Abstract
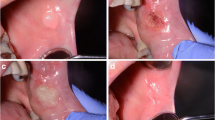
The use of the CO2 laser in the management of oral dysplastic lesions has become a more common practice. Very few studies have evaluated recurrence, residual disease malignant transformation, and overall outcome in patients undergoing such a procedure. In this prospective study, a total of 123 oral dysplastic lesions from 77 consecutive patients were treated with the CO2 laser (resection and/or ablation). The average age was 58 ± 4.8 years. The patients’ recovery was uneventful and no complications were reported. Comparisons with the clinical and histopathological features and rate of recurrence as well as malignant transformation were made. The patients were followed-up for a mean of 6.4 years, and biopsies taken in case of changes suggestive of malignant development. Homogenous leukoplakias were identified in 31 patients, non-homogenous leukoplakias in 34 patients, whereas 12 patients had erythroplakias. Ex- and life-long smokers formed 88.3% of the recruited patients. While people who currently smoke and drink formed 55.8% of the cohort. Erythroplakias were solely identified in heavy life-long smokers. The most common identified primary anatomical locations were the lateral border of tongue, floor of mouth, and buccal mucosa. Moderate dysplasia was identified in 42 patients while 18 patients had severe dysplasia. Laser resection margins in selected cases (68 patients) were clear in 53 and showed mild-moderate dysplasia in the involved margins. The rate of recurrence had no significant association with the location but the severity of epithelial dysplasia. The rate of first recurrence after laser surgery was approximately 19.5%. Malignant transformation was observed in eight patients (10.4%), in the tongue and the floor of mouth. Recurrence and malignant transformation was mainly identified in erythroplakias and non-homogenous leukoplakias. Laser resection/ablation is recommended for oral dysplasia to prevent not only recurrence and malignant transformation but also postoperative oral dysfunction encountered by other conventional modalities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roodenburg JL, Witjes MJ, de Veld DC, Tan IB, Nauta JM (2002) Lasers in dentistry 8. Use of lasers in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd 109(12):470–474
Burkey BB MD, Garrett G (1996) Use of the laser in the oral cavity. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 29(6):949–961
Patel CKN (1964) Continuous-wave laser action on vibrational-rotational transitions of CO2. Phys Rev 136(5A):A1187–A1193
Bornstein MM, Winzap-Kälin C, Cochran DL, Buser D (2005) The CO2 laser for excisional biopsies of oral lesions: a case series study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 25(3):221–229
Tuncer I, Ozçakir-Tomruk C, Sencift K, Cöloğlu S (2010) Comparison of conventional surgery and CO2 laser on intraoral soft tissue pathologies and evaluation of the collateral thermal damage. Photomed Laser Surg 28(1):75–79
Ishii J, Kuriyama T, Komori T (2005) Experimental study on the morphological and functional recovery following partial glossectomy in rabbits: a comparison between CO2 laser and electrocautery. Photomed Laser Surg 23(1):47–51
Chandu A, Smith AC (2005) The use of CO2 laser in the treatment of oral white patches: outcomes and factors affecting recurrence. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34(4):396–400
Hamadah O, Thomson PJ (2009) Factors affecting carbon dioxide laser treatment for oral precancer: a patient cohort study. Lasers Surg Med 41(1):17–25
van der Hem PS, Nauta JM, van der Wal JE, Roodenburg JL (2005) The results of CO2 laser surgery in patients with oral leukoplakia: a 25-year follow up. Oral Oncol 41(1):31–37
Schoelch ML, Sekandari N, Regezi JA, Silverman S Jr (1999) Laser management of oral leukoplakias: a follow-up study of 70 patients. Laryngoscope 109(6):949–953
White JM, Chaudhry SI, Kudler JJ, Sekandari N, Schoelch ML, Silverman S Jr (1998) Nd:YAG and CO2 laser therapy of oral mucosal lesions. J Clin Laser Med Surg 16(6):299–304
Chiesa F, Boracchi P, Tradati N, Rossi N, Costa L, Giardini R, Marazza M, Zurrida S (1993) Risk of preneoplastic and neoplastic events in operated oral leukoplakias. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 29B(1):23–28
Gooris PJ, Roodenburg JL, Vermey A, Nauta JM (1999) Carbon dioxide laser evaporation of leukoplakia of the lower lip: a retrospective evaluation. Oral Oncol 35(5):490–495
Thomson PJ, Wylie J (2002) Interventional laser surgery: an effective surgical and diagnostic tool in oral precancer management. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 31(2):145–153
Werner JA, Dunne AA, Folz BJ, Lippert BM (2002) Transoral laser microsurgery in carcinomas of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. Cancer Control 9(5):379–386
Ishii J, Fujita K, Komori T (2002) Clinical assessment of laser monotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the mobile tongue. J Clin Laser Med Surg 20(2):57–61
Wang CP, Chang SY, Wu JD, Tai SK (2001) Carbon dioxide laser microsurgery for tongue cancer: surgical techniques and long-term results. J Otolaryngol 30(1):19–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jerjes, W., Upile, T., Hamdoon, Z. et al. CO2 laser of oral dysplasia: clinicopathological features of recurrence and malignant transformation. Lasers Med Sci 27, 169–179 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-011-0916-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-011-0916-z