Abstract
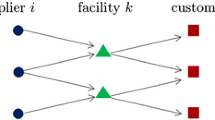
We propose a cutting-plane approach (namely, Benders decomposition) for a class of capacitated multi-period facility location problems. The novelty of this approach lies on the use of a specialized interior-point method for solving the Benders subproblems. The primal block-angular structure of the resulting linear optimization problems is exploited by the interior-point method, allowing the (either exact or inexact) efficient solution of large instances. The consequences of different modeling conditions and problem specifications on the computational performance are also investigated both theoretically and empirically, providing a deeper understanding of the significant factors influencing the overall efficiency of the cutting-plane method. The methodology proposed allowed the solution of instances of up to 200 potential locations, one million customers and three periods, resulting in mixed integer linear optimization problems of up to 600 binary and 600 millions of continuous variables. Those problems were solved by the specialized approach in less than one hour and a half, outperforming other state-of-the-art methods, which exhausted the (144 GB of) available memory in the largest instances.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albareda-Sambola, M., Fernández, E., Hinojosa, Y., Puerto, J.: The multi-period incremental service facility location problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 36, 1356–1375 (2009)
Albareda-Sambola, M., Alonso-Ayuso, A., Escudero, L., Fernández, E., Hinojosa, Y., Pizarro-Romero, C.: A computational comparison of several formulations for the multi-period incremental service facility location problem. TOP 18, 62–80 (2010)
Alumur, S., Kara, B.Y., Melo, T.: Location and logistics. In: Laporte, G., Nickel, S., Saldanha-da-Gama, F. (eds.) Location Science. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Barahona, F., Anbil, R.: The volume algorithm: producing primal solutions with a subgradient method. Math. Program. 87, 385–399 (2000)
Benders, J.F.: Partitioning procedures for solving mixed-variables programming problems. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2, 3–19 (2005). (English translation of the original paper appeared in. Numerische Mathematik 4(238–252), 1962)
Cao, Y., Laird, C.D., Zavala, V.M.: Clustering-based preconditioning for stochastic programs. Comput. Optim. Appl. 64, 379–406 (2016)
Castro, J.: A specialized interior-point algorithm for multicommodity network flows. SIAM J. Optim. 10, 852–877 (2000)
Castro, J.: An interior-point approach for primal block-angular problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 36, 195–219 (2007)
Castro, J.: Interior-point solver for convex separable block-angular problems. Optim. Methods Softw. 31, 88–109 (2016)
Castro, J., Cuesta, J.: Quadratic regularizations in an interior-point method for primal block-angular problems. Math. Program. A 130, 415–445 (2011)
Castro, J., Nasini, S.: Mathematical programming approaches for classes of random network problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 245, 402–414 (2015)
Chvátal, V.: Linear Programming. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York (1983)
Colombo, M., Gondzio, J., Grothey, A.: A warm-start approach for large-scale stochastic linear programs. Math. Program. 127, 371–397 (2011)
Cornuéjols, G.P., Nemhauser, G.L., Wolsey, L.A.: The uncapacitated facility location problem. In: Mirchandani, P.B., Francis, R.L. (eds.) Discrete Location Theory. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1990)
Escudero, L.F., Garín, M.A., Pérez, G., Unzueta, A.: Lagrangian decomposition for large-scale two-stage stochastic mixed 0–1 problems. TOP 20, 347–374 (2012)
Fischetti, M., Ljubić, I., Sinnl, M.: Benders decomposition without separability: a computational study for capacitated facility location problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 253, 557–569 (2016)
Fischetti, M., Ljubić, I., Sinnl, M.: Redesigning Benders decomposition for large scale facility location. Manag. Sci. doi:10.1287/mnsc.2016.2461 (2016)
Gondzio, J.: Multiple centrality corrections in a primal-dual method for linear programming. Comput. Optim. Appl. 6, 137–156 (1996)
Gondzio, J., Sarkissian, R.: Parallel interior-point solver for structured linear programs. Math. Program. 96, 561–584 (2003)
Gondzio, J., Vial, J.-P.: Warm start and \(\epsilon \)-subgradients in the cutting plane scheme for block-angular linear programs. Comput. Optim. Appl. 14, 17–36 (1999)
Gondzio, J., González-Brevis, P., Munari, P.: New developments in the primal-dual column generation technique. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 224, 41–51 (2013)
Held, M., Wolfe, P., Crowder, H.: Validation of subgradient optimization. Math. Program. 6, 62–88 (1974)
Jena, S., Cordeau, J.-F., Gendron, B.: Modeling and solving a logging camp location problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 232, 151–177 (2015)
Jena, S., Cordeau, J.-F., Gendron, B.: Dynamic facility location with generalized modular capacity. Transp. Sci. 49, 484–499 (2015)
Lemaréchal, C., Strodiot, J.J., Bihain, A.: On a bundle algorithm for nonsmooth optimization. In: Mangasarian, O.L., Meyer, R.R., Robinson, S.M. (eds.) Nonlinear Programming 4, pp. 245–282. Academic Press, New York (1981)
Lübbecke, M.E.: Column generation. In: Cochran, J.J., Cox, L.A., Keskinocak, P., Kharoufeh, J.P., Smith, J.C. (eds.) Wiley Encyclopedia of Operations Research and Management Science, Wiley Online Library, Chichester (2011)
Lubin, M., Hall, J.A., Petra, C.G., Anitescu, M.: Parallel distributed-memory simplex for large-scale stochastic LP problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 55, 571–596 (2013)
Magnanti, T.L., Wong, R.T.: Accelerating Benders decomposition: algorithmic enhancement and model selection criteria. Oper. Res. 29, 464–484 (1981)
Magnanti, T.L., Wong, R.T.: Decomposition methods for facility location problems. In: Mirchandani, P.B., Francis, R.L. (eds.) Discrete Location Theory. Wiley, New York (1990)
Malick, J., de Oliveira, W., Zaourar, S.: Nonsmooth optimization using uncontrolled inexact information. In: Technical Report, INRIA Grenoble (2013). http://www.optimization-online.org/DBHTML/2013/05/3892.html
Medhi, D.: Bundle-based decomposition for large-scale convex optimization: error estimate and application to block-angular linear programs. Math. Program. 66, 79–101 (1994)
Melo, M.T., Nickel, S., Saldanha-da-Gama, F.: Dynamic multi-commodity capacitated facility location: a mathematical modeling framework for strategic supply chain planning. Comput. Oper. Res. 33, 181–208 (2006)
Melo, M.T., Nickel, S., Saldanha-da-Gama, F.: Facility location and supply chain management—a review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 196, 401–412 (2009)
Mitchell, J.E., Borchers, B.: Solving real-world linear ordering problems using a primal-dual interior point cutting plane method. Ann. Oper. Res. 62, 253–276 (1996)
Munari, P., Gondzio, J.: Using the primal-dual interior point algorithm within the branch-price-and-cut method. Comput. Oper. Res. 40, 2026–2036 (2013)
Nickel, S., Saldanha-da-Gama, F.: Multi-period facility location. In: Laporte, G., Nickel, S., Saldanha-da-Gama, F. (eds.) Location Science. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Nickel, S., Saldanha-da-Gama, F., Ziegler, H.-P.: A multi-stage stochastic supply network design problem with financial decisions and risk management. Omega 40, 511–524 (2012)
Oliveira, W., Sagastizábal, C., Scheimberg, S.: Inexact bundle methods for two-stage stochastic programming. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 517–544 (2011)
Petra, C.G., Schenk, O., Lubin, M., Gaertner, K.: An augmented incomplete factorization approach for computing the Schur complement in stochastic optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36, C139–C162 (2014)
Polyak, B.T.: Subgradient method: a survey of Soviet research. In: Lemaréchal, C., Mifflin, R. (eds.) Nonsmooth Optimization, pp. 5–28. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1978)
Rei, W., Cordeau, J.-F., Gendreau, M., Soriano, P.: Accelerating Benders decomposition by local branching. INFORMS J. Comput. 21, 333–345 (2009)
Robinson, S.M.: Bundle-based decomposition: description and preliminary results. In: Prékopa, A., Szelezsfin, J., Strazicky, B. (eds.) System Modelling and Optimization, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, vol. 84. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Ruszczyński, A.: An augmented Lagrangian decomposition method for block diagonal linear programming problems. Oper. Res. Lett. 8, 287–294 (1989)
van Ackooij, W., Frangioni, A., de Oliveira, W.: Inexact stabilized Benders’ decomposition approaches with application to chance-constrained problems with finite support. Comput. Optim. Appl. doi:10.1007/s10589-016-9851-z (2016)
Wentges, P.: Accelerating Benders decomposition for the capacitated facility location problem. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 44, 267–290 (1996)
Wright, S.J.: Primal-Dual Interior-Point Methods. SIAM, Philapelphia (1996)
Zakeri, G., Philpott, A.B., Ryan, D.M.: Inexact cuts in Benders decomposition. SIAM J. Optim. 10, 643–657 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The first author has been supported by MINECO/FEDER Grants MTM2012-31440 and MTM2015-65362-R of the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness; the second author has been supported by the European Research Council-ref. ERC-2011-StG 283300-REACTOPS; the third author has been supported by the Portuguese Science Foundation (FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia) under the Project UID/MAT/04561/2013 (CMAF-CIO/FCUL). The authors would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, suggestions and insights that helped improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Tables of numerical experiments of Sect. 4.1
Appendix: Tables of numerical experiments of Sect. 4.1
Tables 8, 9 and 10 contain the CPU times (seconds) required by the Benders decomposition and the branch-and-cut to solve instances of (1)–(8), with one, three and six time periods respectively. The parameter specification has been defined in Table 1, with different combinations of \(\alpha \) and \(\beta \) and for two sizes \(m = n = 500\) and \(m = n = 1000\).
1.1 One period
See Table 8.
1.2 Three periods
See Table 9.
1.3 Six periods
See Table 10.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, J., Nasini, S. & Saldanha-da-Gama, F. A cutting-plane approach for large-scale capacitated multi-period facility location using a specialized interior-point method. Math. Program. 163, 411–444 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-016-1067-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-016-1067-6
Keywords
- Mixed integer linear optimization
- Interior-point methods
- Multi-period facility location
- Cutting planes
- Benders decomposition
- Large-scale optimization