Abstract
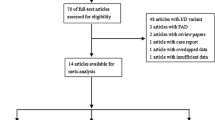
The aim of this study was to determine whether the tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) promoter −308 A/G polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in multi-ethnic populations. MEDLINE and EMBASE databases and manual literature search were used to identify published articles in which TNF-α polymorphism was determined in AD patients and control subjects. Meta-analysis was conducted on the association between the TNF-α −308 A/G polymorphism and AD using allele contrast and the recessive, dominant, and additive models. A total of 16 studies involving 3,826 AD patients and 4,327 control subjects were examined. The meta-analysis showed no association between the TNF-α −308 A allele and AD when all the subjects were considered [odds ratio (OR) = 1.275, 95 % CI 0.966–1.685, p = 0.087]. After stratification by ethnicity, the meta-analysis indicated that the A allele is significantly associated with AD in East Asian (OR = 1.743, 95 % CI 1.256–2.418, p = 0.001), but not in the European (OR = 0.963, 95 % CI 0.822–1.128, p = 0.637) or Middle Eastern populations (OR = 3.921, 95 % CI 0.411–37.42, p = 0.235). Meta-analysis under dominant, recessive, and additive models also showed a similar pattern of results as with the A allele. This meta-analysis shows that the TNF-α −308 A/G polymorphism may represent a significant risk factor for AD in East Asians but not in the European or Middle Eastern populations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boada M, Antunez C, Lopez-Arrieta J, Caruz A, Moreno-Rey C, Ramirez-Lorca R et al (2012) Estrogen receptor alpha gene variants are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(1):198.e15–198.e24
Medway C, Morgan K (2014) Review: the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease; putting flesh on the bones. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 40(2):97–105
Vasto S, Candore G, Listi F, Balistreri CR, Colonna-Romano G, Malavolta M et al (2008) Inflammation, genes and zinc in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Rev 58(1):96–105
Liu L, Chan C (2014) The role of inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 15:6–15
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2001) Polymorphisms in inflammatory genes and the risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 58(11):1790–1792
Perry RT, Collins JS, Wiener H, Acton R, Go RC (2001) The role of TNF and its receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22(6):873–883
Himmerich H, Berthold-Losleben M, Pollmacher T (2009) The relevance of the TNF-alpha system in psychiatric disorders. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 77(6):334–345
Blasko I, Marx F, Steiner E, Hartmann T, Grubeck-Loebenstein B (1999) TNFalpha plus IFNgamma induce the production of Alzheimer beta-amyloid peptides and decrease the secretion of APPs. FASEB J 13(1):63–68
Allen RD (1999) Polymorphism of the human TNF-alpha promoter—random variation or functional diversity? Mol Immunol 36(15–16):1017–1027
D’Alfonso S, Richiardi PM (1994) A polymorphic variation in a putative regulation box of the TNFA promoter region. Immunogenetics 39(2):150–154
Wilson AG, Symons JA, McDowell TL, McDevitt HO, Duff GW (1997) Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(7):3195–3199
Ardebili SM, Yeghaneh T, Gharesouran J, Rezazadeh M, Farhoudi M, Ayromlou H et al (2011) Genetic association of TNF-alpha −308 G/A and -863 C/A polymorphisms with late onset Alzheimer’s disease in Azeri Turk population of Iran. J Res Med Sci 16(8):1006–1013
Shawkatova I, Javor J, Parnicka Z, Vrazda L, Novak M, Buc M (2010) No association between cytokine gene polymorphism and risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Slovaks. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 70(3):303–307
Manoochehri M, Kamali K, Rahgozar M, Ohadi M, Farrokhi H, Khorshid HR (2009) Lack of association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha −308 G/A polymorphism and risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in an Iranian Population. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 1(3):193–197
Yang L, Lu R, Jiang L, Liu Z, Peng Y (2009) Expression and genetic analysis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) G −308A polymorphism in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in a Southern China population. Brain Res 1247:178–181
Tedde A, Putignano AL, Nacmias B, Bagnoli S, Cellini E, Sorbi S (2008) Lack of association between TNF-alpha polymorphisms and Alzheimer’s disease in an Italian cohort. Neurosci Lett 446(2–3):139–142
Wang B, Zhou S, Yang Z, Xie YC, Wang J, Zhang P et al (2008) Genetic analysis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) G −308A and Saitohin Q7R polymorphisms with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 270(1–2):148–151
Ramos EM, Lin MT, Larson EB, Maezawa I, Tseng LH, Edwards KL et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 10 promoter region polymorphisms and risk of late-onset Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 63(8):1165–1169
Lio D, Annoni G, Licastro F, Crivello A, Forte GI, Scola L et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha −308A/G polymorphism is associated with age at onset of Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 127(6):567–571
Laws SM, Perneczky R, Wagenpfeil S, Muller U, Forstl H, Martins RN et al (2005) TNF polymorphisms in Alzheimer disease and functional implications on CSF beta-amyloid levels. Hum Mutat 26(1):29–35
Zhang P, Yang Z, Wan CL, Zheng WD, Zhang CF, Li S et al (2004) Neither the tumor necrosis factor alpha −308 A/G polymorphism nor the alpha2-macroglobulin polymorphism was associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the Chinese population. Yi Chuan Xue Bao 31(1):1–6
Alvarez V, Mata IF, Gonzalez P, Lahoz CH, Martinez C, Pena J et al (2002) Association between the TNFalpha −308 A/G polymorphism and the onset-age of Alzheimer disease. Am J Med Genet 114(5):574–577
Perry RT, Collins JS, Harrell LE, Acton RT, Go RC (2001) Investigation of association of 13 polymorphisms in eight genes in southeastern African American Alzheimer disease patients as compared to age-matched controls. Am J Med Genet 105(4):332–342
Tarkowski E, Liljeroth AM, Nilsson A, Ricksten A, Davidsson P, Minthon L et al (2000) TNF gene polymorphism and its relation to intracerebral production of TNFalpha and TNFbeta in AD. Neurology 54(11):2077–2081
Flex A, Giovannini S, Biscetti F, Liperoti R, Spalletta G, Straface G et al (2014) Effect of proinflammatory gene polymorphisms on the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 13(4):230–236
Gnjec A, D’Costa KJ, Laws SM, Hedley R, Balakrishnan K, Taddei K et al (2008) Association of alleles carried at TNFA -850 and BAT1 -22 with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 5:36
Sarajarvi T, Helisalmi S, Antikainen L, Makinen P, Koivisto AM, Herukka SK et al (2010) An association study of 21 potential Alzheimer’s disease risk genes in a Finnish population. J Alzheimers Dis 21(3):763–767
Lee YH, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2010) Associations between osteoprotegerin polymorphisms and bone mineral density: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 37(1):227–234
Lee YH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2007) PADI4 polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 27(9):827–833
Lee YH, Bae SC, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2011) Associations between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 38(6):3643–3651
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558
Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN (1997) Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ 315(7121):1533–1537
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188
Lee YH, Ji JD, Song GG (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter −308 A/G polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a metaanalysis. J Rheumatol 34(1):43–49
Di Bona D, Candore G, Franceschi C, Licastro F, Colonna-Romano G, Camma C et al (2009) Systematic review by meta-analyses on the possible role of TNF-alpha polymorphisms in association with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Rev 61(2):60–68
Acknowledgments
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or non-financial conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.H., Choi, S.J., Ji, J.D. et al. Association between TNF-α promoter −308 A/G polymorphism and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 36, 825–832 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2102-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2102-8