd, Vallejo RL, Liu S, Palti Y, Weber GM (2012) QTL affecting stress response to crowding in a rainbow trout broodstock population. BMC Genet 13:97
Rexroad CE, Vallejo RL, Liu S, Palti Y, Weber GM (2013) Quantitative trait loci affecting response to crowding stress in an F(2) generation of rainbow trout produced through phenotypic selection. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 15:613–627
Seaton G, Hernandez J, Grunchec JA, White I, Allen J, De Koning DJ, Wei W, Berry D, Haley C, Knoot S (2006) GridQTL: a grid portal for QTL mapping of compute intensive datasets, Proceedings of the 8th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production. Belo Horizonte, Brasil
Solberg LC, Baum AE, Ahmadiyeh N, Shimomura K, Li RH, Turek FW, Takahashi JS, Churchill GA, Redei EE (2006) Genetic analysis of the stress-responsive adrenocortical axis. Physiol Genomics 27:362–369
Svishcheva GR, Axenovich TI, Belonogova NM, Van Duijn CM, Aulchenko YS (2012) Rapid variance components-based method for whole-genome association analysis. Nat Genet 44:1166
Weber GM, Silverstein JT (2007) Evaluation of a stress response for use in a selective breeding program for improved growth and disease resistance in rainbow trout. N Am J Aquacult 69:69–79
Welter D, Macarthur J, Morales J, Burdett T, Hall P, Junkins H, Klemm A, Flicek P, Manolio T, Hindorff L, Parkinson H (2014) The NHGRI GWAS catalog, a curated resource of SNP-trait associations. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1001–D1006
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Zhang H, Wang ZP, Wang SZ, Li H (2012) Progress of genome wide association study in domestic animals. J Anim Sci Biotechno 3:26
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Roseanna Long and Kristy Shewbridge for making the RAD libraries. The mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional file 1
Minimal tilling path of BAC physical contigs based on DNA fingerprinting. The BACs included in each DNA fingerprinting contigs are named using the nomenclature of Dr. Michael Miller (http://www.animalgenome.org). (TXT 547 kb)
Additional file 2
Summary and detailed information of genetic maps of mapping family 2008052. Sheet 1, summary of 29 genetic maps; sheet 2, SNP sequences and mapping results onto the recently published draft sequences of rainbow trout; sheet 3, microsatellite and SNP markers assigned to each chromosome of rainbow trout; and genetic maps of 29 chromosomes are presented in one chromosome per sheet. (XLSX 520 kb)
Additional file 3
Annotation of putative genes in the QTL region on chromosome Omy8 for cortisol response to crowding. (XLSX 9 kb)
Additional file 4
Rainbow trout proteins homologous to the human corticosteroid binding globulin. (XLSX 9 kb)
Additional file 5
Annotation of putative genes in the QTL region on chromosome Omy12 for cortisol response to crowding. (XLSX 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Vallejo, R.L., Gao, G. et al. Identification of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Markers Associated with Cortisol Response to Crowding in Rainbow Trout. Mar Biotechnol 17, 328–337 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-015-9621-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-015-9621-4