Abstract
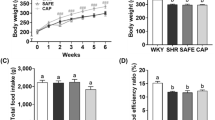
Ginseng possesses a wide spectrum of medicinal effects and has widely been used in traditional medicine for thousands of years. In this study, the antihypertensive effect of Korean wild simulated ginseng in spontaneously hypertensive rats was investigated. Three groups of hypertensive rats—a group without wild simulated ginseng treatment; another group treated with 100 mg of wild simulated ginseng extract/kg of body weight; and the other group treated with 200 mg of wild simulated ginseng extract/kg of body weight were tested over 8 weeks. The two wild simulated ginseng-treated groups showed significantly (p < 0.05) reduced systolic blood pressure at 4 and 6 weeks of wild simulated ginseng treatment. However, the wild simulated ginseng treatment did not adversely affect the food intake, serum electrolytes, osmolality, heart weight, heart rate, and the cross-section of the aorta as well as enzyme activities. The results suggested that Korean wild simulated ginseng is effectively used for reducing high systolic blood pressure in hypertensive patients without causing adverse health effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander RW. Hypertension and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Hypertension 25: 155–161 (1995)
Cooper G, Pickavance L, Wilding J, Halford J, Goudie A. Effects of olanzapine in male rats: Enhanced adiposity in the absence of hyperphagia, weight gain or metabolic abnormalities. J. Psychopharmacol. 21: 405–413 (2007)
Crawford A, Harris H. Balancing act: Na+ sodium K+ potassium. Nursing 41: 44–50 (2011)
Crawford AH. Hyperkalemia: recognition and management of a critical electrolyte disturbance. J. Infusion Nurs. 37: 167–175 (2014)
Fu Y, Ji LL. Chronic ginseng consumption attenuates age-associated oxidative stress in rats. J. Nutr. 133: 3603–3609 (2003)
Geng J, Dong J, Ni H, Lee MS, Wu T, Jiang K, Wang G, Zhou AL, Malouf R. Ginseng for cognition. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 12: CD007769 (2010)
Hur MH, Lee MS, Yang HJ, Kim C, Bae IL, Ernst E. Ginseng for reducing the blood pressure in patients with hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis J. Ginseng Res. 34: 342–347 (2010)
Jang DJ, Lee MS, Shin BC, Lee YC, Ernst E. Red ginseng for treating erectile dysfunction: A systematic review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 66: 444–450 (2008)
Jin X, Che DB, Zhang ZH, Yan HM, Jia ZY, Jia XB. Ginseng consumption and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis. J. Ginseng Res. 40: 269–277 (2016)
Joo IW, Sung KH, Park JM, Lew JH, Oh HJ. Effect of Korean red ginseng on blood pressure and aortic vascular (endothelial) histological changes in rats. J. Ginseng Res. 32: 324–331 (2008)
Kang KS, Kim HY, Yamabe N, Nagai R, Yokozawa T. Protective effect of sun ginseng against diabetic renal damage. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29: 1678–1684 (2006)
Kim MS, Lim HJ, Yang HJ, Lee MS, Shin BC, Ernst E. Ginseng for managing menopause symptoms: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. J. Ginseng Res. 37: 30–36 (2013)
Kim ND, Kang SY, Kim MJ, Park JH, Schini-Kerth VB. The ginsenoside Rg3 evokes endothelium-independent relaxation in rat aorta: role of K + channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 367: 51–57 (1999)
Kim YS, Kim YH, Noh JR, Cho ES, Park JH, Son HY. Protective effect of Korean red ginseng against aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. J. Ginseng Res. 35: 243–249 (2011)
Kimura I, Nakashima N, Sugihara Y, Fu-Jun C, Kimura M. The antihyperglycemic blend effect of traditional Chinese medicine Byakko-ka-ninjin-to on alloxan and diabetic KK-CAy mice. Phytother. Res. 13: 484–488 (1999)
Kimura M, Waki I, Chujo T, Kikuchi T, Hiyama C, Yamazaki K, Tanaka O. Effects of hypoglycemic components in ginseng radix on blood insulin level in alloxan diabetic mice and on insulin release from perfused rat pancreas. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 4: 410–417 (1981)
Kitts DD, Hu C. Efficacy and safety of ginseng. Public Health Nutr. 4: 473–485 (2000)
Lee JM, Lee MA, Do HN, Song YI, Bae RJN, Lee HY, Park SH, Kang JS, Kang J. Historical control data from 13-week repeated toxicity studies in Crj:CD (SD) rats. Lab. Anim. Res. 28: 115–121 (2012)
Lee KH, Bae IY, Park SI, Park JD, Lee HG. Antihypertensive effect of Korean red ginseng by enrichment of ginsenoside Rg3 and arginine-fructose. J. Ginseng Res. 40: 237–244 (2016)
Lee MS, Yang EJ, Kim JI, Ernst E. Ginseng for cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 18: 339–344 (2009)
Lee TK, Johnke RM, Allison RR, O’Brien KF, Dobbs LH, Jr. Radioprotective potential of ginseng. Mutagenesis 20: 237–243 (2005)
Liwa AC, Smart LR, Frumkin A, Epstein HA, Fitzgerald DW, Peck RN. Traditional herbal medicine use among hypertensive patients in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 16: 437 (2014)
Morton PG, Fontaine DK. Critical Care Nursing: A Holistic Approach. 10th ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, USA. pp. 261–262 (2013)
Padwal R, Hackam D, Khan N, Tobe S. Primary prevention of CVD: Modification of diet in people with hypertension. Clin Evidence 1: 214 (2016)
Park EY, Kim HJ, Kim YK, Park SU, Choi JE, Cha JY, Jun HS. Increase in insulin secretion induced by panax ginseng berry extracts contributes to the amelioration of hyperglycemia in streptozotocininduced diabetic mice. J. Ginseng Res. 36: 153–160 (2012a)
Park HJ, Kim DH, Park SJ, Kim JM, Ryu JH. Ginseng in traditional herbal prescriptions. J. Ginseng Res. 36: 225–241 (2012b)
Ramesh T, Kim SW, Hwang SY, Sohn SH, Yoo SK, Kim, SK. Panax ginseng reduces oxidative stress and restores antioxidant capacity in aged rats. Nutr. Res. 32: 718–726 (2012)
Seo HW, Suh JH, So SH, Kyung JS, Kim YS, Han CK. Subacute oral toxicity and bacterial mutagenicity study of Korean red ginseng oil. J. Ginseng Res. 41: 595–601 (2017)
Sibbritt D, Davidson P, DiGiacomo M, Newton P, Adams J. Use of complementary and alternative medicine in women with heart disease, hypertension and diabetes (from the Australian longitudinal study on women’s health). Am. J. Cardiol. 115: 1691–1695 (2015)
Sotaniemi EA, Haapakoski E, Rautio A. Ginseng therapy in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients: Effects on psychophysical performance, glucose homeostasis, serum lipids, serum aminoterminalpropeptide concentration, and body weight. Diabetes Care 18: 1373–1375 (1995)
Stavro PM, Hana AK, Vuksan V. The effect of Korean red ginseng extracts with escalating levels of ginsenoside Rg3 on blood pressure in individuals with high normal blood pressure or hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 15: 34–44 (2002)
Suzuki Y, Ito Y, Konno C, Furuya T. Effects of tissue cultured ginseng on gastric secretion and pepsin activity. Yakugaku Zasshi 111: 770–774 (1991)
von Wilmsdorff M, Bouvier ML, Henning U, Schmitt A, Gaebel W. The impact of antipsychotic drugs on food intake and body weight and on leptin levels in blood and hypothalamic ob-r leptin receptor expression in wistar rats. Clinics 65: 885–894 (2010)
Vuksan V, Stavro MP, Sievenpiper JL, Beljan-Zdravkovic U, Leiter LA, Josse RG, Xu ZH. Similar postprandial glycemic reductions with escalation of dose and administration time of American ginseng in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 23: 1221–1226 (2000)
WHO. A global brief on hypertension: Silent killer, global public health crisis. WHO Press, Geneva, Switzerland (2013)
Yokozawa T, Kim HY, Kim HJ, Tanaka T, Sugino H, Okubo T, Chu DC, Juneja LR. Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) attenuates age-related renal dysfunction by oxidative stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55: 7744–7752 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, JN., Kim, JK., Lee, S. et al. Antihypertensive effects of Korean wild simulated ginseng (Sanyangsam) extracts in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 1563–1569 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00617-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00617-5