Abstract
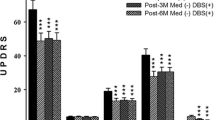
Preliminary reports in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) showed that subthalamic nucleus (STN) stimulation was able to reverse parkinsoniam state. Since 1998 we evaluated the safety and the efficacy of STN stimulation in 7 patients affected by advanced PD. All patients were included using CAPIT protocol. Motor functions and quality of life were evaluated, before and after surgery, with UPDRS and PDQ38, respectively. At the 6-month follow-up, the off medication/on stimulation UPDRS motor score improved by 50.6% and the on medication/on stimulation by 20.3%. Motor fluctuations were reduced by 57.2% and dyskinesias by 73.5%. The total D-dopa equivalent daily dose was reduced by 40.7%. PDQ38 ameliorated by 49.9%. We did not observe any perioperatory complication and only mild and tolerable side effects after stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capus, L., Melatini, A., Zorzon, M. et al. Chronic bilateral electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci 22, 57–58 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100720170045
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100720170045