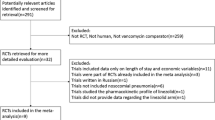
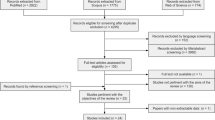
Abstract
As long-standing clinical problems, a series of complicated infections are more difficult to treat due to the development of antibiotic resistance, especially caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VRE), and multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). Moreover, the treatment options available to against these infections are also becoming increasingly limited. Linezolid is the first synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with a unique mechanism of action, and its efficacy against Gram-positive bacteria has been clearly demonstrated. However, the limitations of linezolid alone for the treatment of these complicated infections have been reported in the recent years. Combination therapy may be a good approach to enhance efficacy and prevent the development of resistance. In this review, the results of multiple linezolid combination therapies from in vitro, animal studies, and clinical cases for the treatment of MRSA, VRE, and multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains will be discussed, and thus provide more relevant information for clinician in clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gasch O, Ayats J, Angeles Dominguez M, Tubau F, Linares J, Pena C, Grau I, Pallares R, Gudiol F, Ariza J et al (2011) Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bloodstream infection: secular trends over 19 years at a university hospital. Medicine 90(5):319–327
Hidron AI, Edwards JR, Patel J, Horan TC, Sievert DM, Pollock DA, Fridkin SK (2013) NHSN annual update: antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006-2007. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 29(11):996–1011
DeRyke CA, Lodise TP Jr, Rybak MJ, McKinnon PS (2005) Epidemiology, treatment, and outcomes of nosocomial bacteremic Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Chest 128(3):1414–1422
Hayakawa K, Martin ET, Gudur UM, Marchaim D, Dalle D, Alshabani K, Muppavarapu KS, Jaydev F, Bathina P, Sundaragiri PR et al (2014) Impact of different antimicrobial therapies on clinical and fiscal outcomes of patients with bacteremia due to vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(7):3968–3975
Duplessis C, Crum-Cianflone NF (2011) Ceftaroline: a new cephalosporin with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Clinical medicine reviews in therapeutics.3,pii: a2466
Tsakris A, Pournaras S, Maniatis AN, Douboyas J, Antoniadis A (2001) Increasing prevalence of high-level gentamicin resistance among enterococci isolated in Greece. Chemotherapy 47(2):86–89
Padmasini E, Padmaraj R, Ramesh SS (2014) High level aminoglycoside resistance and distribution of aminoglycoside resistant genes among clinical isolates of Enterococcus species in Chennai, India. Sci World J 2014(1):329157
Ribes S, Pachón-Ibáñez ME, Domínguez MA, Fernández R, Tubau F, Ariza J, Gudiol F, Cabellos C (2010) In vitro and in vivo activities of linezolid alone and combined with vancomycin and imipenem against Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 29(11):1361–1367
Barber KE, Smith JR, Raut A, Rybak MJ (2016) Evaluation of tedizolid against Staphylococcus aureus and enterococci with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin, daptomycin or linezolid. J Antimicrob Chemother 71(1):152–155
Stevens DL, Dotter B, Madaras-Kelly K (2004) A review of linezolid: the first oxazolidinone antibiotic. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 2(1):51–59
Ager S, Gould K (2012) Clinical update on linezolid in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections. Infect Drug Resist 5:87–102
Smith JR, Barber KE, Raut A, Aboutaleb M, Sakoulas G, Rybak MJ (2015) β-Lactam combinations with daptomycin provide synergy against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. J Antimicrob Chemother 70(6):1738–1743
Maltempe FG (2017) Caleffi-Ferracioli KR, do Amaral RCR, de Oliveira Demitto F, Siqueira VLD, de Lima Scodro RB, Hirata MH, Pavan FR, Cardoso RF: activity of rifampicin and linezolid combination in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 104:24–29
Takahashi Y, Takesue Y, Nakajima K, Ichiki K, Tsuchida T, Tatsumi S, Ishihara M, Ikeuchi H, Uchino M (2011) Risk factors associated with the development of thrombocytopenia in patients who received linezolid therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 17(3):382–387
Billington EO, Phang SH, Gregson DB, Pitout JD, Ross T, Church DL, Laupland KB, Parkins MD (2014) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes for Enterococcus spp. blood stream infections: a population-based study. Int J Infect Dis 26:76–82
Jumbe NLNS, Drusano GL (2011) A model-based PK/PD antimicrobial chemotherapy drug development platform to simultaneously combat infectious diseases and drug resistance. Springer New York p.251–279
Zabransky RJ (2002) Linezolid: the first of a new class of antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Newsl 24(4):25–30
Nam HS, Koh WJ, Kwon OJ, Cho SN, Shim TS (2009) Daily half-dose linezolid for the treatment of intractable multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(1):92–93
Myrianthefs P, Markantonis SL, Vlachos K, Anagnostaki M, Boutzouka E, Panidis D, Baltopoulos G (2006) Serum and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of linezolid in neurosurgical patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(12):3971–3976
Viaggi B, Paolo AD, Danesi R, Polillo M, Ciofi L, Tacca MD, Malacarne P (2011) Linezolid in the central nervous system: comparison between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma pharmacokinetics. Scand J Infect Dis 43(9):721
Cepeda JA, Whitehouse T, Cooper B, Hails J, Jones K, Kwaku F, Taylor L, Hayman S, Shaw S, Kibbler C et al (2004) Linezolid versus teicoplanin in the treatment of gram-positive infections in the critically ill: a randomized, double-blind, multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother 53(2):345–355
Rayner CR, Forrest A, Meagher AK, Birmingham MC, Schentag JJ (2003) Clinical pharmacodynamics of linezolid in seriously ill patients treated in a compassionate use programme. Clin Pharmacokinet 42(15):1411–1423
Smith PF, Birmingham MC, Noskin GA, Meagher AK, Forrest A, Rayner CR, Schentag JJ (2003) Safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of linezolid for treatment of resistant gram-positive infections in cancer patients with neutropenia. Ann Oncol 14(5):795–801
Matsumoto K, Shigemi A, Takeshita A, Watanabe E, Yokoyama Y, Ikawa K, Morikawa N, Takeda Y (2014) Analysis of thrombocytopenic effects and population pharmacokinetics of linezolid: a dosage strategy according to the trough concentration target and renal function in adult patients. Int J Antimicrob Agents 44(3):242–247
Tang HJ, Chen CC, Cheng KC, Toh HS, Su BA, Chiang SR, Ko WC, Chuang YC (2012) In vitro efficacy of fosfomycin-containing regimens against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in biofilms. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(4):944–950
Tang HJ, Chen CC, Cheng KC, Wu KY, Lin YC, Zhang CC, Weng TC, Yu WL, Chiu YH, Toh HS (2013) In vitro efficacies and resistance profiles of rifampin-based combination regimens for biofilm-embedded methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(11):5717–5720
Natsumoto B, Yokota K, Omata F, Furukawa K (2014) Risk factors for linezolid-associated thrombocytopenia in adult patients. Infection 42(6):1007–1012
Bonora MG, Solbiati M, Stepan E, Zorzi A, Luzzani A, Catania MR, Fontana R (2006) Emergence of linezolid resistance in the vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium multilocus sequence typing C1 epidemic lineage. J Clin Microbiol 44(3):1153
Raad II, Hanna HA, Hachem RY, Dvorak T, Arbuckle RB, Chaiban G, Rice LB (2004) Clinical-use-associated decrease in susceptibility of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium to linezolid: a comparison with Quinupristin-Dalfopristin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(9):3583–3585
Arias CA, Murray BE (2012) The rise of the Enterococcus: beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(4):266–278
Liu Y, Wang Y, Schwarz S, Li Y, Shen Z, Zhang Q, Wu C, Shen J (2013) Transferable multiresistance plasmids carrying cfr in Enterococcus spp. from swine and farm environment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(1):42–48
Swaminathan A, Cros PD, Seddon JA, Mirgayosieva S, Asladdin R, Dusmatova Z (2017) Peripheral neuropathy in a diabetic child treated with linezolid for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Infect Dis 17(1):417
Ventola CL (2015) The antibiotic resistance crisis: part 1: causes and threats. PT 40(4):277–283
Cabellos C, Garrigós C, Taberner F, Force E, Pachón-Ibañez ME (2014) Experimental study of the efficacy of linezolid alone and in combinations against experimental meningitis due to Staphylococcus aureus strains with decreased susceptibility to beta-lactams and glycopeptides. J Infect Chemother 20(9):563–568
Zhou YF, Xiong YQ, Tao MT, Li L, Bu MX, Sun J, Liao XP, Liu YH (2018) Increased activity of linezolid in combination with rifampicin in a murine pneumonia model due toMRSA. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy 73(7):1899–1907
Chiang FY, Climo M (2003) Efficacy of linezolid alone or in combination with vancomycin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(9):3002–3004
Patel R, Piper KE, Rouse MS, Steckelberg JM (2000) Linezolid therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(12):3438–3440
Kashef N, Akbarizare M, Razzaghi MR (2017) In vitro activity of linezolid in combination with photodynamic inactivation against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 9(1):44–48
Perez-Laguna V, Perez-Artiaga L, Lampaya-Perez V, Garcia-Luque I, Ballesta S, Nonell S, Paz-Cristobal MP, Gilaberte Y, Rezusta A (2017) Bactericidal effect of photodynamic therapy, alone or in combination with mupirocin or linezolid, on Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 8:1002
Hachem R, Afif C, Gokaslan Z, Raad I (2001) Successful treatment of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus meningitis with linezolid. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 20(6):432–434
Noskin GA, Siddiqui F, Stosor V, Kruzynski J, Peterson LR (1999) Successful treatment of persistent vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium bacteremia with linezolid and gentamicin. Clin Infect Dis 28(3):689–690
Lewis JS 2nd, Owens A, Cadena J, Sabol K, Patterson JE, Jorgensen JH (2005) Emergence of daptomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium during daptomycin therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(4):1664–1665
de Knegt GJ, van der Meijden A, de Vogel CP, Aarnoutse RE, de Steenwinkel JE (2017) Activity of moxifloxacin and linezolid against mycobacterium tuberculosis in combination with potentiator drugs verapamil, timcodar, colistin and SQ109. Int J Antimicrob Agents 49(3):302–307
Reyjurado E, Tudó G, Soy D, Gonzálezmartín J (2013) Activity and interactions of levofloxacin, linezolid, ethambutol and amikacin in three-drug combinations against mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in a human macrophage model. Int J Antimicrob Agents 42(6):524
Bababeygy SR, Silva RA, Sun Y, Jain A (2009) Rifampin and linezolid in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus preseptal cellulitis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 25(3):227–228
Pea F, Viale P, Cojutti P, Del PB, Zamparini E, Furlanut M (2012) Therapeutic drug monitoring may improve safety outcomes of long-term treatment with linezolid in adult patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(8):2034–2042
Hashimoto S, Honda K, Fujita K, Miyachi Y, Isoda K, Misaka K, Suga Y, Kato S, Tsuchiya H, Kato Y et al (2018) Effect of coadministration of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of linezolid: clinical and animal studies. J Pharm Health Care Sci 4:27
Kale-Pradhan PB, Mariani NP, Wilhelm SM, Johnson LB 2015 Meta-analysis: vancomycin treatment failures for MRSA bacteremia based on MIC determined by E-test. J Pharm Technol. 32(2):65-70
Chang W, Ma X, Gao P, Lv X, Lu H, Chen F (2015) Vancomycin MIC creep in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from 2006 to 2010 in a hospital in China. Indian J Med Microbiol 33(2):262–266
Bernardo K, Pakulat N, Fleer S, Schnaith A, Utermohlen O, Krut O, Muller S, Kronke M (2004) Subinhibitory concentrations of linezolid reduce Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor expression. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(2):546–555
Stevens DL, Ma Y, Salmi DB, McIndoo E, Wallace RJ, Bryant AE (2007) Impact of antibiotics on expression of virulence-associated exotoxin genes in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis 195(2):202–211
Le J, Bookstaver PB, Rudisill CN, Hashem MG, Iqbal R, James CL, Sakoulas G (2010) Treatment of meningitis caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium: high-dose and combination daptomycin therapy. Ann Pharmacother 44(12):2001–2006
Zinner SH, Gilbert D, Lubenko IY, Greer K, Firsov AA (2008) Selection of linezolid-resistant Enterococcus faecium in an in vitro dynamic model: protective effect of doxycycline. J Antimicrob Chemother 61(3):629–635
Migliori GB, Sotgiu G, Gandhi NR, Falzon D, DeRiemer K, Centis R, Hollm-Delgado MG, Palmero D, Perez-Guzman C, Vargas MH et al (2013) Drug resistance beyond extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 42(1):169–179
Jaspard M, Elefant-Amoura E, Melonio I, De Montgolfier I, Veziris N, Caumes E (2017) Bedaquiline and linezolid for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in pregnant woman. Emerg Infect Dis. 23(10):1731-1732
Parra-Ruiz J, Bravo-Molina A, Pena-Monje A, Hernandez-Quero J (2012) Activity of linezolid and high-dose daptomycin, alone or in combination, in an in vitro model of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(11):2682–2685
Kelesidis T, Humphries R, Ward K, Lewinski MA, Yang OO (2011) Combination therapy with daptomycin, linezolid, and rifampin as treatment option for MRSA meningitis and bacteremia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 71(3):286–290
Jacqueline C, Caillon J, Le MV, Miegeville AF, Donnio PY, Bugnon D, Potel G (2003) In vitro activity of linezolid alone and in combination with gentamicin, vancomycin or rifampicin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by time-kill curve methods. J Antimicrob Chemother 51(4):857
Singh SR, Bacon AE, Young DC, Couch A (2009) K: in vitro 24-hour time-kill studies of vancomycin and linezolid in combination versus methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(10):4495–4497
Sahuquillo Arce JM, Colombo Gainza E, Gil Brusola A, Ortiz Estevez R, Canton E, Gobernado M (2006) In vitro activity of linezolid in combination with doxycycline, fosfomycin, levofloxacin, rifampicin and vancomycin against methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Esp Quimioter 19(3):252–257
Pachon-Ibanez ME, Ribes S, Dominguez MA, Fernandez R, Tubau F, Ariza J, Gudiol F, Cabellos C (2011) Efficacy of fosfomycin and its combination with linezolid, vancomycin and imipenem in an experimental peritonitis model caused by a Staphylococcus aureus strain with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30(1):89–95
Chai D, Liu X, Wang R, Bai Y, Cai Y (2016) Efficacy of linezolid and Fosfomycin in catheter-related biofilm infection caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biomed Res Int 2016:6413982
Jacqueline C, Navas D, Batard E, Miegeville AF, Mabecque VL, Kergueris MF, Bugnon D, Potel G, Caillon J (2005) In vitro and in vivo synergistic activities of linezolid combined with subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(1):45–51
Luther MK, Arvanitis M, Mylonakis E, Laplante KL (2014) Activity of daptomycin or linezolid in combination with rifampin or gentamicin against biofilm-forming Enterococcus faecalis or E. faecium in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model using simulated endocardial vegetations and an in vivo survival assay using gall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(8):4612–4620
Knoll BM, Hellmann M, Kotton CN (2013) Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium meningitis in adults: case series and review of the literature. Scand J Infect Dis 45(2):131–139
Conradie F, Diacon A, Everitt D, Mendel C, Van Niekerk C, Howell P (2017) The NIX-TB trial of pretomanid, bedaquiline and linezolid to treat XDR-TB. In: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections. 13–16. Available from: http://www.croiconference.org/sessions/nix-tb-trialpretomanidbedaquiline-and-linezolid-treat-xdr-tb
Vinh DC, Rubinstein E (2009) Linezolid: a review of safety and tolerability. J Infect 59(Suppl 1):S59–S74
Jang HC, Kim SH, Kim KH, Kim CJ, Lee S, Song KH, Jeon JH, Park WB, Kim HB, Park SW et al (2009) Salvage treatment for persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: efficacy of linezolid with or without carbapenem. Clin Infect Dis 49(3):395–401
Nguyen S, Pasquet A, Legout L, Beltrand E, Dubreuil L, Migaud H, Yazdanpanah Y, Senneville E (2009) Efficacy and tolerance of rifampicin-linezolid compared with rifampicin-cotrimoxazole combinations in prolonged oral therapy for bone and joint infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 15(12):1163–1169
Cai Y, Fan Y, Wang R, An MM, Liang BB (2009) Synergistic effects of aminoglycosides and fosfomycin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and biofilm infections in a rat model. J Antimicrob Chemother 64(3):563–566
Jori G (2006) Photodynamic therapy of microbial infections: state of the art and perspectives. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 25(1–2):505–519
Sandoe JA, Wysome J, West AP, Heritage J, Wilcox MH (2006) Measurement of ampicillin, vancomycin, linezolid and gentamicin activity against enterococcal biofilms. J Antimicrob Chemother 57(4):767–770
Oliva A, Furustrand Tafin U, Maiolo EM, Jeddari S, Betrisey B, Trampuz A (2014) Activities of fosfomycin and rifampin on planktonic and adherent Enterococcus faecalis strains in an experimental foreign-body infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(3):1284–1293
Allen GP, Cha R, Rybak MJ (2002) In vitro activities of quinupristin-dalfopristin and cefepime, alone and in combination with various antimicrobials, against multidrug-resistant staphylococci and enterococci in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(8):2606
Paulson T (2013) Epidemiology: a mortal foe. Nature 502(7470):S2–S3
Tangg SJ, Zhang Q, Zheng LH, Sun H, Gu J, Hao XH, Liu YD, Yao L, Xiao HP (2011) Efficacy and safety of linezolid in the treatment of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Jpn J Infect Dis 64(6):509–512
Borisov SE, Dheda K, Enwerem M, Romero Leyet R, D'Ambrosio L, Centis R, Sotgiu G, Tiberi S, Alffenaar JW, Maryandyshev A et al (2017) Effectiveness and safety of bedaquiline-containing regimens in the treatment of MDR- and XDR-TB: a multicentre study. Eur Respir J. 49(5):1700387
ClinicalTrials.gov [database on the Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); (2000). Safety and efficacy of various doses and treatment durations of linezolid plus bedaquiline and pretomanid in participants with pulmonary TB, XDR-TB, Pre- XDR-TB or Non-responsive/Intolerant MDR-TB (ZeNix). Available from:https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03086486. Accessed September 9, 2019
ClinicalTrials.gov [database on the Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); (2000). An open-label RCT to evaluate a new treatment regimen for patients with multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (NEXT). Available from:https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02454205. Accessed September 9, 2019
ClinicalTrials.gov [database on the Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); (2000). Evaluating newly approved drugs for multidrug-resistant TB (endTB). Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02754765. Accessed September 9, 2019
ClinicalTrials.gov [database on the Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); (2000). Pragmatic clinical trial for a more effective concise and less toxic MDR-TB treatment regimen(s) (TB-PRACTECAL). Available from:https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/nct02589782. Accessed September 9, 2019
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (81173133); the Fund of Excellent Talents in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province, China (gxbjZD06); and the Fund of Academic leaders of Anhui Province, China (2015D068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hao Chen, XiaoHui Huang, and Yan Du conceived the idea, designed the study, and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the qualitative and quantitative synthesis of the included trials. Quan Xia, Yan Li, and Shuai Song revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Du, Y., Xia, Q. et al. Role of linezolid combination therapy for serious infections: review of the current evidence. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39, 1043–1052 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03801-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03801-x