Abstract
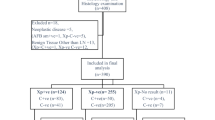
Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) is recommended for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated pulmonary tuberculosis but not extrapulmonary tuberculosis. We assessed the performance of Xpert for HIV-associated lymph node tuberculosis (LNTB), the most common type of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Among HIV-infected adults suspected of LNTB presenting for fine needle aspirate (FNA) at a South African hospital, we assessed the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert using either FNA culture or a composite of microscopy, culture, and cytology as the reference standard, and evaluated the impact of different diagnostics on patient management. Among 344 adults with valid FNA culture and Xpert results, 84 (24 %) were positive on microscopy, 149 (43 %) on culture, 152 (53 %) on Xpert, and 181 (57 %) had a cytology result suggestive of tuberculosis. Using liquid culture as the reference standard, the specificity of a single Xpert was suboptimal (88.2 %) but the sensitivity was high [93.3 %, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 87.6–96.6] and increased with decreasing CD4 count (from 87.0 % for CD4 >250 to 98.6 % for CD4 <100 cells/mm3). Using a composite reference standard reduced the sensitivity to 79.2 % but increased the specificity to 98.6 %. All Xpert-positive patients initiated treatment within one day, compared to 70 % of culture-positive but Xpert-negative and 13 % of culture- and Xpert-negative but cytology-positive patients. Xpert is accurate and effective and could be endorsed as the initial diagnostic for HIV-associated LNTB.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallo RC, Salahuddin SZ, Popovic M, Shearer GM, Kaplan M, Haynes BF, Palker TJ, Redfield R, Oleske J, Safai B, White G, Foster P, Markham PD (1984) Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science 224(4648):500–503
Barré-Sinoussi F, Chermann JC, Rey F, Nugeyre MT, Chamaret S, Gruest J, Dauguet C, Axler-Blin C, Vézinet-Brun F, Rouzioux C, Rozenbaum W, Montagnier L (1983) Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 220(4599):868–871
Fauci AS, Masur H, Gelmann EP, Markham PD, Hahn BH, Lane HC (1985) NIH conference. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an update. Ann Intern Med 102(6):800–813
Bottles K, McPhaul LW, Volberding P (1988) Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): experience in an outpatient clinic. Ann Intern Med 108(1):42–45
Voetberg A, Lucas SB (1991) Tuberculosis or persistent generalised lymphadenopathy in HIV disease? Lancet 337(8732):56–57. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(91)93380-R
Daley P, Thomas S, Pai M (2007) Nucleic acid amplification tests for the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis: a systematic review. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 11(11):1166–1176
Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Hillemann D, Nicol MP, Shenai S, Krapp F, Allen J, Tahirli R, Blakemore R, Rustomjee R, Milovic A, Jones M, O’Brien SM, Persing DH, Ruesch-Gerdes S, Gotuzzo E, Rodrigues C, Alland D, Perkins MD (2010) Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N Engl J Med 363(11):1005–1015
Boehme CC, Nicol MP, Nabeta P, Michael JS, Gotuzzo E, Tahirli R, Gler MT, Blakemore R, Worodria W, Gray C, Huang L, Caceres T, Mehdiyev R, Raymond L, Whitelaw A, Sagadevan K, Alexander H, Albert H, Cobelens F, Cox H, Alland D, Perkins MD (2011) Feasibility, diagnostic accuracy, and effectiveness of decentralised use of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance: a multicentre implementation study. Lancet 377(9776):1495–1505. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60438-8
Chang K, Lu W, Wang J, Zhang K, Jia S, Li F, Deng S, Chen M (2012) Rapid and effective diagnosis of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance with Xpert MTB/RIF assay: a meta-analysis. J Infect 64(6):580–588. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2012.02.012
Scott L, Gous N, Perovic O, Stevens W (2011) Dried culture spots for Xpert MTB/RIF external quality assessment. Paper presented at the 6th International AIDS Society Conference, Rome, Italy, July 2011
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, Lijmer JG, Moher D, Rennie D, de Vet HC; Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy (2003) Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: The STARD Initiative. Ann Intern Med 138(1):40–44. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh103
Moure R, Martín R, Alcaide F (2012) Effectiveness of an integrated real-time PCR method for detection of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in smear-negative extrapulmonary samples in an area of low tuberculosis prevalence. J Clin Microbiol 50(2):513–515. doi:10.1128/JCM.06467-11
Ioannidis P, Papaventsis D, Karabela S, Nikolaou S, Panagi M, Raftopoulou E, Konstantinidou E, Marinou I, Kanavaki S (2011) Cepheid GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis detection and rifampin resistance identification in patients with substantial clinical indications of tuberculosis and smear-negative microscopy results. J Clin Microbiol 49(8):3068–3070. doi:10.1128/JCM.00718-11
Hanif SN, Eldeen HS, Ahmad S, Mokaddas E (2011) GeneXpert® MTB/RIF for rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in pulmonary and extra-pulmonary samples. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 15(9):1274–1275. doi:10.5588/ijtld.11.0394
Armand S, Vanhuls P, Delcroix G, Courcol R, Lemaître N (2011) Comparison of the Xpert MTB/RIF test with an IS6110-TaqMan real-time PCR assay for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory and nonrespiratory specimens. J Clin Microbiol 49(5):1772–1776. doi:10.1128/JCM.02157-10
Malbruny B, Le Marrec G, Courageux K, Leclercq R, Cattoir V (2011) Rapid and efficient detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory and non-respiratory samples. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 15(4):553–555. doi:10.5588/ijtld.10.0497
Ligthelm LJ, Nicol MP, Hoek KG, Jacobson R, van Helden PD, Marais BJ, Warren RM, Wright CA (2011) Xpert MTB/RIF for rapid diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis from fine-needle-aspiration biopsy specimens. J Clin Microbiol 49(11):3967–3970. doi:10.1128/JCM.01310-11
Vadwai V, Boehme C, Nabeta P, Shetty A, Alland D, Rodrigues C (2011) Xpert MTB/RIF: a new pillar in diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis? J Clin Microbiol 49(7):2540–2545. doi:10.1128/JCM.02319-10
Tortoli E, Russo C, Piersimoni C, Mazzola E, Dal Monte P, Pascarella M, Borroni E, Mondo A, Piana F, Scarparo C, Coltella L, Lombardi G, Cirillo DM (2012) Clinical validation of Xpert MTB/RIF for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Eur Respir J 40(2):442–447. doi:10.1183/09031936.00176311
Sharma SK, Mohan A (2004) Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res 120(4):316–353
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), Geneva, Switzerland, for providing access to the Xpert MTB/RIF instrument and cartridges at preferential pricing. We thank Melinda Wilson, USAID South Africa, for her support for the study. We thank Sr. Caroline Tshoana and Phindile Mathe of the fine needle aspirate clinic of the Helen Joseph Hospital for performing the final needle aspirate procedures, and Natasha Gous from the Department of Molecular Medicine and Haematology, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, for the laboratory support.
This work was supported by the United States Agency for International Development (PEPFAR in a grant to Right to Care 674-A-00-08-00007-00) and the National Institutes of Health (ICOHRTA AIDS/TB U2RTW007370).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Rie, A., Page-Shipp, L., Mellet, K. et al. Diagnostic accuracy and effectiveness of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of HIV-associated lymph node tuberculosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32, 1409–1415 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1890-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1890-0