Abstract
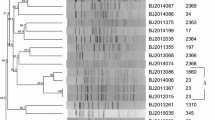
We determined the fecal carriage rate of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae in healthy Koreans and studied their genetic relationship with liver abscess isolates. We compared the carriage according to the country of residence. The stool specimens were collected through health promotion programs in Korea. K. pneumoniae strains were selected and tested for K1 by PCR. Serotype K1 isolates were characterized by multilocus sequence typing and pulsed field gel electrophoresis. A total of 248 K. pneumoniae isolates were obtained from 1,174 Koreans. Serotype K1 was identified in 57 (4.9%), of which 54 (94.7%) were ST 23 and were closely related to the liver abscess isolates. Participants aged >25 years showed a higher fecal carriage rate than those ≤ 25 (P = 0.007). The proportion of serotype K1 out of K. pneumoniae isolates in foreigners of Korean ethnicity who had lived in other countries was lower compared with those who had lived in Korea (5.6% vs 24.1%, P = 0.024). A substantial proportion of Koreans >25 years carries serotype K1 K. pneumoniae ST23 strains, which are closely related to liver abscess isolates. Differences in carriage rates by country of residence suggests that environmental factors might play an important role in the carriage of this strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung DR, Lee SS, Lee HR, Kim HB, Choi HJ, Eom JS, Kim JS, Choi YH, Lee JS, Chung MH, Kim YS, Lee H, Lee MS, Park CK (2007) Emerging invasive liver abscess caused by K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae in Korea. J Infect 54:578–583
Ko WC, Paterson DL, Sagnimeni AJ, Hansen DS, von Gottberg A, Mohapatra S, Casellas JM, Goossens H, Mulazimoglu L, Trenholme G, Klugman KP, McCormack JG, Yu VL (2002) Community-acquired Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: global differences in clinical patterns. Emerg Infect Dis 8:160–166
Fang FC, Sandler N, Libby SJ (2005) Liver abscess caused by magA + Klebsiella pneumoniae in North America. J Clin Microbiol 43:991–992
Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, Holzman RS (2004) Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis 39:1654–1659
Chung DR, Lee HR, Lee SS, Kim SW, Chang HH, Jung SI, Oh MD, Ko KS, Kang CI, Peck KR, Song JH (2008) Evidence for clonal dissemination of the serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae strain causing invasive liver abscesses in Korea. J Clin Microbiol 46:4061–4063
Mizuta K, Ohta M, Mori M, Hasegawa T, Nakashima I, Kato N (1983) Virulence for mice of Klebsiella strains belonging to the O1 group: relationship to their capsular (K) types. Infect Immun 40:56–61
Lin JC, Chang FY, Fung CP, Xu JZ, Cheng HP, Wang JJ, Huang LY, Siu LK (2004) High prevalence of phagocytic-resistant capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in liver abscess. Microbes Infect 6:1191–1198
Blanchette EA, Rubin SJ (1980) Seroepidemiology of clinical isolates of Klebsiella in Connecticut. J Clin Microbiol 11:474–478
Cryz SJ Jr, Mortimer PM, Mansfield V, Germanier R (1986) Seroepidemiology of Klebsiella bacteremic isolates and implications for vaccine development. J Clin Microbiol 23:687–690
Jenney AW, Clements A, Farn JL, Wijburg OL, McGlinchey A, Spelman DW, Pitt TL, Kaufmann ME, Liolios L, Moloney MB, Wesselingh SL, Strugnell RA (2006) Seroepidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae in an Australian Tertiary Hospital and its implications for vaccine development. J Clin Microbiol 44:102–107
Kim JK, Chung DR, Wie SH, Yoo JH, Park SW (2009) Risk factor analysis of invasive liver abscess caused by the K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28:109–111
Han SHB (1995) Review of hepatic abscess from Klebsiella pneumoniae. An association with diabetes mellitus and septic endophthalmitis. West J Med 162:220–224
Tomás JM, Ciurana B, Jofre JT (1986) New, simple medium for selective, differential recovery of Klebsiella spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1361–1363
Struve C, Bojer M, Nielsen EM, Hansen DS, Krogfelt KA (2005) Investigation of the putative virulence gene magA in a worldwide collection of 495 Klebsiella isolates: magA is restricted to the gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule serotype K1. J Med Microbiol 54:1111–1113
Diancourt L, Passet V, Verhoef J, Grimont PA, Brisse S (2005) Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J Clin Microbiol 43:4178–4182
Podschun R, Pietsch S, Holler C, Ullmann U (2001) Incidence of Klebsiella species in surface waters and their expression of virulence factors. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3325–3327
Struve C, Krogfelt KA (2004) Pathogenic potential of environmental Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Environ Microbiol 6:584–590
Favre-Bonté S, Licht TR, Forestier C, Krogfelt KA (1999) Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule expression is necessary for colonization of large intestines of streptomycin-treated mice. Infect Immun 67:6152–6156
Financial support
This work was supported by Samsung Biomedical Research Institute (SBRI) Grant, CA73091.
Potential conflict of interest
None of the authors had any conflicts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, D.R., Lee, H., Park, M.H. et al. Fecal carriage of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains closely related to liver abscess isolates in Koreans living in Korea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31, 481–486 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1334-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-011-1334-7