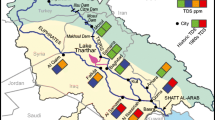
Abstract
The water salinity of the Euphrates River as it enters Iraq, expressed as total dissolved solids (TDS), has more than doubled compared to that of 1973. Downstream of Al Hindia Barrage, south of Baghdad, the salinity has increased gradually over the last 30 years. The annual average TDS at Al Nassiriah, in the lower reaches of the Euphrates, has increased from 1,080 ppm in 1979 to more than 4,500 ppm in 2001. Water quality of the Euphrates within Iraq has deteriorated due to the decreased flow that is entering Iraq, diverted flows to the river from Al Tharthar Lake, and irrigation-return flow. The decreased flow from upstream sources was due to reservoir construction projects. Water from Al Tharthar Lake and from irrigation return flow is being diverted to the Euphrates to compensate for the upstream deficit. An environmental flow rate of 178 m3/s (annual minimum flow, 5.6 bcm or about one-third of historic minimum flow) is proposed as the minimum discharge that must be flowing into Iraq to preserve the environment of the Euphrates River in Iraq. A flow of twice this amount would allow more reasonable downstream management with an input average salinity of 760 ppm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hadithi AH (1978) Optimal utilization of the water resources of the Euphrates River in Iraq. Doctoral Dissertation. University of Arizona
Al-Najim M (2003) Impact of Tigris and Euphrates water crisis on the environmental catastrophe of Iraqi Marshlands, p 13
Ali M, Salewicz KA (2005) Study on the salinity of Euphrates–Tigris Rivers, Iraq-model development status. Third Expert Meeting on Euphrates/Tigris River Basin Management. Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, The University of Tokyo
Altinbilek D (2004) Development and management of the Euphrates–Tigris basin. Water Resour Dev 20(1):15–33. doi:10.1080/07900620310001635584
Arab Science and Technology Foundation (2005) A preliminary survey of Iraqi capabilities, part three. Sharjah, UAE, p 12
Beaumont P (1978) The River Euphrates: an international problem of water development resources. Environ Conserv 5(1):35–44
Beaumont P (1996) Agricultural and environmental changes in the upper Euphrates catchment of Turkey and Syria and their political and economic implications. Appl Geogr 16(2):137–157. doi:10.1016/0143-6228(95)00033-X
Beaumont P (1998) Restructuring of water usage in the Tigris–Euphrates Basin: the impact of modern water management policies. In: Albert J, Bernhadsson M, Kenna R (eds) Transformation of Middle Eastern natural environments: legacies and lessons, vol 103. Bulletin Series, Yale School of Forestry and Environmental Studies. New Haven, Yale University Press
Bilen O (1997) Turkey and water issues in the Middle East. Southern Anatolia Project (GAP). Regional Development Administration. Ankara, Turkey
Dyson M, Bergkamp G, Scanlon J (eds) (2003) Flow. The essential of environmental flows. IUCN, Gland
Fact Finding Mission to the Ilisu Dam Region (2002). Draft report, The Ilisu Dam Campaign. The Kurdish Human Rights Project and the Corner House, p 47
FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations) (1976) Water quality for agriculture, vol 29. FAO, Rome
FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations) (2003) Towards sustainable agricultural development in Iraq; the transition from relief, rehabilitation and reconstruction to development, Rome. Available at http://www.fao.org/docrep/006/y9870e/y9870e00.htm
Fattah QN, Abdul Baki J (1980) Effect of drainage systems on water quality in major Iraqi rivers. The influence of man on the hydrological regime with special references to representative experimental basins. In: Proceedings of the Helsinki symposium, IAHS-AISH publication, vol 130
Grego S, Micangeli A, Esposto S (2004) Water purification in the Middle East crisis: a survey on WTP and CU in Basrah (Iraq) area within a research and development program. Desalination 165:73–79
Hanna AB, Al Talbani K (1970) Evaluation of water quality in Iraq. First Technical Conference. Arab Federation of Agricultural Engineers, Khartoum
Hillel D (1994) Rivers of Eden: the struggle foe water and the quest for peace in the Midde East. Oxford University Press, New York
Kolars J (1994) Problems of international river management: the case of the Euphrates. In: Biswas AK (ed) International waters of the Middle East—from Euphrates–Tigris to Nile. Oxford University Press, London, pp 44–94
Metropolitan Water District of Southern California (MWD) and the United States Bureau of Reclamation (USBR) (1999) Salinity management study. Final report: long-term strategy and recommended action plan, p 70
Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) and Ministry of Irrigation (MI) Baghdad (1999) The division of waters in the International Law: facts on the joint waters with Turkey. Baghdad, Iraq (Unpublished)
Ministry of Irrigation (1998) Hydrological survey program of Iraq. Baghdad (Unpublished data)
Ministry of Irrigation (2002) Hydrogeological investigations of Al Atshan River (in Arabic). Baghdad, Iraq (unpublished)
Ministry of Municipalities (1980) Al Nassiriah drinking water project: planning report, Baghdad, Iraq (Unpublished)
Mirza MMQ (1998) Diversion of the Ganges water at Farakka and its effect on salinity in Bangladesh. Environ Manage 22(5):711–722. doi:10.1007/s002679900141
Murakami M (1995) Managing water for peace in the Middle East: alternative strategies. United Nations University Press, Tokyo, p 320
Partow H (2001) The Mesopotamian Marshlands: demise of an ecosystem early warning and assessment technical report, UNEP/DEWA/TR.01–3 Rev. 1 Division of Early Warning and Assessment. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi
Pierson WL, Bishop KA, Van Senden D, Horton PR, Adamantidis CA (2002) Environmental water requirements to maintain estuarine processes, Water Research Laboratory Technical Report 2000/11, Environmental Flows Initiative Technical Report, 3, National River Health Program, Report prepared for Environment Australia
Rahi KA (2002) Deterioration of the Euphrates water quality downstream of Al Kufa Barrage (in Arabic). Ministry of Irrigation, Baghdad
Scheumann W (1993) New irrigation scheme in Southeast Anatolia and in Northern Syria: more competition and conflict over the Euphrates. Q J Int Agric 32(3):240–259
Tennant DL (1976) Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation, and related environmental resources. In: Instream flow needs II: Boise, Idaho. Proceedings of the symposium and specialty conference on instream flow needs. May 3–6, American Fisheries Society
The Iraqi Foundation (2003) Draft report: physical characteristics of Mesopotamian Marshlands of Southern Iraq (unpublished)
Topkaya (1998) Water resources in the Middle East: forthcoming problems and solutions for sustainable development of the region. Available at http://www.akdeniz.edu.tr/muhfak/publications/gap.html
Ubell K (1971) Iraq’s water resources. Nat Resour 7(2):3–9
UNEP (United Nations Environmental Program) 2003, Desk Study on the Environment of Iraq, Switzerland, p 96
United Nations (1997) Watercourses Convention and the Euphrates–Tigris Rivers UNEP (United Nations Environmental Program), 2003. Desk study on the environment of Iraq
U. S. Agency for International Development (USAID) (2004) Iraqi Marshlands restoration program: action plan
WHO (World Health Organization) (1997) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: surveillance and control of community supplies, 2nd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgments
Partial support of Khayyun Rahi for this research is from the Environmental Science Graduate Program of Oklahoma State University. We would like to thank Eliot Atekwana, Meghan Dailey, and Tim Sickbert for helpful discussion and comments on this work. We would also like to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful comments which improved our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahi, K.A., Halihan, T. Changes in the salinity of the Euphrates River system in Iraq. Reg Environ Change 10, 27–35 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-009-0083-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-009-0083-y