Abstract
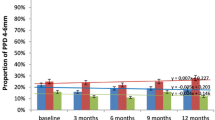
The objective of this work was to compare the effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (PDT), diode soft laser therapy (DSL), and thorough deep scaling and root planing (SRP) for treatment of residual pockets. Thirty-two subjects with a history of non-surgical treatment for chronic periodontitis were included. Residual pockets >4 mm and bleeding upon probing were debrided with an ultrasonic device and then subjected to either PDT, DSL, or SRP. Pocket probing depth (PPD), bleeding on probing (BOP), and gingival recession were monitored over 6 months. Counts of four microorganisms were determined by direct hybridization with RNA probes. PPD decreased from 5.6 ± 1.0 to 3.8 ± 1.1 in 6 months (p < 0.001), and BOP decreased from 100% to 52% (p < 0.01). The risk for a site to remain >4 mm with BOP depended on initial PPD (p = 0.036) and was higher if treated with DSL (p = 0.034). Frequencies of three microorganisms were significantly lower in PDT- and SRP-treated than in DSL-treated quadrants (p = 0.02) after 14 days, but not at months 2 and 6. All three treatments resulted in a significant clinical improvement. PDT and SRP suppressed Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, and Treponema denticola stronger, and resulted in fewer persisting pockets after 6 months, than DSL application.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Weijden GA, Timmerman FA (2002) A systematic review on the clinical efficacy of subgingival debridement in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 29(Suppl 3):55–71
Axelsson P, Nystrom B, Lindhe J (2004) The long-term effect of a plaque control program on tooth mortality, caries and periodontal disease in adults. Results after 30 years of maintenance. J Clin Periodontol 31:749–757
Cionca N, Giannopoulou C, Ugolotti G, Mombelli A (2009) Amoxicillin and metronidazole as an adjunct to full-mouth scaling and root planing of chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol 80:364–371
Mombelli A, Cionca N, Almaghlouth A (2011) Does adjunctive antimicrobial therapy reduce the perceived need for periodontal surgery? Periodontol 2000 55:205–216
Mombelli A, Schmid B, Rutar A, Lang NP (2000) Persistence patterns of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia/nigrescens, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans after mechanical therapy of periodontal disease. J Periodontol 71:14–21
Magnusson I, Lindhe J, Yoneyama T, Liljenberg B (1984) Recolonization of a subgingival microbiota following scaling in deep pockets. J Clin Periodontol 11:193–207
Quirynen M, Bollen CML, Vandekerckhove BNA, Dekeyser C, Papaioannou W, Eyssen H (1995) Full- vs. partial-mouth disinfection in the treatment of periodontal infections: short-term clinical and microbiological observations. J Dent Res 74:1459–1467
Sbordone L, Ramaglia L, Gulletta E, Iacono V (1990) Recolonization of the subgingival microflora after scaling and root planing in human periodontitis. J Periodontol 61:579–584
Kocher T, Fanghanel J, Sawaf H, Litz R (2001) Substance loss caused by scaling with different sonic scaler inserts—an in vitro study. J Clin Periodontol 28:9–15
Flemmig TF, Petersilka GJ, Mehl A, Hickel R, Klaiber B (1998) The effect of working parameters on root substance removal using a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler in vitro. J Clin Periodontol 25:158–163
Ritz L, Hefti AF, Rateitschak KH (1991) An in vitro investigation on the loss of root substance in scaling with various instruments. J Clin Periodontol 18:643–647
Zappa U, Smith B, Simona C, Graf H, Case D, Kim W (1991) Root substance removal by scaling and root planing. J Periodontol 62:750–754
Moëne R, Décaillet F, Andersen E, Mombelli A (2010) Subgingival plaque removal using a new air-polishing device. J Periodontol 81:79–88
Moritz A, Schoop U, Goharkhay K, Schauer P, Doertbudak O, Wernisch J, Sperr W (1998) Treatment of periodontal pockets with a diode laser. Lasers Surg Med 22:302–311
Moritz A, Gutknecht N, Doertbudak O, Goharkhay K, Schoop U, Schauer P, Sperr W (1997) Bacterial reduction in periodontal pockets through irradiation with a diode laser: a pilot study. J Clin Laser Med Surg 15:33–37
Schwarz F, Aoki A, Becker J, Sculean A (2008) Laser application in non-surgical periodontal therapy: a systematic review. J Clin Periodontol 35:29–44
Karlsson MR, Diogo Lofgren CI, Jansson HM (2008) The effect of laser therapy as an adjunct to non-surgical periodontal treatment in subjects with chronic periodontitis: a systematic review. J Periodontol 79:2021–2028
Azarpazhooh A, Shah PS, Tenenbaum HC, Goldberg MB (2010) The effect of photodynamic therapy for periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol 81:4–14
Haffajee AD, Socransky SS, Gunsolley JC (2003) Systemic anti-infective periodontal therapy. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol 8:115–181
Herrera D, Sanz M, Jepsen S, Needleman I, Roldán S (2002) A systematic review on the effect of systemic antimicrobials as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol 29:136–159
Silness J, Löe H (1964) Periodontal disease in pregnancy II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol Scand 22:121–135
Löe H, Silness J (1963) Periodontal disease in pregnancy I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odontol Scand 21:533–551
Dix K, Watanabe SM, McArdle S, Lee DI, Randolph C, Moncla B, Schwartz DE (1990) Species-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the identification of periodontal bacteria. J Clin Microbiol 28:319–323
Sigusch BW, Engelbrecht M, Volpel A, Holletschke A, Pfister W, Schutze J (2010) Full-mouth antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in Fusobacterium nucleatum-infected periodontitis patients. J Periodontol 81:975–981
Yilmaz S, Kuru B, Kuru L, Noyan U, Argun D, Kadir T (2002) Effect of gallium arsenide diode laser on human periodontal disease: a microbiological and clinical study. Lasers Surg Med 30:60–66
Andersen R, Loebel N, Hammond D, Wilson M (2007) Treatment of periodontal disease by photodisinfection compared to scaling and root planing. J Clin Dent 18:34–38
Christodoulides N, Nikolidakis D, Chondros P, Becker J, Schwarz F, Rossler R, Sculean A (2008) Photodynamic therapy as an adjunct to non-surgical periodontal treatment: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 79:1638–1644
Braun A, Dehn C, Krause F, Jepsen S (2008) Short-term clinical effects of adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in periodontal treatment: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 35:877–884
de Oliveira RR, Schwartz-Filho HO, Novaes AB Jr, Taba M Jr (2007) Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in the non-surgical treatment of aggressive periodontitis: a preliminary randomized controlled clinical study. J Periodontol 78:965–973
Chondros P, Nikolidakis D, Christodoulides N, Rossler R, Gutknecht N, Sculean A (2009) Photodynamic therapy as adjunct to non-surgical periodontal treatment in patients on periodontal maintenance: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Lasers Med Sci 24:681–688
Ge L, Shu R, Li Y, Li C, Luo L, Song Z, Xie Y, Liu D (2011) Adjunctive effect of photodynamic therapy to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. Photomed Laser Surg 29:33–37
Theodoro LH, Silva SP, Pires JR, Soares GH, Pontes AE, Zuza EP, Spolidorio DM, de Toledo BE, Garcia VG (2011) Clinical and microbiological effects of photodynamic therapy associated with nonsurgical periodontal treatment. A 6-month follow-up. Lasers Med Sci
Hauser K, Walsh D (2008) Visual analogue scales and assessment of quality of life in cancer. J Support Oncol 6:277–282
Dexter F, Chestnut DH (1995) Analysis of statistical tests to compare visual analog scale measurements among groups. Anesthesiology 82:896–902
Gallagher EJ, Bijur PE, Latimer C, Silver W (2002) Reliability and validity of a visual analog scale for acute abdominal pain in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 20:287–290
Williams JM, Murray JJ, Lund CA, Harkiss B, de Franco A (1985) Anxiety in the child dental clinic. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 26:305–310
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the following companies: Helbo Photodynamic Systems GmbH & Co KG, Walldorf, Germany, who provided the material for the photodynamic therapy and the 660-nm diode laser free of charge, Elexxion AG, Radolfzell, Germany who provided the 810-nm diode laser free of charge, and the Institut für angewandte Immunologie, Zuchwil, Switzerland, who provided the microbiological analyses free of charge.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappuyns, I., Cionca, N., Wick, P. et al. Treatment of residual pockets with photodynamic therapy, diode laser, or deep scaling. A randomized, split-mouth controlled clinical trial. Lasers Med Sci 27, 979–986 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-011-1027-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-011-1027-6