Abstract
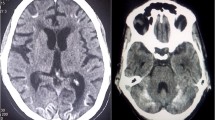
Organotin compounds are commonly used in industrial and agriculture. It causes toxic effects on skin, eyes, respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, and nervous system. After cleaning a di-methyl tin tank, 43-year-old man showed a dizziness, disorientation, visual hallucination, and agitation. Through a measurement by liquid chromatography and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, di-methyl tin and tri-methyl tin was detected. Although magnetic resonance (MR) image 3 days after exposure showed no abnormal signal intensity, follow-up MR images 15 days after exposure revealed abnormal extensive signal intensities in the white matter that was not ever coincident with previous reports. It was hardly explainable that previous abnormal signal intensities of MR image nearly disappeared 4 months later. We present a case of a patient who developed acute toxic leukoencephalopathy from an acute inhalational exposure to methyl tin with sequential MR images showing an involvement of white matter that was not ever reported.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge WN, Brown AW, Brierley JB, Verschoyle RD, Street BW (1981) Brain damage due to trimethyl tin compounds. Lancet 2:692–693
Barnes JM, Stoner HB (1959) The toxicology of tin compounds. Pharmacol Rev 11:211–231
Besser R, Kramer G, Thumler R, Bohl J, Gutmann L, Hopf HC (1987) Acute trimethyltin limbic-cerebellar syndrome. Neurology 37:945–950
Bouldin TW, Goines ND, Bagnell RC, Krigman MR (1981) Pathogenesis of trimethyltin neuronal toxicity. Ultrastructural and cytochemical observations. Am J Pathol 104:237–249
Brown AW, Aldridge WN, Street BW, Verschoyle RD (1979) The behavioral and neuropathologic sequelae of intoxication by trimethyltin compounds in the rat. Am J Pathol 97:59–82
Brown AW, Verschoyle RD, Street BW, Aldridge WN, Grindley H (1984) The neurotoxicity of trimethyltin chloride in hamsters, gerbils and marmosets. J Appl Toxicol 4:12–21
Chang LW (1990) The neurotoxicology and pathology of organomercury, organolead, and organotin. J Toxicol Sci 15(Suppl 4):125–151
Ebisu T, Naruse S, Horikawa Y, Ueda S, Tanaka C, Uto M, Umeda M, Higuchi T (1993) Discrimination between different types of white matter edema with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 3:863–868
Feldman RG, White RF, Eriator II (1993) Trimethyltin encephalopathy. Arch Neurol 50:1320–1324
Fortemps E, Amand G, Bomboir A, Lauwerys R, Laterre EC (1978) Trimethyltin poisoning. Report of two cases. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 41:1–6
Grunner J (1958) Damage to the central nervous system after ingestion of an ethyl tin compound(Stalinon). Rev Neurol (Paris) 98:106–109
Gui-bin J, Qun-fang Z, Bin H (2000) Tin compounds and major trace metal elements in organotin-poisoned patient’s urine and blood measured by gas chromatography-flame photometric detector and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 65:277–284
Kreyberg S, Torvik A, Bjorneboe A, Wiik-Larsen W, Jacobsen D (1992) Trimethyltin poisoning: report of a case with postmortem examination. Clin Neuropathol 11:256–259
Krigman MR, Silverman AP (1984) General toxicology of tin and its organic compounds. Neurotoxicology 5:129–139
Perretta G, Righi FR, Gozzo S (1993) Neuropathological and behavioral toxicology of trimethyltin exposure. Ann Ist Super Sanita 29:167–174
Piver WT (1973) Organotin compounds: industrial applications and biological investigation. Environ Health Perspect 4:61–79
Reiter LW, Ruppert PH (1984) Behavioral toxicity of trialkyltin compounds: a review. Neurotoxicology 5:177–186
Yanofsky NN, Nierenberg D, Turco JH (1991) Acute short-term memory loss from trimethyltin exposure. J Emerg Med 9:137–139
Acknowledgments
No commercial party having a direct financial interest in the results of the research supporting this article has or will confer a benefit upon the authors or upon any organization with which the authors are associated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted upon request of the author since he unwillingly reported clinical data already published in the article "A case of Acute Organotin Poisoning" (C.I. Yoo, Y. Kim et al. J. Occup Health 2007; 49:305-3010, DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.1539/joh.49.305).
The retraction note to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-0988-y
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, C.H. RETRACTED ARTICLE: The sequential magnetic resonance images of tri-methyl tin leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Sci 30, 153–158 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-009-0028-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-009-0028-8