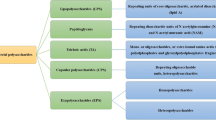
Abstract
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are high molecular weight carbohydrate polymers that make up a substantial component of the extracellular polymers surrounding most microbial cells in the marine environment. EPSs constitute a large fraction of the reduced carbon reservoir in the ocean and enhance the survival of marine bacteria by influencing the physicochemical environment around the bacterial cell. Microbial EPSs are abundant in the Antarctic marine environment, for example, in sea ice and ocean particles, where they may assist microbial communities to endure extremes of temperature, salinity, and nutrient availability. The microbial biodiversity of Antarctic ecosystems is relatively unexplored. Deep-sea hydrothermal vent environments are characterized by high pressure, extreme temperature, and heavy metals. The commercial value of microbial EPSs from these habitats has been established recently. Extreme environments offer novel microbial biodiversity that produces varied and promising EPSs. The biotechnological potential of these biopolymers from hydrothermal vent environments as well as from Antarctic marine ecosystems remains largely untapped.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alldredge A (2000) Interstitial dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations within sinking marine aggregates and their potential contribution to carbon flux. Limnol Oceanogr 45: 1245–1253
Alldredge A, Jackson GA (1995) Aggregation in marine systems. Deep-Sea Res 42: 1–7
Alldredge A, Silver MW (1988) Characteristics, dynamics, significance of marine snow. Prog Oceanogr 20: 41–82
Antoine E, Guezennec J, Meunier JR, Lesongeur F, Barbier G (1995) Isolation and characterization of extremely thermophilic Archaebacteria related to the genus Thermococcus from deep-sea hydrothermal Guaymas basin. Curr Microbiol 31: 186–192
Apollonio S, Pennington M, Cota GF (2002) Stimulation of phytoplankton photosynthesis by bottom-ice extracts in the Arctic. Polar Biol 25: 350–354
Archer SD, Leakey RJG, Burkill PH, Sleigh MA, Appleby CJ (1996) Microbial ecology of sea ice at a coastal Antarctic site: community composition, biomass and temporal change. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 135: 179–195
Arias S, del Moral A, Ferrer MR, Tallon R, Quesada E, Béjar V (2003) Mauran, an exopolysaccharide produced by the halophilic bacterium Halomonas maura, with a novel composition and interesting properties for biotechnology. Extremophiles 7: 319–326
Asper VL, Smith J, Walker O (2003) Abundance, distribution and sinking rates of aggregates in the Ross Sea Antarctica. Deep-Sea Res 50: 131–150
Azam F (1998) Microbial control of oceanic carbon flux. Science 280: 694–696
Azam F, Smith DC, Steward GF, Hagstrom A (1994) Bacteria: organic-matter coupling and its significance for oceanic carbon cycling. Mcrob Ecol 28: 167–179
Becker A, Katzen F, Puhler A, lelpi L (1998) Xanthan gun biosynthesis and application: a biochemical/genetic perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50: 145–152
Benner R, Pakulski JD, McCartney M, Hedges JI, Hatcher PG (1992) Bulk chemical characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the ocean. Science 255: 1561–1564
Biddanda BA (1985) Microbial synthesis of macroparticulate matter. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 20: 241–251
Biddanda BA (1986) Structure and function of microbial aggregates. Oceanol Acta 9: 209–211
Biddanda BA (1988) Microbial aggregation and degradation of phytoplankton-derived detritus in seawater, II: microbial metabolism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 42: 89–95
Biddanda BA, Pomeroy LR (1988) Microbial aggregation and degradation of phytoplankton-derived detritus in seawater, I: microbial succession. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 42: 79–88
Bitton G, Friehofer V (1978) Influence of extracellular polysaccharide on the toxicity of copper and cadmium toward Klebsiella aerogenes. Microb Ecol 4: 119–125
Bouchotroch S, Quesada E, Izquierdo I, Rodriguez M, Bejar V (2000) Bacterial exopolysaccharides produced by newly discovered bacteria belonging to the genus Halomonas, isolated from hypersaline environments in Morocco. J Ind Microbiol Biot 24: 374–378
Bowman JP, (1998) Pseudoalteromonas prydzensissp sp. nov., a psychrotrophic, halotolerant bacterium from Antarctic sea ice. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48: 1037–1041
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Brown MV, Nichols DS, McMeekin TA (1997) Diversity and association of psychrophilic bacteria in Antarctic sea ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 3068–3078
Boyd PW, Watson AJ, Law CS, Abraham ER, Trull T, Murdoch R, Bakker DCE, Bowie AR, Buesseler KO, Chang H, Charette M, Croot P, Downing K, Frew R, Gall M, Hadfield M, Hall J, Harvey M, Jameson G, LaRoche J, Liddicoat M, Ling R, Maldonado MT, McKay RM, Nodder S, Pickmere S, Pridmore R, Rintoul S, Safi K, Sutton P, Strzepek R, Tanneberger K, Turner S, Waite A, Zeldis J (2000) A mesoscale phytoplankton bloom in the polar Southern Ocean stimulated by iron fertilization. Nature 407: 695–702
Boyle CD, Reade AE (1983) Characterization of two extracellular polysaccharides from marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 46: 392–399
Bozal N, Manresa A, Castellvi J, Guinea J (1994) A new bacterial strain of Antarctica Alteromonas sp, that produces a heteropolymer slime. Polar Biol 14: 561–567
Bozal N, Tudela E, Rossello-Mora R, Lalucat J, Guinea J (1997) Pseudoalteromonas Antarctica. sp nov, isolated from an Antarctic coastal environment. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47: 345–351
Bozzi L, Milas M, Rinaudo M (1996a) Characterization and solution properties of a new exopolysaccharide excreted by the bacterium Alteromonas sp strain 1644. Int J Biol Macromol 18: 9–17
Bozzi L, Milas M, Rinaudo M (1996b) Solution and gel rheology of a new exopolysaccharide excreted by the bacterium Alteromonas sp strain 1644. Int J Biol Macromol 18: 83–91
Brinkmeyer R, Knittel K, Jurgens J, Weyland H, Amann R, Helmke E (2003) Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 6610–6619
Brown MJ, Lester JN (1979) Metal removal in activated sludge: the role of bacterial extracellular polymers. Water Res 13: 817–837
Brown MJ, Lester JN (1982) Role of bacterial extracellular polymers in metal uptake in pure bacterial culture and activated sludge. Water Res 16: 1539–1548
Brown MRW, Gilbert P (1993) Sensitivity of biofilms to antimicrobial agents. J Appl Bacteriol Suppl 74: 87S–97S
Brown MV, Bowman JP (2001) A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea-ice microbial communities (SIMCO). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35: 267–275
Bull AT, Ward AC, Goodfellow M (2000) Search and discovery strategies for biotechnology: the paradigm shift. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64: 573–606
Cambon-Bonavita MA, Raguénès G, Jean J, Vincent P, Guezennec J (2002) A novel polymer produced by a bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete annelid. J Appl Microbiol 93: 310–315
Caron DA (1987) Grazing of attached bacteria by heterotrophic microflagellates. Microb Ecol 13: 203–218
Chin WC, Orellana MV, Verdugo P (1998) Spontaneous assembly of marine dissolved organic matter into polymer gels. Nature 391: 568–571
Christensen BE (1999) Physical and chemical properties of extracellular polysaccharides associated with biofilms and related substances. In: Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC, eds. Microbial Extracellular Substances: Characterization Structure and Function, (New York, NY: Springer) pp 144–154
Christensen BE, Kjosbakken J, Smidsrod O (1985) Partial chemical and physical characterization of two extracellular polysaccharides produced by marine, periphytic Pseudomonas sp. strain NCMB 2021. Appl Environ Microbiol 50: 837–845
Cocera M, Lopez O, Parra JL, Mercade ME, Guinea J, de la Maza A (2000) Protective effect caused by the exopolymer excreted by Pseudoalteromonas antarctica NF3 on liposomes against the action of octyl glucoside. Int J Pharm 207: 39–47
Cocera M, Lopez O, Sabes M, Parra JL, Guinea J, de la Maza A (2001) Assembly properties and application of a new exopolymeric compound excreted by Pseudoalteromonas antarctica NF3. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 12: 409–427
Colliec-Jouault S, Chevolet L, Helley D, Ratiskol J, Bros A, Sinquin C, Roger O, Fischer AM (2001) Characterization, chemical modifications and in vitro anticoagulant properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by Alteromonas in fern us. Biochim Biophys Acta 1528: 141–151
Corpe WA (1970) An acid polysaccharide produced by primary film forming bacteria. Dev Ind Microbiol 16: 249–255
Costerton JW (1974) Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 38: 87–110
Costerton JW (1984) Mechanisms of microbial adhesion to surfaces: Direct ultrastructural examinations of adherent bacterial populations in natural pathogenic ecosystems. In: Klug MJ, Reddy CA (eds.). Current Perspectives in Microbial Ecology Prog 3rd Int Symp Microbial Ecol, (Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology) pp 115–123
Costerton JW (1999) The role of bacterial exopolysaccharides in nature and disease [Reprinted from Developments in Industrial Microbiology, 26, 249–261, 1985]. J Ind Microbiol Biot 22: 551–563
Costerton JW, Lappin-Scott HM, Cheng KJ (1992) Glycocalyx, bacterial. In: Lederberg J (eds.). Encyclopedia of Microbiology vol. 2, (San Diego, Calif.: Academic Press) pp 311–317
Dade WB, Davis JD, Nichols PD, Nowell ARM, Thistle D, Trexler MR, White DC (1990) Effects of exopolymer adhesion on the entrainment of sand. Geomicrobiol J 8: 1–16
Decho AW (1990) Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments: their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. In: Barnes M. (ed.). Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev, (Aberdeen, u.k.: Aberdeen Univ Press) pp 73–153
Decho AW, Herndl GJ (1995) Microbial activities and the transformation of organic matter within mucilaginous material. Sci Total Environ 165: 33–42
Decho AW, Lopez GR (1993) Exopolymer microenvironments of microbial flora — multiple and interactive effects on trophic relationships. Limnol Oceanogr 38: 1633–1645
Delille D (1992) Marine bacterioplankton at the Weddell Sea ice edge, distribution of psychrophilic and psychrotrophic populations. Polar Biol 12: 205–210
Delille D, Rosier C (1996) Seasonal changes of Antarctic marine bacterioplankton and sea ice bacterial assemblages. Polar Biol 16: 27–34
Deming JW (1998) Deep ocean environmental biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 9: 283–287
Deming JW, Baross JA (1998) Survival, dormancy and non-culturable cells in extreme deep-sea environments. In: Colwell RR, Grimes DJ (eds.). Non-culturable Organisms in the Environment, (New York, N.Y.: Chapman and Hall) pp
Dudman WF (1977) The role of surface polysaccharides in natural environments. In: Sutherland IW (ed.). Surface Carbohydrates of the Procaryotic Cell, (New York, N.Y.: Academic Press) pp 357–414
Emmerichs N, Wingender J, Flemming HC, Mayer C (2004) Interaction between alginates and manganese cations: identification of preferred binding sites. Int J Biol Macromol 34: 73–79
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2001) Relevance of microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) — part I: structural and ecological aspects. Water Sci Technol 43: 1–8
Flemming HC, Wingender J, Moritz R, Borchard W, Mayer C (1997) Physico-chemical properties of biofilm — a short review. In: Keevil CW, Godfree A, Holt D, Dow C (eds.). Biofilms in the Aquatic Environment, (Cambridge, U.K.: The Royal Society of Chemistry) pp 1–12
Fletcher M (1988) Effects of electrolytes on the attachment of aquatic bacteria to solid surfaces. Estuaries 11: 226–230
Fletcher M, Floodgate GD (1973) An electron microscopic demonstration of an acidic polysaccharide involved in adhesion of a marine bacterium to solid surfaces. J Gen Microbiol 74: 325–334
Fowler SW, Knauer GA (1986) Role of large particles in the transport of elements and organic compounds through the oceanic water column. Prog Oceanogr 16: 147–194
Geesey GG (1982) Microbial exopolymers:ecological and economic considerations. Am Soc Microbiol News 48: 9–14
Geider RJ (1999) Complex lessons of iron uptake. Nature 400: 815–816
Gleitz M, Thomas DN (1993) Variation in phytoplankton standing stock, chemical composition and physiology during sea-ice formation in the southeastern Weddell Sea. J Exp MarBiol Ecol 173: 211–230
Gleitz M, Grossmann S, Scharek R, Smetacek V (1996) Ecology of diatom and bacterial assemblages in water associated with melting summer sea ice in the Weddell sea Antarctica. Antarct Sci 8: 135–146
Grossmann S, Dieckmann GS (1994) Bacterial standing stock, activity and carbon production during formation and growth of sea ice in the Weddell Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 60: 2746–2753
Guezennec J (2002) Deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A new source of innovative bacterial exopolysaccharides of biotechnological interest? J Ind Microbiol Biot 29: 204–208
Guezennec J, Pignet P, Raguénès G, Deslandes E, Lijour Y, Centric E (1994) Preliminary chemical characterization of unusual eubacterial exopolysaccharides of deep-sea origin. Carbohydr Polym 24: 287–294
Harder W, Dijkhuizen L (1983) Physiological responses to nutrient limitation. Annu Rev Microbiol 37: 1–23
Harris RH, Mitchell R (1973) The role of polymers in microbial aggregation. Annu Rev Microbiol 27: 27–50
Harvey RW, Luoma SN (1985) Effect of adherent bacteria and bacterial extracellular polymers upon assimilation by Macoma baltica of sediment-bound Cd Zn and Ag. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 22: 281–289
Heissenberger A, Herndl GJ (1994) Formation of high molecular weight material by free-living marine bacteria. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 111: 129–135
Heissenberger A, Leppard GG, Herndl GJ (1996) Ultrastructure of marine snow IIMicrobiological considerations. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 135: 211–308
Helmke E, Weyland H (1995) Bacteria in the sea ice and underlying water on the eastern Weddell Sea in midwinter. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 117: 269–287
Hermannson M, Marshall KC (1985) Utilization of surface localized substrate by non-adhesive marine bacteria. Microb Ecol 11: 91–105
Holmstrom C, Kjelleberg S (1999) Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30: 285–293
Jeanthon C, Prieur D (1990) Susceptibility to heavy metals and characterization of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from two hydrothermal vent polychaete annelids Alvinella pompejana and Alvinella caudata. Appl Environ Microbiol 56: 3308–3314
Junge K, Eicken H, Deming JW (2004) Bacterial activity at −2 to −20°C in Arctic wintertime sea ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 550–557
Karl DM (1993) Microbial processes in the Southern Ocean. In: Friedmann EI (ed.). Antarctic Microbiology, (New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons) pp 1–64
Karl DM, Tilbrook BD, Tien G (1991) Seasonal coupling of organic matter production and particle flux in the western Bransfield Straight Antarctica. Deep-Sea Res 38: 1097–1126
Kenne L, Lindberg B (1983) Bacterial polysaccharides. In: Aspinall GO (ed.). The Polysaccharides vol. 2, (New York, N.Y.: Academic Press) pp 287–363
Kennedy AFD, Sutherland IW (1987) Analysis of bacterial exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 9: 12–19
Kiorboe T (2001) Formation and fate of marine snow: small-scale processes with large scale implications. Sci Mar 65: 57–71
Ko SH, Lee HS, Park SH, Lee HK (2000) Optimal conditions for the production of exopolysaccharide by marine microorganism Hahella chenjuensis. Biotechnol Bioproc Eng 5: 181–185
Korstgens V, Flemming HC, Wingender J, Borchard W (2001) Influence of calcium ions on the mechanical properties of a model biofilm of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water Sci Technol 43: 49–57
Krembs C, Engel A (2001) Abundance and variability of microorganisms and transparent exopolymer particles across ice-water interface of melting first-year sea ice in the Laptev Sea (Arctic). MarBiol 138: 173–185
Krembs C, Eicken H, Junge K, Deming JW (2002) High concentrations of exopolymeric substances in Arctic winter sea ice: implications for the polar ocean carbon cycle and cryoprotection of diatoms. Deep-Sea Res 49: 2163–2181
Leppard GG, (1995) The characterization of algal and microbial mucilages and their aggregates in aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 165: 103–131
Leppard GG, Heissenberger A, Herndl GJ (1996) Ultrastructure of marine snow, I: Transmission electron microscopy methodology. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 135: 289–298
Lewis K, (2000) Programmed death in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64: 503–514
Loaec M, Olier R, Guezennec J (1997) Uptake of lead, cadmium and zinc by a novel bacterial exopolysaccharide. Water Res 31: 1171–1179
Loaec M, Olier R, Guezennec J (1998) Chelating properties of bacterial exopolysaccharides from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr Polym 35: 65–70
Logan BE, Hunt JR (1987) Advantages to microbes of growth in permeable aggregates in marine systems. Limnol Oceanogr 32: 1034–1048
Lupton FS, Marshall KC (1984) Mechanisms of specific bacterial adhesion to cyanobacterial heterocysts. In: Klug MJ, Reddy CA (eds.). Current Perspectives in Microbial Ecology, (Washnington, DC: American Society for Microbiology) pp
Mackey DJ, Zirino A (1994) Comments on trace-metal speciation in seawater or do onions grow in the sea. Anal Chim Acta 284: 635–647
Maldonado M, Price NM (1999) Utilization of iron bound to strong organic ligands by plankton communities in the subarctic Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res 46: 2447–2473
Manca MC, Lama L, Improta R, Esposito A, Gambacorta A, Nicolaus B (1996) Chemical composition of two exopolysaccharides from Bacillus thermoantarcticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 3265–3269
Mancuso Nichols C, Garon S, Bowman JP, Raguénès G, Guezennec J (2004) Production of exopolysaccharides by Antarctic marine bacterial isolates. J Appl Microbiol 96: 1057–1066
Mancuso Nichols C, Garon Lardiere S, Bowman JP, Nichols PD, Gibson JAE, Guezennec J (2005) Chemical characterization of exopolysaccharides from Antarctic marine bacteria. Microb Ecol (in press)
Marchant H, Davidson A, Wright S, Glazebrook J (2000) The distribution and abundance of viruses in the Southern Ocean during spring. Antarct Sci 12: 414–417
Marshall KC (1980) Bacterial adhesion in natural environments. In: Berkeley RCW (ed.). Microbial Adhesion to Surfaces, (Chichester, UK: Ellis Howood Limited) pp 187–196
Marshall KC (1985) Mechanisms of bacterial adhesion at solid-water interfaces. In: Savage DC, Fletcher M (eds.). Bacterial Adhesion, (New York, NY: Plenum Press) pp 133–161
Matou S, Colliec-Jouault S, Galy-Fauroux I, Ratiskol J, Sinquin C, Guezennec J, Fischer AM, Helley D (2005) Effect of oversulfated exopolysaccharide on angiogenisis induced by fibroblast growth factor 2 or vascular endothelial growth factor in vitro. Biochemical Pharmacol 69: 751–759
McBain A, Gilbert P (2001) Biofilms: Adverse Economic Impacts and Their Avoidance, Royal Society for Chemistry
McCarthy M, Hedges J, Benner R (1996) Major biochemical composition of dissolved high molecular weight organic matter in sea water. Mar Chem 55: 281–297
Mueller-Niklas G, Schuster S, Kaltenboeck E, Herndl GJ (1994) Organic content and bacterial metabolism in amorphous aggregations of the northern Adriatic Sea. Limnol Oceanogr 39: 58–68
Neilsen PH, Andreas J (1999) Extraction of EPS. In: Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (eds.). Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Characterization Structure and Function, (New York, NY: Springer-Verlag) pp 49–72
Nichols DS, Sanderson K, Buia A, Van de Kamp J, Holloway P, Smith M, Nichols PD, Mancuso Nichols C (2001) Bioprospecting and Biotechnology in Antarctica. In: Jabour-Green J, Haward M (eds.). The Antarctic: Past Present and Future, (Hobart Tasmania: Antarctic CRC) pp 85–95
Paerl HW (1975) Microbial attachment to particles in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Microb Ecol 2: 73–83
Paerl HW (1976) Specific associations of blue-green algae Anabaena and Aphanizomenon with bacteria in freshwater blooms. J Phycol 12: 431–435
Passow U (2000) Formation of transparent exopolymer particles TEP, from dissolved precursor material. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 192: 1–11
Passow U, Alldredge A (1994) Distribution, size and bacterial colonization of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in the ocean. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 113: 185–198
Raguénès G, Christen R, Guezennec J, Pignet P, Barbier B (1997a) Vibrio diabolicus sp. nov, a new polysaccharide-secreting organism isolated from a deep-sea vent polychaete annelid Alvinella pompejana. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47: 989–995
Raguénès GHC, Peres A, Ruimy R, Pignet P, Christen R, Loaec M, Rougeaux H, Barbier G, Guezennec JG (1997b) Alteromonas infernus sp. nov, a new polysaccharide-producing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. J Appl Microbiol 82: 422–430
Rath J, Wu KY, Herndl GJ, Delong EF (1998) High phylogenetic diversity in a marine-snow-associated bacterial assemblage. Aquat Microb Ecol 14: 261–269
Roberts IS (1996) The biochemistry and genetic of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 141: 2023–2031
Rougeaux H, Pichon R, Kervarec N, Raguénès GHC, Guezennec JG (1996) Novel bacterial exopolysaccharides from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr Polym 31: 237–242
Rougeaux H, Guezennec J, Carlson RW, Kervarec N, Pichon R, Talaga P (1999) Structural determination of the exopolysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas strain HYD 721 isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Carbohydr Res 315: 273–285
Rue EL, Bruland KW (1995) Complexation of iron (III) by natural organic ligands in the Central North Pacific as determined by a new competitive ligand equilibrium/adsorptive cathode stripping voltametric method. Mar Chem 50: 117–138
Samain E, Milas M, Bozzi L, Dubreucq M, Rinaudo M (1997) Simultaneous production of two different gel-forming exopolysaccharides by an Alteromonas strain originating from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr Polym 34: 235–241
Scharek R, Vanleeuwe MA, Debaar HJW (1997) Responses of southern ocean phytoplankton to the addition of trace metals. Deep-Sea Res 44: 209–227
Selbmann L, Onofri S, Fenice M, Frederico F, Petriuccioli M (2002) Production and structural characterization of the exopolysaccharde of the Antarctic fungus Phoma herbarum CCFEE 5080 Res Microbiol 153: 585–592
Sidhu MS, Olsen I (1997) S-layers of Bacillus species. Microbiology (UK) 143: 1039–1052
Simon M, Alldredge A, Azam F (1990) Bacterial carbon dynamics on marine snow. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 65: 205–211
Smith DC, Simon M, Alldredge A, Azam F (1992) Intense hydrolytic enzyme activity on marine aggregates and implications for rapid particle dissolution. Nature 359: 139–141
Snelgrove PVR, Grassle JF (1995) The deep sea: desert and rainforest — debunking the desert analogy. Oceanus 38: 25–28
Spaeth R, Flemming HC, Wuertz S (1998) Sorption properties of biofilms. Water Sci Technol 37: 207–210
Staley JT, Gosink JJ (1999) Poles apart: biodiversity and biogeography of sea ice bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 53: 189–215
Stetter KO (1998) Hyperthermophiles: isolation, classification and properties. In: Horikoshi K, Grant WD (eds.). Extremophiles: Microbial Life in Extreme Environments, (New York, NY: Wiley-Liss) pp 1–24
Sullivan CW, Palmisano AC (1984) Sea ice microbial communities: distribution, abundance and diversity of ice bacteria in McMurdo Sound Antarctica, in 1980. Appl Environ Microbiol 47: 788–795
Sutherland IW (1972) Bacterial exopolysaccharides. Adv Microbial Phys 8: 143–213
Sutherland IW (1977) Microbial exopolysaccharide synthesis. In: Sanford PA, Laskin A (eds.). Extracellular Microbial Polysaccharides vol. 45, (Washington DC: American Chemical Society) pp 40–57
Sutherland IW (1979) Microbial exopolysaccharides: control of synthesis and acetylation. In: Berkeley RCW (ed.). Microbial Polysaccharides and Polysaccharases, (New York, NY: Academic Press) pp 1–34
Sutherland IW (1980) Polysaccharides in adhesion of marine and freshwater bacteria. In: Berkeley RCW (ed.). Microbial Adhesion to Surfaces, (Chichester, UK: Ellis Harwood Limited) pp 329–338
Sutherland IW (1982) Biosynthesis of microbial exopolysaccharides. Adv Microbial Phys 23: 79–150
Sutherland IW (1994) Structure-function relationships in microbial exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol Adv 12: 393–448
Sutherland IW (1998) Novel and established applications of microbial Polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol 16: 41–46
Sutherland IW, (1999) Biofilm exopolysaccharides. In: Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (eds.). Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Characterization Structure and Function, (New York, NY: Springer-Verlag) pp 73–92
Sutherland IW (2001) Biofilm exopolysaccharides: a strong and sticky framework. Microbiology (UK) 147: 3–9
Szewzyk U, Holmstrom C, Wrangstadh M, Samuelsson MO, Maki JS, Kjelleberg S (1991) Relevance of the exopolysaccharide of marine Pseudomonas sp strain S9 for the attachment of Ciona intestinalis larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 75: 259–265
Talmont F, Vincent P, Fontaine T, Guezennec J, Prieur D, Fournet B (1991) Structural investigation of an industrial exopolysaccharide from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent marine bacteria. Food Hydrocolloid 5: 171–172
Uhlinger DJ, White DC (1983) Relationship between physiological status and formation of extracellular polysaccharide glycocalyx in Psuedomonas atlantica. Appl Environ Microbiol 45: 64–70
van Loosdrecht MC, Lyklema J, Norde W, Scharaa G, Zehnder AJ (1987) The role of cell wall hydrophobicity in adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol 1987: 1893–1897
van Loosdrecht MC, Norde W, Zehnder AJ (1990) Physical chemical description of bacterial adhesion. J Biomater Appl 5: 91–106
Vincent P, Pignet P, Talmont F, Bozzi L, Fournet B, Guezennec JG (1994) Production and characterization of an exopolysaccharide excreted by a deep-sea hydrothermal vent bacterium isolated from the polychaete annelid Alvinella pompejana. Appl Environ Microbiol 60: 4134–4141
Weiner RM (1997) Biopolymers from marine prokaryotes. Trends Biotechnol 15: 390–394
White DC (1986) Quantitative physiochemical characterization of bacterial habitats. In: Poindexter JS, Leadbetter ER (eds.). Methods and Special Applications in Bacterial Ecology vol. 2, (New York, NY: Plenum Press) pp 177–203
Williams AG, Wimpenny JTW (1978) Exopolysaccharide production by Pseudomonas NCIB11264 grown in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol 104: 47–57
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (1999) What are bacterial extracellular polymer substances? In: Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (eds.). Microbial Extracellular Polymer Substances, (Berlin, Germany: Springer) pp 1–19
Wolfaardt GM, Lawrence JR, Korber DR (1999) Function of EPS In: Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (eds.). In Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Characterization Structure and Function, (New York, NY: Springer-Verlag) pp 171–200
Wood P, Caldwell DE, Evan E, Jones M, Korber DR, Wolfaardt GM, Wilson M, Gilbert P (1998) Surface-catalysed disinfection of thick Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 84: 1092–1098
Wu JF, Boyle E, Sunda W, Wen LS (2001) Soluble and colloidal iron in the oligotrophic North Atlantic and North Pacific. Science 293: 847–849
Wuertz S, Muller E, Spaeth R, Pfleiderer P, Flemming HC (2000) Detection of heavy metals in bacterial bofilms and microbial floes with the fluorescent complexing agent Newport Green. J Ind Microbiol Biot 24: 116–123
Yayanos AA (1998) Empirical and theoretical aspects of life at high pressure in the deepsea. In: Horikoshi K, Grant WD (eds.). Extremophiles: Microbial Life in Extreme Environments, (New York, NY: Wiley-Liss) pp 47–92
Zanchetta P, Guezennec J (2001) Surface thermodynamics of osteoblasts: relation between hydrophobicity and bone active biomaterials. Colloids Surfaces 22: 301–307
Zanchetta P, Lagarde M, Guezennec J (2003a) A new bone-healing material: A hyaluronic acid-like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif Tissue Int 72: 74–79
Zanchetta P, Lagarde N, Guezennec J (2003b) Systematic effects on bone healing of a new hyaluronic acid-like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif Tissue Int 73: 232–236
Zobell CE (1943) The effect of solid surfaces upon bacterial activity. J Bacteriol 46: 75–82
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Drs. June Olley and Peter Nichols for their careful reading and helpful suggestions during the preparation of this manuscript. The efforts of three anonymous referees are acknowledged as their comments significantly improved this review. C.M.N. was supported by a Tasmanian Post-graduate Research Scholarship and by funding provided by the Australian Antarctic Division. C.M.N. also received a travel award from the Australian Academy of Science and the French Embassy in Canberra, Australia. Figures 1–4 are reprinted with kind permission of Springer Science+Business Media.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nichols, C.M., Guezennec, J. & Bowman, J. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Environments with Special Consideration of the Southern Ocean, Sea Ice, and Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents: A Review. Mar Biotechnol 7, 253–271 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-004-5118-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-004-5118-2